* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physics B Midterm Study Guide
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Nanogenerator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
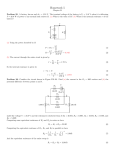
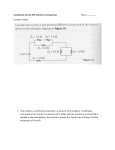
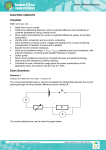
Physics B Final Study Guide The final for Physics B is cumulative – that is, you are responsible for knowing the material from the midterm as well as the material we’ve covered since then. Be sure to review the Midterm Study Guide as well. All of the values and formulae that you need to complete the questions on this study guide appear at the end of page 3. Short Questions 1. Explain how materials become electrically polarized. 2. Explain how materials conduct charge. 3. Explain how electrostatic spraying works. 4. Explain how a diode works. 5. Describe how buoyant force works. 6. Describe how Bernoulli’s principle allows for flight. 7. If an object gains 3.4x1019 electrons, what is its charge? 8. If an object gains 3.55 C of charge, how many electrons did it gain? 9. In a circuit, an emf source has a potential difference of 9.0V. The circuit has a current of 1.5 A. What is the resistance of the circuit? 10. If three resistors of 4.00Ω, 6.00Ω, and 8.00Ω are in a series, what is their equivalent resistance? 11. If three resistors of 4.00Ω, 6.00Ω, and 8.00Ω are in parallel, what is their equivalent resistance? 12. Explain why capacitors can be dangerous even when not plugged in to an emf source, and how they can be rendered safe. 13. If 93.0 C of charge passes through a circuit in 1.50 min, what is the current? 14. If a capacitor has a capacitance of 6.5 mF and it is connected to an emf source with a 9.0 V potential difference, how much charge is stored? 15. If an object has a mass of 2340 kg and it takes up 3.2m3, what is its mass density? 16. If a fluid applies 1500 N to a 5m2 area, what is the pressure? 17. A boat is 25m wide and 155m long. It is floating in seawater. If a 1.52 x 103 kg mass is loaded onto it, how far will the boat lower into the water? Long Questions 18. A 122μF capacitor is connected to a 12.0 V battery. a. What is the charge on each plate? b. What is the potential energy stored in the capacitor? 19. Two charges are 9.98μC and -4.92 μC. What is the electric force if they are a. 100.0 m apart? b. 1.000 m apart? 20. What is the electric field strength 100.0 m away from a charge of – a. 4.3 C? b. 6.45μC? 21. A circuit is created which contains an emf source with a potential difference of 120V, and has a resistance of 21.5 Ω. a. What is the current in the wire? b. What is the power rating of the resistor? 22. A circuit is created with a four resistors (4.00Ω, 6.00Ω, 8.00Ω and 10.0 Ω) in series. The potential difference of the power source is 120V. a. What is the equivalent resistance of the resistors? b. What is the current across the entire circuit? c. What is the current across each resistor? d. What is the potential difference across each resistor? 23. A circuit is created with a four resistors (4.00Ω, 6.00Ω, 8.00Ω and 10.0 Ω) in parallel. The potential difference of the power source is 120V. a. What is the equivalent resistance of the resistors? b. What is the current across the entire circuit? c. What is the current across each resistor? d. What is the potential difference across each resistor? 24. A material weighs 97 N in air, 63 N in water, and 72 N in a mystery fluid. a. What is the mass density of the material? b. What is the mass density of the mystery fluid? Formulae and Values • C = 6.2 x 1018 electrons • ρ = m/V • Felec = kC (q1•q2 / r2) • P = F/A • kC = 8.99 x 109 N•m2 / C2 • FB = mfluidg • E = kC (q / r2) • FB = mobjg • C = Q/∆V • P = P0 + gh • PEelec = ½ Q∆V • Fg/FB = ρobj/ρfluid • I = ∆Q/∆t • A1V1 = A2V2 • ∆V = IR • ρ water = 1.00 x 103 kg/m3 • P = I2R = I∆V • ρ salt water = 1.025 x 103 kg/m3 • Rseries = R1 + R2 + R3… • P0 = 1.01 x 105 Pa • 1/Rparallel = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 …