* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Virtual Cell Learning Objectives Draft (ETC Excerpt)
Gaseous detection device wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
Conservation and restoration of photographs wikipedia , lookup
Ultrafast laser spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
Photomultiplier wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
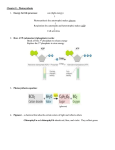
Virtual Cell Learning Objectives Draft (Photosynthesis Excerpt) Ganesh Padmanabhan 3/29/2004 Module Photosynthesis: 1. The learner should recognize that photosynthesis is a process that occurs within the chloroplasts of a eukaryotic cell. 2. The learner should recognize that photosynthesis is divided into two sets of reactions light reactions and dark reactions. 3. The learner should recognize that the light reactions of photosynthesis require light in order to work. 4. The learner should recognize if the light reactions of photosynthesis were to cease, the dark reactions would eventually also stop. 5. The learner should recognize that chlorophyll is a key molecule used to harvest energy from light. 6. The learner should recognize that the light reactions of photosynthesis occur across the thylakoid membrane inside the chloroplast. 7. The learner should recognize that the role of light in photosynthesis is to energize electrons so that they continue to move through an electron transport chain imbedded within the thylakoid membrane. 8. The learner should recognize that the light reactions of photosynthesis are an electron transport chain which contain two components which interact with light (photosystem I and II). 9. Given a cross-sectional diagram of the thylakoid membrane and a visual representation of the concentration of hydrogen ions on both sides of the membrane, the learner should be able to identify which way, if any, the ions would flow if the membrane were removed. 10. The learner should be able to identify the important product of the light reactions, namely ATP. 11. The learner should be able to identify the final electron recipient in the light reactions, namely NADP. 12. The learner should be able to identify the primary donor of electrons to the light reactions of photosynthesis, namely water (h2o). 13. The learner should recognize that the light reactions are a variation of the electron transport chain found in the mitochondrion. 14. The learner should be able to discriminate what is different about the ETC in the light reactions of photosynthesis and the reactions within the mitochondria. 15. Given a cross-sectional diagram of the thylakoid membrane and four empty slots, the learner should be able to order from left to right indicating the flow of electrons between the following four components involved in the light reactions of photosynthesis (photosystem I, cytochrome b6-f, photosystem II, NADP reducatase). 16. Given the following electron carriers (h2o, photosystem I, photosystem II, plastiquinone, cytochrome b6-f, ferridoxin, NADP reductase, NADP), the learner should be able to order these carriers in the sequence that electrons would flow normally in the light reactions. 17. The learner should recognize that photosystem I is activated by photons with a wavelength of 700 nm. 18. The learner should recognize that photosystem II is activated by photons with a wavelength of 680 nm. 19. The learner should be able to identify which of the following components of the light reactions are directly involved in pumping H+ across the thylakoid membrane, namely cytochrome b6-f. 20. The learner should recognize that the light reactions of photosynthesis are a process that is auxiliary to ATP production. 21. The learner should recognize that the ETC’s role in photosynthesis is to pump hydrogen ions out of the thylakoid space and into the stroma so that ATP can be produced. 22. The learner should be able to identify which terms amongst those involved in photosynthesis and other cellular processes are directly involved in the light reactions of photosynthesis. 23. The learner should be able to diagram a chloroplast and label the outer membrane, inner membrane, thylakoid membrane, inter-membrane space, stroma, and thylakoid space. 24. Given a diagram of a chloroplast, and ATP synthase oriented properly across the thylakoid membrane, the learner should be able to orient a hydrogen ion pump appropriately so that ATP synthase can produce ATP. 25. The learner should recognize that the following terms are related to ATP synthesis in the light reactions of photosynthesis: O2, H2O, ATP, NADP, NADP reductase, plastiquinone, ferridoxin, cytochrome b6-f, photosystem I, photosystem II, ATP synthase, P680, P700. 26. Given a list of the electron carriers in the light reactions of photosynthesis (H2O, ATP, NADP, NADP reductase, plastiquinone, ferridoxin, cytochrome b6-f, photosystem I, photosystem II), the learner should be able to identify which ones pump ions across the membrane. 27. Given a list of the electron carriers in the light reactions of photosynthesis (H2O, ATP, NADP, NADP reductase, plastiquinone, ferridoxin, cytochrome b6-f, photosystem I, photosystem II), the learner should be able to identify which ones shuttle electrons between components embedded in the membrane. 28. Given a list of the electron carriers in the light reactions of photosynthesis (H2O, ATP, NADP, NADP reductase, plastiquinone, ferridoxin, cytochrome b6-f, photosystem I, photosystem II), the learner should be able to identify which one is the final recipient of electrons. 29. Given a list of the electron carriers in the light reactions of photosynthesis (H2O, ATP, NADP, NADP reductase, plastiquinone, ferridoxin, cytochrome b6-f, photosystem I, photosystem II), the learner should be able to identify which ones are not bound by the membrane.. 30. Given a list of the electron carriers in the light reactions of photosynthesis (H2O, ATP, NADP, NADP reductase, plastiquinone, ferridoxin, cytochrome b6-f, photosystem I, photosystem II), the learner should be able to identify which ones bring electrons out of the light reactions of photosynthesis. 31. Given a list of the electron carriers in the light reactions of photosynthesis (H2O, ATP, NADP, NADP reductase, plastiquinone, ferridoxin, cytochrome b6-f, photosystem I, photosystem II), the learner should be able to identify which ones bring electrons into the light reactions of photosynthesis. 32. The learner should recognize that two water molecules donate electrons at the start of the light reactions. 33. The learner should be able to calculate how many NADP are reduced when two water molecules initiate the light reactions of photosynthesis. 34. The learner should be able to identify whether electrons “enter” the light reactions from the stroma space or the thylakoid space. 35. The learner should be able to identify whether electrons “exit” the light reactions from the stroma space or the thylakoid space. 36. For each transmembrane component involved in the light reactions, the learner should be able to identify both from which carrier it receives electrons and to which carrier it donates electrons. 37. For each electron carrier shuttle, the learner should be able to identify between which two components the carrier shuttles electrons.