* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download THE CIVIL WAR THE YANKEES VS. THE REBELS: Conflict and
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Carpetbagger wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Radical Republican wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
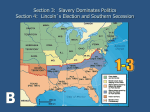
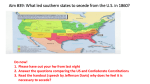
THE CIVIL WAR THE YANKEES VS. THE REBELS: Conflict and Compromise Missouri Compromise Missouri applies for statehood as a __________ state Northern Massachusetts will become the state of ____________ ____________ line becomes the division of ________/ __________ area in territories Expansion Victory in the _______________________ raised an important question about U.S. expansion. As new states formed and joined the Union, would they allow ___________? In Congress, only a perfect ______________ between slave and anti-slave states meant ___________ ______________________ for both sides. Bleeding Kansas In Kansas, the ___________________ left the issue of slavery for the _______________ to decide, though there were widely differing opinions. Before Kansas could apply for _________________, voters had to approve a _________________ to ___________ or ______ slavery. To win _______, both sides raised money and organized to bring in more _______________. So much violence took place that the area was called “_____________________________.” During the 1850s, several violent ___________ took place between pro-slavery and anti-slavery forces, including the __________________________________, when a gang of ____ pro-slavery men gunned down _____ anti-slavery settlers and killed __________. In __________________, Kansas, a sheriff's posse attacked ___________________ newspapers and ______________ buildings in what is known as the ________ of Lawrence. John Brown In response, John Brown, an abolitionist, and others killed five pro-slavery settlers on __________________________ Creek in Kansas. Kansas was eventually admitted as a __________ state, which deepened _______________ ______________________. John Brown’s Raid Abolitionist _________________ planned a raid on the U.S. arsenal at ________________ to get guns for a slave revolt. U.S. ____________ stormed the arsenal and captured Brown and his followers They were tried for ____________ and ____________, though many northerners thought Brown was a ______________. Hostilities in Congress Congressman Preston ___________ attacks Senator Charles ____________ with his ______ in ___________________ Congressmen started to bring _____________ to Congress Dred Scott Case Dred Scott and his wife, both slaves who lived in _____________ which was _______ soil, ___________ for their freedom. The Supreme Court ruled in __________________________ that slaves are ____________ even if they move to a free state because of the _____ Amendment. Uncle Tom’s Cabin Harriet Beecher Stowe writes ______________________ about the evils of slavery. Abraham Lincoln refers to this as “The little ______________ who wrote the ________ that made this _______.” The Threat of Secession The Southern leaders threatened to _____________ from the _________ if a Republican was elected president in 1860. The Democrats characterize the Republican party as ______________ on _________ Abraham Lincoln Upbringing Lincoln was born in 1809 in a one-room cabin near Louisville, Kentucky. Lincoln’s family was very ________, held no _________, and _____________ slavery. They moved to the _________________ Territory in 1816. In 1828 he got a job on a riverboat from Indiana to New Orleans, and there had his first contact with slavery at a New Orleans ___________________. Lincoln’s Early Political Career Lincoln moved to Illinois and ran for state _____________________. He won a seat in the Illinois General Assembly. He married ___________________, the daughter of a Kentucky slaveholder. In 1846 he was elected to Congress, and proposed the radical idea of “________________ _________________,” or paying slave owners to free their slaves. He resigned from Congress in 1849 and went home to Illinois. However, the __________________________ Act, sparked him to reenter politics as a ____________________. The Lincoln - Douglas Debates Lincoln defeated ___________________________ in the Senatorial race. In his acceptance speech, he called the U.S. “_______________________________” on the issue of slavery. National news attention about the speech led to the ________________________________. – Lincoln challenged Douglas on _______________________________. – In the ______________________ Doctrine, Douglas said people could stop slavery by refusing to pass laws allowing it. – Lincoln called slavery ___________________ but denied proposing racial equality. The Election of 1860 Two years later, Lincoln and Douglas ran against each other for ___________________, facing hard battles. The ____________________ were divided and split completely, as southern Democrats _______________________ of the nominating convention. The remaining Democrats nominated Douglas, and southern Democrats elected John _______________________. Southern moderates started their own party, the ___________________________ Party. The Republicans chose _________________ because his abolitionist views were ___________ but ____________________. Lincoln won the election in the _______________ and became president with only 40% of the vote. Southern Secession: Causes and Effects A week after Lincoln’s election, the South Carolina called a convention to consider ________________ the Union. _____________________ secedes followed, including Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, ___________________, Louisiana, and Texas. Four other states—_________________, North Carolina, ________________, and Arkansas—also threatened to secede. Causes of Secession o The Compromise of _________ o The ___________________________ Act o The ___________________________ Debates o The _______________ of 1860 Effects of Secession o South Carolina fears a northern-controlled ________________ will act against _______________ and _____________________ from the Union. o Several states follow, forming the _________________________________. The Confederate States of America In February ___________, _________ seceded states met in Montgomery, Alabama, to form a new ________________. They created the Confederate States of America, or the _______________________, which, problematically, lacked national __________________ and official _____________________. They chose ____________________________, a former U.S. Senator from Mississippi, as president. The Capital was ____________________________ The Civil War The Union The Confederacy The Yankees The Rebels Population of ____ million Population of ___ million of which 3 million Resources were ____________ More ___________________ • ____________________________ Stronger ___________ leaders and • Transportation - _______________ ______________ • _________ mills & ______ mines Only had to fight a _______________ war Fort Sumter 4/61 - The __________________ bombs the _____________ Fort in the harbor of _______________, South Carolina until they surrendered. Bull’s Run - Manassas, VA 7/61 - 1st major battle outside ___________________________ People came out to watch, the ___________ had a surprising victory. Untrained troops on both sides transformed the battle to chaos and ended hopes for a short war. Monitor and the Merrimack Ironsides battle at Hampton Roads. CSS ______________ (USS Merrimack) vs.USS _________________ The North had a ___________________ on the ______ and _________________ all southern ports. The War in the West Gaining control of the ___________________ River would split the Confederacy in ___ Grant moved South, winning a major victory at the __________________________ in Tennessee, but the fierce battle dashed northern hopes that the rebellion would collapse on its own. 20,000 killed. A Union fleet under Admiral David __________________ moved north along the Mississippi, capturing _________________________ and other river cities. Antietam 9/62 - Biggest _____ day bloodbath. Over _________________ killed and wounded. Ended in a _______________ victory when McClellan stopped Lee’s advance into Maryland. Lee retreats to _______________. When McClellan doesn’t pursue, Lincoln puts _______________ in command. Fredericksburg 12/62 - The South (_______ and _______________) defeat the North (______________) in Virginia when Burnside tries a _________________________ and is massacred. Burnside resigns and Joseph _____________ takes over the Union Command Chancellorsville 5/63 - ______ defeats ______________ despite 120,000 to 60,000 advantage. Gen. ___________________________ is accidentally shot and later dies. Vicksburg 7/63 - Gen. ____________________ and the North defeat the South at _________________ taking _______________ of the Mississippi River. The Final Battles Grant fights _______ in three battles in his attempt to take the Capital of _______________ Virginia Wilderness, Spotsylvania, and Cold Harbor Grant lost as many __________________ as there were serving in Lee’s __________ Lee __________________ at ____________________ Courthouse Results A. Losses: 1. Union: _______________ 2. Confederate: _______________ 3. ________________ wounded B. ________________ assassinated by ____________________ five days after the South __________________ Reconstruction Lincoln’s Plan _____________ country - ___________ Plan _____% of men eligible to vote in South must swear ________________ to __________ Vetoed the ______________________ - ______________ had to take oath Andrew Johnson’s Plan Outspoken ____________ of southern traitors Plan was lenient on the ____________, following _______________ lead ___________________ - Pardon to Confederates who sign oath Special Pardons-for _____________________ & _______________ worth more than $_________________ Congress Reconstruction Acts Five ______________________ & Federal Troops stationed ____________________ refused to seat Southern representatives because of the _____________________ which restricted the rights of newly ________________________ Civil Rights Act - citizenship to ___________________________ ________ Amendment - prevented states from denying rights or privileges of any citizen 15th Amendment - the right to ________ cannot be denied for ________, color, or former servitude. _________________________________ - prosecute anyone who violate 14th or 15th Amendment Southern Reconstruction Whites refused to vote in _____________________________ African Americans influenced the _________ The ______________________ Party controlled all of the _________ governments African Americans _____________________ whites in the ____________________ Congress tried to ____________________ Johnson for firing Sec. of War Edwin Stanton _______________ Congress approval. He is _________________ by one vote in the Senate. Ku Klux Klan The first Klan was founded in 1865 by Tennessee _____________ of the __________________ Army. Groups spread throughout the _____________. Its purpose was to restore white __________________ in the ________________ of the Civil War. The Klan resisted _____________________ by ________________, _______________ and intimidating _______________ and white Republicans. Ulysses S. Grant __________________ wins Presidency 18th President ______________ control south again and will continue until the election of ___________________ Freedmen’s Bureau Federal agency set up to give freed slaves _______, food, _______________, horses and mules 40,000 African Americans established _____________ in South Illiteracy _______________ Former Slaves in the South __________________________ - land given in exchange for a portion of the crops not much different than slavery, still lived in same conditions __________________ - fee paid to vote, kept poor and blacks from voting _________________________ - redrawing district boundaries to lessen black voting power Southern Governments Carpetbaggers ____________________ who ran Southern __________________________ many were __________________ and involved in _______________ Scalawags _______________________ who opposed secession and who participated in the _____________________ Governments with the Northerners The End of Reconstruction Election of 1876 - Rutherford _________ vs. Samuel _________ -Close election, disputes in 4 states (3 in South) -Settled by ___________________ giving ________________ to the South -Hayes elected by 1 Electoral College vote -Ending Reconstruction -___________ troops pulled out of South _______________________ overturns Enforcement Act & Civil Rights Act Former slaves still have no _______, no ___________, no _____________. Many African Americans move _________.