* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TOPIC # 8 – 6: Solving Systems by Elimination
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Kerr metric wikipedia , lookup
Unification (computer science) wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Two-body problem in general relativity wikipedia , lookup
Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Perturbation theory wikipedia , lookup
Calculus of variations wikipedia , lookup
BKL singularity wikipedia , lookup
Differential equation wikipedia , lookup
Schwarzschild geodesics wikipedia , lookup
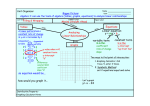
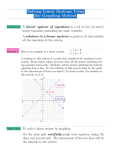
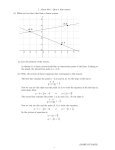
Unit 6: Systems of Equations Algebra I 2011-2012 TOPIC # 8 – 3: GRAPHING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS Solve each system by graphing. Put each equation into y= mx + b form then use y= in your calculator to graph the system. 1. y = 2x – 8 y = -x +1 m = _______ b = ______ m = _______ b = ______ Intersection __________ 2. 2x + y = 2 x–y=4 y= x+ m = _______ b = ______ y= x+ m = _______ b = ______ Intersection __________ 3. x – 3y = 6 x – 3y = -3 y= x+ m = _______ b = ______ y= x+ m = _______ b = ______ Intersection __________ 4. 2x – y = 1 6x – 3y = 3 y= x+ m = _______ b = ______ y= x+ m = _______ b = ______ Intersection __________ State whether the given ordered pair is a solution to the system. Show all work and circle yes or no. 1 5. y = 2 x + 2 Y=x–2 (8,6) Yes or No 6. 2x – y = 1 -3x + y = 4 ( 2, -1 ) Yes or No 7. 2x + 3y = 6 X – 4 = 2y ( 4, -1 ) 8. y = 3x – 2 2x – y = 4 ( -2, -8) Yes or No Yes or No Solving Linear Systems by Graphs and Tables (pp. 1 of 4) A _________________________ is two (or more) equations comprised of two (or more) related variables. 5x + 3y = 6 X – 4y = 9 The solution for the first equation above is a set of points represented by the line y = -5/3x + 2 The solution for the second equation above is a set of points represented by the line y = ¼ x – 9/4 The solution for the system of equations is the point or set of points where the two lines intersect. The intersection can occur in three different ways. The different possible solutions can be seen in the alignment of the two lines when graphed on a plane. (x,y) R Ø Solving Linear Systems by Graphs and Tables (pp. 2 of 4) Systems of linear equations can be solved using ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ o ____________________________ o ____________________________ Solve systems ______________________ A. Graph both equations by one of the following methods. Find the y-intercept (0, y) and x-intercept (x, 0), and draw the line through the intercept points. Solve each equation for y, and graph using slope (m) and y-intercept (b). Solve each equation for y, and enter them into the graphing calculator in y1 and y2. When using the graphing calculator, the WINDOW may need to be adjusted so that the intersection of the lines is viewable in the window. B. Find the intersection point of the two lines. Read the point from the graph. Use the graphing calculator and graph the lines. Press 2nd CALC, select INTERSECT, get the cursor close to the point of intersection, and ENTER ENTER ENTER. Verify the solution by checking the table function of the calculator. The solution will be the x value where both values in y1 and y2 of the table are equal. Example y=x–4 y = -x + 10 X Y1 X Y2 Solving Linear Systems by Graphs and Tables (pp. 3 of 4) Guided Practice: 2. y = 3 – x y=x+1 X Special Cases: 3. y = 1/2x – 3/2 4y -2x = -6 Y1 4. 2y – x = 3 4y – 2x = -3 X Y2 Solving Linear Systems by Graphs and Tables (pp. 4 of 4) Practice Problems: Find the solutions to the following systems of equations. Round solutions to the nearest tenth. System 9. x+y=4 2x + y = 6 10. X – y = -5 X+y=3 11. 3x + y = -2 4x + y = -4 12. X–y=0 5x – 3y = 10 13. X + 2y = 1 5x – 4y = -23 14. 4x + 3y = 8 X – 2y = 13 15. 10x + 16y = 140 5x – 8y = 60 16. 2x + 3y = -12 8x – 5y = 40 Y = mx + b form Sketch of graph Solution Check by table TOPIC # 8 – 4: Solving Systems of Equations by Substitution 1. y = 3x x+y=8 Solve for a single variable(get in y=) Substitute and Solve(plug n chug) Find other value and write solution Intersection______ 2. 2x + y = 9 x + 4y = 1 Solve for a single variable(get in y=) Substitute and Solve(plug n chug) Find other value and write solution Intersection______ 3. 2a – b = 1 5a – 3b = 0 Solve for a single variable(get in y=) Substitute and Solve(plug n chug) Find other value and write solution Intersection______ 4. 2x – y = 8 x+y=1 Solve for a single variable(get in y=) Substitute and Solve(plug n chug) Find other value and write solution Intersection______ TOPIC # 8 – 5: SOLVING SYSTEMS BY ELIMINATION PART 1 Solve each system by ELIMINATION. 1. 5x – y = 12 3x + y = 4 2. 6c + 7d = -15 6c – 2d = 12 Solution:__________ Solution:__________ 3. 8m + 12n = 20 5m + 12n = -1 4. 4x – 3y = -2 2x + 3y = 26 Solution:__________ Solution:__________ TOPIC # 8 – 6: Solving Systems by Elimination The Sequel Solve each system by elimination. 1. 2x – 3y = 4 x + 4y = -9 Solution:__________ 2. 4x – 5y = 23 3x + 10y = 31 Solution:__________ 3. 4s – 5t = 3 3s + 2t = -15 Solution:__________ 4. 3a + 4b = 2 5a + 9b = 1 Solution:__________