* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Female Reproductive Cycle
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
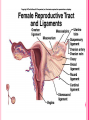
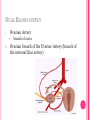
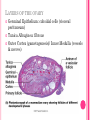
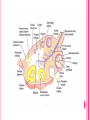
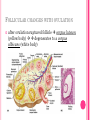
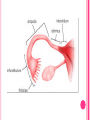
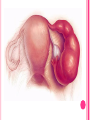
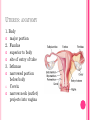
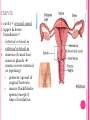
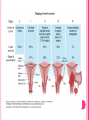
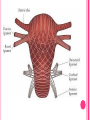
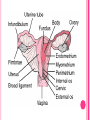
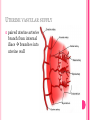
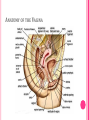
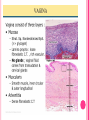
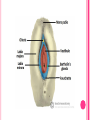
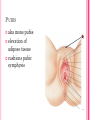
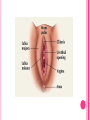
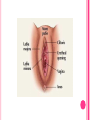
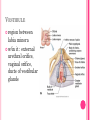
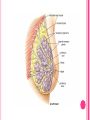
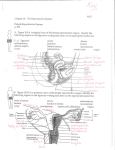
THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE CYCLE Honors Anatomy & Physiology Part 1 FUNCTIONS OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Ovaries produce 2° oocytes & hormones (E, P, inhin, & relaxin) Uterine tubes transport 2° oocyte uterus; sites of fertilization Uterus site of implantation of fertilized ovum, development of fetus during pregnancy & labor Vagina receives penis during intercourse; birth canal Mammary glands synthesize, secrete, & eject milk for nourishment of newborn ANATOMY OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Internal Genitalia 1. 2. 3. 4. Internal Genitalia: Ovaries = Female Gonads Fallopian tubes Uterus Vagina External Genitalia Vulva OVARIES almond-shaped (2x size) flank either side of uterus: suspended medially to uterus by ovarian ligament anchored laterally by suspensory ligament mesovarium a part of the broad ligament which drapes over all 3 ligaments DUAL BLOOD SUPPLY 1. Ovarian Artery 2. branch of aorta Ovarian branch of the Uterine Artery (branch of the internal iliac artery) LAYERS OF THE OVARY Germinal Epithelium: cuboidal cells (visceral peritoneum) Tunica Albuginea: fibrous Outer Cortex (gametogenesis)/ Inner Medulla (vessels & nerves) OVARIAN FOLLICLES in cortex contain 1 immature ovum called an oocyte surrounded by follicular cells (1 layer) or granulosa cells (>1 layer) Range of Stages of Maturation 1. Primordial Follicle surrounded by follicular cells 2. Tertiary Follicle (pre-ovulatory follicle) a fully mature follicle surrounded by granulosa cells bulges on ovarian surface FOLLICULAR CHANGES WITH OVULATION after ovulation ruptured follicle corpus luteum (yellow body) degenerates to a corpus albicans (white body) FALLOPIAN TUBES aka uterine tubes: ~10 cm in length receive ovulated oocyte: *site of fertilization empty into superolateral region of uterus 5 parts: (medial lateral) 1. Interstitium: w/in uterine wall 2. Isthmus: constricted portion 3. Ampulla: widens 4. Infundibulum: funnel-shaped 5. Frimbria (fringe) ciliated finger-like projections draped over ovary 1 or more attached to ovary FALLOPIAN TUBE performs a “dance” around time of ovulation fimbriae stiffen & sweep surface of ovary wall has sheets of smooth muscle peristalsis moves oocyte toward uterus lined with folds of ciliated & nonciliated mucosa externally covered by peritoneum & supported by portion of the broad ligament: mesosalpinx http://www.gettyimages.com/detail/video/egg-cellin-a-fallopian-tube-animation-stock-videofootage/618590467 HOMEOSTATIC IMBALANCE Ectopic Pregnancy pregnancy outside the uterus peritoneal cavity or w/in fallopian tube hemorrhage shock PID: Pelvic Inflammatory Disease infection spreading from other parts of reproductive tract. Gonorrhea, Chlamydia can scar tubes infertility or ectopic pregnancy UTERUS Latin for womb anterior to rectum in pelvic cavity& posterosuperior to bladder hollow, thick-walled muscular organ with shape of inverted pear anteverted: tipped forward retroverted: tipped back receives, retains, & nourished fertilized ovum UTERUS: ANATOMY 1. Body major portion 2. Fundus superior to body site of entry of tube 3. Isthmus narrowed portion below body 4. Cervix narrow neck (outlet) projects into vagina CERVIX 1. 2. cavity = cervical canal upper & lower boundaries = internal cervical os external cervical os mucosa of canal has mucous glands mucus covers external os (opening) protects: spread of vaginal bacteria mucus thick(blocks sperm) except @ time of ovulation HOMEOSTATIC IMBALANCE Pap Smear: Papanicula Smear sampling of cells from endocervical canal screening test for cervical cancer 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. cervical ca risk factors: frequent cervical inflammation HPV starting sex activity @ early age multiple pregnancies/early 1st pregnancy unprotected intercourse smoking multiple sex partners CERVICAL CANCER ~13,000 new cases/yr in USA ~4,100 women die from cervical cancer/yr in USA rate has dropped >50% in past 30 yrs (b/4 that was most common cancer death in USA) by race: Hispanic > African American> Asian & Pacific Islands > white most diagnosed age 20 – 50, 15% >65 yrs Gardisil vaccination protects against HPV induced cancer recommended for all 11 – 12 yr old girls UTERINE LIGAMENTS 1. 2. 3. Broad Ligaments mesentery portion, lateral suspension Cardinal Ligaments extend from cervix & superior vagina lateral walls of the pelvis (inferior to broad ligament support) Uterosacral Ligaments secure uterus to sacrum posteriorly UTERINE WALL 1. 2. 3. 3 layers: (external internal) Perimetrium serous layer Myometrium muscle Endometrium mucosal lining of the uterine cavity 2 strata: stratum functionalis: cyclic changes, sheds with menstruation stratum basalis: thinner, deeper layer: forms a new stratum functionalis after menstruation UTERINE VASCULAR SUPPLY paired uterine arteries branch from internal iliacs branches into uterine wall VAGINA “sheath”/ aka birth canal thin-walled tube 8 – 10 cm in length lies between bladder & rectum extends from cervix to body exterior parallel to urethra Function: 1. passageway for delivery of newborn or menstrual flow 2. receives the penis during sexual intercourse ANATOMY OF THE VAGINA HYMEN thin fold of vascularized mucous membrane that forms a border around & partially closes the inferior end of the vaginal opening to the exterior imperforate hymen: completely or partially closes off the orifice VULVA external genitalia of females made up of: 1. Pubis 2. Labia Majora 3. Labia Minora 4. Clitoris 5. vestibule &Vestibular Glands PUBIS aka mons pubis elevation of adipose tissue cushions pubic symphysis LABIA MAJORA 2 longitudinal folds of skin extending inferiorly & posteriorly from mons pubis covered by skin & pubic hair contain: adipose tissue, sebaceous (oil) & apocrine (sweat) glands are homologous to the scrotum LABIA MINORA medial to labial majora no pubic hair, few sudoriferous glands many sebaceous glands homologous to spongy urethra CLITORIS small cylindrical mass of erectile tissue & nerves Located at anterior junction of labia minora homologous to glans penis VESTIBULE region between labia minora w/in it : external urethral orifice, vaginal orifice, ducts of vestibular glands SKENE’S GLANDS “minor” vestibular or paraurethral glands secrete mucus homologous to prostate BARTHOLIN’S GLANDS either side of vaginal orifice “greater” vestibular glands produce small amt mucus during sexual arousal providing lubrication homologous to Cowper’s glands MAMMARY GLANDS Nipples Areola : circular, pigmented area around each Lactiferous Ducts: closely spaced openings where milk emerges Suspensory Ligament: strands of CT between skin & deep fascia that support the breast Mammary Gland: modified sudoriferous (sweat)glands separated by adipose surrounded by myoepithelial cells (smooth muscle): contraction milk let down