* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Female pelvic anatomy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
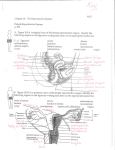
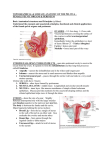
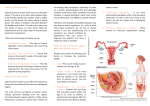
Female pelvic anatomy The Lig. Infudibulo‐pelvicum contains the ovarian vessels, lymphatics and nerves (1) The two uterine tubes (2) lie on each side of the uterus in the upper margin of the broad ligament (3) (mesosalpinx). 1 1 22 5 3 5 4 4 The internal iliac atery devides into an anterior and posterior trunk. The anterior trunk branches in the superior and inferior vesical artery, the middle rectal artery , the vaginal artery (4), the obturator artery and uterine artery (5). The uterine veins form a plexus in the parametrium below the uterine arteries, draining into the internal iliac veins The broad ligament (1) is a double fold of peritoneum extendingfrom the uterus towards the pelvic side‐ wall (2). 4 3 1 6 5 7 2 The hilum of the ovary arises from its posterior surface (3). Between the leaves of this fold, the uterine and ovarian blood vessels form an anastomotic loop. The ovarian ligament connects the cornu of the uterus to the medial pole of the ovary (4). The cardinal ligaments (5+6) provide support to the internal genital organ and consists of connective tissue around the vessels and nerve plexuses They are fused with the fascia surrounding the cervix and upper part of the vagina (7). The main blood supply of the uterus is from the uterine arteries. Each passes medially in the base of the broad ligament above the ureter, and ascends along the lateral aspect of the uterus 1 2 The descending ureters (1+2) are narrow muscular tubes which cross into the pelvis close to the bifurcation of the common iliac arteries. They lie immediately under the peritoneum. Approaching the bladder, the ureters pass medially in front of the upper vagina, and enter the bladder base obliquely at the upper angles of the trigone. 1 2 3 4 5 The endometrium (1) is the epithelial lining of the cavity. The surface consists of a single layer of columnar ciliated cells. Picture shows an intracavitär myom (3) The smooth muscle fibres of the uterine wall form the Myometrium (2), a myoma located in this layer is called a intramural myoma (4) The posterior surface of the uterus is completely covered by peritoneum. Anteriorly the peritoneum is reflected off the uterus at a much higher level A myoma located directly under the peritoneum is called a subserös one (5) The uterus is in the middle of the pelvic cavity The uterus is mobile and moves under pressure of the full bladder or full rectum anteriorly. Increased intra abdominal pressure pushes it downwards. Under normal circumstances the suspensory part keeps the uterus in anteflexion and anteversion It is important to distinguish retroversion from anteversion before introducing a sond or similar instrument into the uterine cavity, to avoid perforation of the uterine wall. Position of uterus: ”Retroverted”: Tipped backward "Anteverted": Tipped forward Position of fundus: "Anteflexed": Fundus is pointing forward relative to the cervix Retroflexed": Fundus is pointing backwards relative to Cervix The picture shows the bimanual palpation of an anteverted and anteflexed livmoder x1 2 1 x Picture 1: First step of abdominal Hysterectomy: The round ligament is grasped and divided with ligation or electrocautery. After cutting this ligament, the posterior leaf of the broad ligament (x) can be incised giving access to the retroperitoneal space. It is important to identify the ureter in the Retroperitoneum. Picture 2: The anterior part of the broad ligament is cut in order to reach the vesico‐uterine junction (x1). At this point the peritoneum is incised to free the bladder. Laparoscopic resection of an intramural myoma. In the picture the serosa of the uterus has already been incised and gives view over the myoma lying under the surface. Subserös and intramural myoma can be easily removed with a minimal invasiv laparoscopic operation mons pubis x Perineum The term vulva generally encompasses all the external female genitalia, i.e. the mons pubis, the labia majora and minora, the clitoris, and the structures within the vestibule – the external urinary meatus and the hymen. External borders of the vulva: ‐Anterior: The mons pubis (x) ‐Lateral: The labia majora ‐Posterior: The perineum Internal border: ‐Hymenal ring