* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Faraday`s Law and the Genecon
Loading coil wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Capacitor discharge ignition wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Ignition system wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
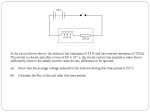
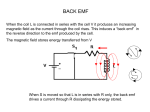
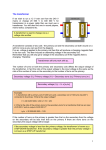
Faraday’s Law – Genecon and Transformer Equipment: genecon ac power supply connecting wires voltmeter stopwatch full transformer set Multi-meter Overview: In this lab we will further explore the phenomena associated with magnets and coils of wire. A generator is a device which uses relative motion between wires and magnetic fields. The voltage output of a DC generator such as the Genecon can be written as: V() = 0.707NBA. where is the rotational rate of the coil in rad/s, N = #turns of wire on the coil, B = strength of the magnetic field in tesla, and A = area around which the turns of wire are wound. A. Preliminaries 1. A coil of wire has the following parameters, A = 98cm2, N = 2122. Write clear work showing that if this coil is rotated at 688 rpm (revolutions per minute) in a 0.33 tesla field that the DC output would be 349 volts. 2. If the rotational rate were increased by 10% what percentage change in output voltage would be observed on this generator? _____ Why? B. Experiment 3. Use your Genecon to produce 2.0 volts as steadily as you can for a time of 15 seconds. DO NOT ATTEMPT TO PRODUCE MORE THAN 4.0 VOLTS AT ANY TIME. While the Genecon is producing 2.0 volts count the number of turns of the handle during the 15 seconds that you time. Number of turns of handle = _______________ in 15 seconds time (2.0 V output) frequency in revs/s = (Number of turns of handle)/15s = ____________________ rev/s = angular speed in rad/s = 2f = _____________________ rad/s 4. The gears of the Genecon amplify the rotational speed of the generator wires by a factor of 48 times over the rotational speed of the crank. Thus actual = 48. If we assume that the Genecon has coil-area 1.0 cm2 in a field of 0.25 tesla, calculate the number of turns of wire on the coil inside the Genecon using V = 0.707NBAactual. Show work. Transformers Equipment: ac power supply connecting wires full transformer set Multi-meter Introduction: Transformers transform one ac signal into another ac signal through a shared electromagnetic wave interaction. The changing magnetic flux of the driven primary circuit induces a current in the secondary passive circuit. If 100% of the changing magnetic flux is shared by both circuits, then Faraday’s Law allows us to write: Vp Np ( BA) Vs t Ns where Vp and Np are the voltage and number of turns on the primary circuit, and Vs and Ns are the corresponding voltage and number of turns in the secondary circuit. In reality, only a portion of the magnetic flux will be shared by the secondary circuit. We will call this portion the efficiency of the transformer, and use the equation: (1) Vs V p efficiency . We will explore this relationship experimentally in this lab. Ns N p Procedure: 1. With the power supply off, connect AC output of the power supply to the coil with the smallest number of turns. Connect the voltmeter in 20V ac~ mode to the secondary coil with the smallest number of turns. 2. Turn the voltage adjustment all the way counter clockwise. Set the power supply to the lowest range ac voltage. Turn on the power supply. 3. Adjust the voltage to about 5.0V. Record the voltage induced in the secondary coil. 4. Turn down the voltage and exchange your secondary coil with the coil with the next higher number of turns. Readjust the voltage to 5.0V and record the voltage induced in the secondary coil. Repeat for subsequently larger number of turn secondary coils. Complete the remaining calculations in the table. Np Ns Ns / N p Vp Vs Vs / V p Vs / V p Ns / N p Questions: 1. Which column in the table represents the efficiency of the transformer? ______ Show this using equation (1). 2. A transformer has an efficiency of 80%. How many turns would have to be on the secondary coil to achieve a voltage of 2400V if the primary coil has 500 turns and the input voltage is 120V? Show formulas and work. 3. A student wants to create a 6.0V AA “battery” from a 1.5V AA battery. Can the student do this using an 80% efficient transformer? If so, give an example transformer coil ratio. If not, why not?