* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 19. oral cavity+pharynx2010-10-01 03:411.2 MB
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
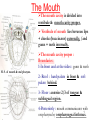
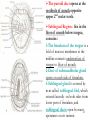
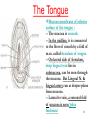
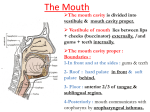
The Mouth The mouth cavity is divided into vestibule & mouth cavity proper. Vestibule of mouth lies between lips + cheeks (buccinator) externally, /and gums + teeth internally. H. S. of mouth & oral pharynx. The mouth cavity proper : Boundaries : 1-In front and at the sides : gums & teeth 2- Roof : hard palate in front & soft palate behind. 3- Floor : anterior 2/3 of tongue & sublingual region. 4-Posteriorly : mouth communicates with 1 oropharynx by oropharyngeal isthmus. The parotid duct opens at the vestibule of mouth opposite upper 2nd molar tooth. Sublingual Region : lies in the floor of mouth below tongue, contains : 1-The frenulum of the tongue is a fold of mucous membrane in the midline connects undersurface of tongue to floor of mouth. 2-Duct of submandibular gland opens on each side of frenulum. 3-Sublingual gland is covered by m.m called sublingual fold, which extends laterally on both sides from lower part of frenulum, and sublingual ducts open by many2 aperatures on its summit. Sensory nerve supply of mucous membrane of mouth : • Roof (palate) : greater palatine & Nasopalatine nerves from Maxillary N. • Floor (anterior 2/3 of tongue) : lingual N. of mandibular N. (general sensation), + chorda tympani N. of facial N. (taste sensation). • Cheek : buccal nerve, a branch of mandibular N. 3 The Tongue It is a mass of striated muscle covered with mucous membrane. Its anterior 2/3 lies in mouth (oral part), while posterior 1/3 lies in pharynx (pharyngeal part). It is divided into right & left halves by a median fibrous septum. 4 The Tongue Mucous membrane of the Upper surface of tongue (dorum of tongue) --Oral & pharyngeal parts are separated by a V-shaped groove called sulcus terminalis, the apex of sulcus is marked by a pit called foramen coecum ( is an embryologic remnant of upper end of thyroglossal duct). --The mucous membrane of oral part (anterior 2/3) contains vallate papillae. --The mucous membrane of pharyngeal part (post.1/3) devoid of papillae, but it has a nodular irrigular5 The Tongue Mucous membrane of inferior surface of the tongue : -- The mucosa is smooth. -- In the midline, it is connected to the floor of mouth by a fold of m.m. called frenulum of tongue. -- On lateral side of frenulum, deep lingual vein lies in submucosa, can be seen through the mucosa. But Lingual N. & lingual artery run at deeper plane from mucosa. -- Lateral to vein, a serrated fold of mucosa is seen ‘plica fimbriata’ 6 Innervation of the Tongue : (vagus) Motor Nerves : -- All intrinsic & extrinsic muscles are supplied by hypoglossal N. EXCEPT palatoglossus is supplied by pharyngeal plexus via vagus N. Sensory Nerves : 1-Anterior 2/3 : general sensations : by lingual N….taste sensations (excluding vallate paoillae) : by chorda tympani. 2-Posterior 1/3, including vallate papillae : general & taste sensations by glossopharyngeal N. 3-Root of tongue ( most posterior part) : internal laryngeal branches of vagus. 7 Blood Supply of Tongue • Lingual artery : branch of external carotid artery, it supply most of tongue (the main arterial supply) • Tonsillar (branch of facial) + Ascending pharyngeal artery (branch of ext.carotid artery) : they supply posterior part of tongue. • Veins of tongue form lingual vein ,which drains into internal jugular vein. 8 Lymph Drainage of Tongue Tip of tongue : drain into submental L.Ns. The remainder of anterior 2/3 of tongue : drains into submandibular + inferior deep cervical L.Ns. Posterior 1/3 of tongue : drains into superior deep cervical L.Ns. 9 Muscles of Tongue • Intrinsic muscles : -They are not attached to bone. -They consist of longitudinal, transverse & vertical fibers (inside the tongue). -Origin : median septum & submucosa. -Insertion : mucous membrane. -Nerve supply : hypoglossal N. -function : Alter the shape of tongue. 10 Extrinsic Muscles of Tongue Extrinsic muscles : -They connect tongue to styloid process & soft palate above, /and to mandible & hyoid bone below. -They are : 1-Genioglossus. 2-Hyoglossus. 3-Styloglossus. 4-palatoglossus. 11 Extrinsic Muscles of Tongue Genioglossus : -Origin : superior mental tubercle of mandible. -Insertion : it is fan-shaped, blends with other muscles of tongue (into tongue, & body of hyoid bone). -Action : -The 2 muscles : protrude tip of tongue through mouth. -One muscle : protrudes the tongue to opposite side. 12 Extrinsic Muscles of Tongue Hyoglossus : -Origin : body + greater cornu of Hyoid bone. -Insertion : it is quadrilateral, runs upward deep to mylohyoid muscle to insert at side of post.part of tongue. -Action : Depress tongue and increase mouth cavity during swallowing. 13 Structures Superficial to Hyoglossus Superficial relations : 1-Mylohyoid + Styloglossus. 2-Lingual N. 3-Hypoglossal N. 4-Submandibular ganglion. 5-Deep part of submandibular gland. ligual artery (deep to hyoglossus) 14 Extrinsic Muscles of Tongue Styloglossus : -Origin : styloid process. -Insertion :blends with other muscles of tongue.(whole length of side of tongue). Action : Pulls tongue upward and backward (retraction + elevation) during swallowing. It passes between superior & middle constrictors of pharynx to reach tongue. 15 Extrinsic Muscles of Tongue Palatoglossus : -Origin : from undersurface of palatine aponeurosis (soft palate). -Insertion : into the side of post.1/3 of tongue. -Action : pulls root of tongue upward & backward, (retraction + elevation), so narrows oropharyngeal isthmus and prevents regurgitation of food. 16 Movements of Tongue Protrusion : genioglossus on both sides acting together. Retraction : styloglossus + hyoglossus Ms. on both sides. Depression : hyoglossus + genioglossus Ms. on both sides. Retraction & elevation of posterior 1/3 of tongue : Styloglossus + Palatoglossus, on both sides. 17 The Palate It forms the roof of mouth. It is divided into : hard palate anterior & soft palate posterior. Hard palate : -It forms anterior 2/3 of palate. -it is formed by palatine processes of maxillae + horizontal plates of palatine bones. -It is bounded laterally by alveolar arches and continuous behind with soft palate. -It forms floor of nasal cavities. –It is covered with muco18 periosteum. Soft Palate It forms the posterior 1/3 of palate. It is a mobile fold attached anteriorly to the hard palate. Soft palate Its posterior free end forms a conical projection in the midline called the Uvula. It lies between the naso pharynx & oropharynx. Laterally , it is attached to side wall of pharynx. 19 Structures of Soft Palate Mucous Membrane : covers its upper & lower surfaces. Palatine aponeurosis Soft palate is seen from behind Palatine aponeurosis : it is a fibrous sheet in the middle, attached to posterior border of hard palate, it is the expanded tendon of Tensor veli palatini on both sides. Muscles of Soft Palate : 1-Tensor vili palatini. 2-Levator vili palatini. 3-Palatoglossus. 4-Palatopharyngeus. 5-Musculus uvulae. 20 Muscles of Soft Palate Tensor veli palatini : -Origin : spine of sphenoid + auditory tube. -Insertion :with muscle of other side forms palatine aponeurosis which is inserted into palatine crest (posterior border of hard palate). –N.supply : N. to medial perygoid from mandibular N. -Action : tense soft palate. Soft palate is seen from behind 21 Muscles of Soft Palate Levator veli palatini : -Origin : Petrous part of temporal bone + auditory tube. -Insertion : palatine aponeurosis. - N.supply : pharyngeal plexus. -Action : elevates soft palate, shutting off nasopharynx fron oropharynx in swallowing. Soft palate is seen from behind. Palatopharyngeus : -Origin : palatine aponeurosis. -Insertion : posterior border of thyroid cartilage+ wall of pharynx. It lies in a fold of m.m of lateral wall of pharynx, called palatopharyngeal arch. -N.supply : pharyngeal plexus. -Action : The 2 muscles elevate wall of pharynx + closing of ‘‘pharyngeal isthmus’’ during swallowing (communicating channel between nasal & oral parts of pharynx). 22 Muscles of Soft Palate Palatoglossus : -Origin : palatine aponeurosis. -Insertion : side of post.1/3 of tongue, it lies in a fold of m.m. of lateral wall of oro-pharynx, called palatoglossal arch, which lies in front of palatine tonsile. -N.supply : pharyngeal plexus. -Action : the 2 muscles pull root of tongue upward & backward, causing narrowing of ‘oropharyngeal isthmus’ and prevent regurgitation Musculus uvulae : of food. -Origin : posterior border of hard palate (post. Nasal spine). -Insertion : m.m.of uvulae. -N.supply : pharyngeal plexus. 23 -Action : elevates uvulae. palatoglossal & palatopharyngeal arches : are folds of mucous membranes covering the muscles of sot palte, palatoglossus &/ palatopharyngeus in the oropharynx. Oropharyngeal isthmus : it is a sphincter between mouth & oral part of pharynx, and it is marked by the interval between 2 palatoglossal arches. Pharyngeal isthmus : it is the opening between the free end of soft palate & posterior wall of pharynx ( communication between the nasal 24 and / oral parts of pharynx) Innervations of Soft Palate • Motor : all palatine muscles are supplied by pharyngeal plexus EXCEPT tensor veli palatini. (by N.to medial pterygoid from mandibular N.). • Sensory : 1- Greater & Lesser palatine Ns. of maxillary, 2Nasopalatine N. of maxillary N. 25 Blood Supply & Lymph Drainage of soft Palate : • Greater palatine from maxillary artery. • Ascending palatine from facial artery. • Ascending pharyngeal artery from external carotid artery. • Veins of palate : end in pterygoid & tonsillar venous plexus. • Lymph vessels of palate : end in deep cervical L.Ns. 26