* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A Guide to the Accelerated Elimination Procedure for AUBAGIO(R
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
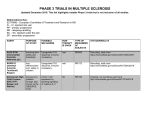
A GUIDE TO THE ACCELERATED ELIMINATION PROCEDURE FOR AUBAGIO® (teriflunomide) WARNING: HEPATOTOXICITY and RISK OF TERATOGENICITY AUBAGIO is available in 14 mg and 7 mg tablets. Hepatotoxicity Severe liver injury including fatal liver failure has been reported in patients treated with leflunomide, which is indicated for rheumatoid arthritis. A similar risk would be expected for teriflunomide because recommended doses of teriflunomide and leflunomide result in a similar range of plasma concentrations of teriflunomide. Concomitant use of AUBAGIO with other potentially hepatotoxic drugs may increase the risk of severe liver injury. Obtain transaminase and bilirubin levels within 6 months before initiation of AUBAGIO therapy. Monitor ALT levels at least monthly for six months after starting AUBAGIO. If drug induced liver injury is suspected, discontinue AUBAGIO and start an accelerated elimination procedure with cholestyramine or charcoal. AUBAGIO is contraindicated in patients with severe hepatic impairment. Patients with pre-existing liver disease may be at increased risk of developing elevated serum transaminases when taking AUBAGIO. Risk of Teratogenicity Based on animal data, AUBAGIO may cause major birth defects if used during pregnancy. Pregnancy must be excluded before starting AUBAGIO. AUBAGIO is contraindicated in pregnant women or women of childbearing potential who are not using reliable contraception. Pregnancy must be avoided during AUBAGIO treatment or prior to the completion of an accelerated elimination procedure after AUBAGIO treatment. References: 1. AUBAGIO (teriflunomide) [package insert]. Cambridge, MA: Genzyme Corporation; September 2012. 2. Data on file, Sanofi/Genzyme. www.genzyme.com © 2013 Genzyme Corporation, a Sanofi company. All rights reserved. MS.US.PO1245.0113 AUBAGIO is available in 14 mg and 7 mg tablets. Please see Important Safety Information on pages 8-11 and accompanying Full Prescribing Information, including boxed WARNING. AUBAGIO is available in 14 mg and 7 mg tablets. The safety and effectiveness of AUBAGIO have not been established in pediatric patients and in patients aged >65 years. The most frequent adverse reactions (≥10% and ≥2% greater than placebo) with AUBAGIO 7 mg and 14 mg and placebo, respectively, were ALT increased (12% and 14% vs 7%), alopecia (10% and 13% vs 3%), diarrhea (15% and 18% vs 9%), influenza (9% and 12% vs 10%), nausea (9% and 14% vs 7%), and paresthesia (9% and 10% vs 8%). The type or dose of oral contraceptives used in combination with teriflunomide should be considered because of increased ethinylestradiol and levonorgestrel levels following repeated doses of teriflunomide. A 25% decrease in peak international normalized ratio (INR) was observed when teriflunomide was coadministered with warfarin vs warfarin alone. Close INR follow-up and monitoring are recommended. Teriflunomide is an inhibitor of CYP2C8 and may be a weak inducer of CYP1A2. Monitor patients when teriflunomide is coadministered with drugs metabolized by these pathways. Interstitial lung disease and worsened preexisting interstitial lung disease have been reported with leflunomide, with a similar risk expected with teriflunomide. Increased blood pressure has occurred with AUBAGIO. Hypertension was reported in 4% of patients taking AUBAGIO vs 2% on placebo. Measure blood pressure at treatment initiation and manage appropriately during treatment. 11 What is the accelerated elimination procedure? Drug elimination processes can be used in certain situations to reduce plasma concentrations of some drugs. A reliable accelerated elimination procedure is available for AUBAGIO® (teriflunomide), indicated for the treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis. When is the accelerated elimination procedure required? The accelerated elimination procedure should be used after discontinuation of AUBAGIO when1: •P regnancy occurs during AUBAGIO therapy (use of this procedure may decrease risk to the fetus) •A patient taking AUBAGIO wants to become pregnant or father a child •D rug-induced liver injury is suspected •A ccelerated removal of drug is clinically desired (eg, overdose or serious skin reactions) The procedure is also recommended after discontinuation of therapy in women of childbearing potential or in the event of clinically significant toxicity.1 2 Please see Important Safety Information on pages 8-11 and accompanying Full Prescribing Information, including boxed WARNING regarding hepatotoxicity and use in pregnancy. Why is accelerated elimination required in these cases? AUBAGIO is eliminated slowly from the plasma. Without accelerated elimination, it takes an average of 8 months, or up to 2 years in some patients, to reach plasma concentrations <0.02 mcg/mL (<0.02 mg/L).1 With the accelerated elimination procedure, these low plasma drug levels can be reached within 11 days. What is the accelerated elimination regimen for AUBAGIO? The recommended procedure is administration of oral cholestyramine 8 g three times daily for 11 days. In patients who do not tolerate this regimen, the dosage may be reduced to 4 g. If tolerability is an issue, cholestyramine administration does not need to occur on consecutive days unless there is a need to lower teriflunomide plasma concentrations rapidly. Oral activated charcoal (50 g twice daily for 11 days) may be substituted for cholestyramine.1 Accelerated elimination regimens for AUBAGIO Agent Dosage Duration of treatment Cholestyramine 8 g tid 11 days Cholestyramine 4 g tid 11 days 50 g bid 11 days Activated charcoal AUBAGIO is available in 14 mg and 7 mg tablets. 3 After 11 days of cholestyramine or activated charcoal administration, plasma concentrations of teriflunomide are reduced by >98%.1,2 Accelerated elimination using cholestyramine appears to be more efficient than charcoal.2 In patients who are pregnant or wish to become pregnant, or in males who wish to father a child, a blood sample should be taken to confirm that blood levels are <0.02 mcg/mL, a level expected to have minimal risk to the fetus.1 Teriflunomide plasma concentration (mcg/mL) Plasma concentrations of teriflunomide after accelerated elimination2 40 Activated charcoal 50 g bid (n≤30) Cholestyramine 4 g tid (n≤16) Cholestyramine 8 g tid (n≤14) 30 20 10 0 0 13 14 16 Day 20 24 First administration of accelerated elimination procedure Teriflunomide was administered from days 1–12. •A t the end of 11 days, both regimens successfully accelerated teriflunomide elimination 4 Please see Important Safety Information on pages 8-11 and accompanying Full Prescribing Information, including boxed WARNING regarding hepatotoxicity and use in pregnancy. How does accelerated elimination of AUBAGIO® (teriflunomide) work? AUBAGIO normally undergoes enterohepatic recycling,2 a process in which bile acids and other substances excreted by the liver are absorbed by the intestinal mucosa and returned to the liver via the portal vein. Cholestyramine and activated charcoal bind and sequester teriflunomide in the small intestine and prevent it from being reabsorbed, thus accelerating its elimination.2 Liver Plasma Reabsorption Excretion Teriflunomide Gut Bile Feces Cholestyramine and activated charcoal sequester teriflunomide in the small intestine, preventing reabsorption and enterohepatic recirculation2 AUBAGIO is available in 14 mg and 7 mg tablets. 5 Are there any adverse events associated with the accelerated elimination procedure? The accelerated elimination procedure is generally well tolerated.2 In some cases, patients may experience transient, mild to moderate gastrointestinal side effects such as upset stomach or nausea.2 Consult the product information for cholestyramine or activated charcoal for more information. Use of the accelerated elimination procedure may potentially result in return of disease activity if the patient had been responding to AUBAGIO® (teriflunomide) treatment.1 Do I need to confirm that the drug has been successfully eliminated? When the accelerated elimination procedure is used for women who are or wish to become pregnant, or men who wish to father a child, a blood test is used to confirm that plasma drug concentrations are reduced to <0.02 mcg/mL, a level expected to have minimal risk to the fetus. Eleven days of treatment with cholestyramine or activated charcoal is usually effective in accelerating AUBAGIO elimination, leading to a >98% decrease in teriflunomide plasma concentrations. However, if drug levels remain above this level, a second course of cholestyramine or charcoal is recommended. When the procedure is used in situations unrelated to current or potential pregnancy, confirmation of plasma levels is NOT necessary. 6 Please see Important Safety Information on pages 8-11 and accompanying Full Prescribing Information, including boxed WARNING regarding hepatotoxicity and use in pregnancy. Is there anything I should know about how to prescribe cholestyramine? It is recommended that patients take other medications at least 1 hour before or 4 to 6 hours after taking cholestyramine. If I do need to confirm my patient’s plasma levels of teriflunomide, how do I obtain the assay? Confirmation of elimination via an assay is only recommended for women who are or wish to become pregnant or men wishing to father a child. The assay is available through LabCorp and is paid for by Genzyme. Forms to set up an account with LabCorp are available from your Genzyme representative or by contacting MS One to One™ at 1-855-MSOne2One (1-855-676-6326). Once your account is set up, you will be provided with assay requisition forms and can order the assay for your patients as needed. AUBAGIO is available in 14 mg and 7 mg tablets. 7 INDICATION AUBAGIO® (teriflunomide) is indicated for the treatment of patients with relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis. IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION Hepatotoxicity—AUBAGIO is contraindicated in patients with severe hepatic impairment and in patients taking leflunomide. Severe liver injury, including fatal liver failure, has been reported in patients treated with leflunomide, which is indicated for rheumatoid arthritis. Teriflunomide is the principal active metabolite of leflunomide. A similar risk would be expected for teriflunomide because recommended doses of teriflunomide and leflunomide provide similar plasma concentrations of teriflunomide. Obtain transaminase and bilirubin levels within 6 months before starting AUBAGIO; monitor ALT levels at least monthly for 6 months after starting AUBAGIO. Patients with preexisting liver disease may be at increased risk of elevated serum transaminases when taking AUBAGIO. Patients with preexisting acute or chronic liver disease, or those with serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) >2 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) before initiating treatment, should not normally be treated with AUBAGIO. In clinical trials, if ALT elevation was >3 times the ULN on 2 consecutive tests, AUBAGIO was discontinued and patients underwent accelerated elimination. Consider additional monitoring if coadministering AUBAGIO with other potentially hepatotoxic drugs because of increased risk of severe liver injury; monitor patients who develop symptoms suggestive of hepatic dysfunction (e.g., unexplained nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fatigue, anorexia, or jaundice and/or dark urine). If drug-induced liver injury is suspected, discontinue use of AUBAGIO, start accelerated elimination, and monitor liver tests weekly until normalized. 8 Please see accompanying Full Prescribing Information, including boxed WARNING regarding hepatotoxicity and use in pregnancy. Risk of Teratogenicity—AUBAGIO is contraindicated in pregnant women or women of childbearing potential who are not using reliable contraception. Based on animal data, AUBAGIO may cause major birth defects if used during pregnancy. Before starting therapy, pregnancy must be excluded, use of reliable contraception confirmed, and the patient fully counseled. Patients having delayed onset of menses or other reason to suspect pregnancy should immediately notify their physician and be apprised of the potential hazards to the fetus. If the patient is pregnant or wishes to become pregnant, treatment should be discontinued immediately, followed by accelerated elimination until plasma concentrations of <0.02 mcg/mL are verified. It is not known whether AUBAGIO passes into breast milk; patients should be counseled on whether they should take AUBAGIO or breastfeed—they should not do both at the same time. Women who become pregnant while taking AUBAGIO should enroll in the AUBAGIO Pregnancy Registry to monitor fetal outcomes, by calling 1-800-745-4447, option 2. AUBAGIO is eliminated slowly from the plasma. Without accelerated elimination, reaching plasma concentrations of <0.02 mcg/mL takes an average of 8 months or, in some patients, up to 2 years. Accelerated elimination may cause disease activity to return in patients who were responding to AUBAGIO treatment. AUBAGIO is detected in human semen. Men not wishing to father a child should use reliable contraception to minimize possible risk. Men wishing to father a child should discontinue AUBAGIO and undergo accelerated elimination until plasma concentrations of <0.02 mcg/mL are verified. (cont.) AUBAGIO is available in 14 mg and 7 mg tablets. 9 ADDITIONAL SAFETY INFORMATION Decreases in white blood cell counts, mainly of neutrophils and lymphocytes, and platelets have been reported in clinical studies of AUBAGIO. Obtain a complete blood cell count within 6 months before starting treatment. Further monitoring should be based on symptoms suggestive of bone marrow suppression. AUBAGIO is not recommended for patients with severe immunodeficiency, bone marrow disease, or severe uncontrolled infections. Treatment in patients with infection(s), acute or chronic, should not be started until the infection(s) is resolved. Medications such as teriflunomide have immunosuppressive potential; patients may therefore be more susceptible to infections. The risk of malignancy, particularly lymphoproliferative disorders, is increased with some immunosuppressive medications. Vaccination with live vaccines is not recommended. Tuberculosis has been observed in clinical studies of AUBAGIO. Before starting treatment, screen patients for latent tuberculosis infection with a tuberculin skin test. Peripheral neuropathy, including polyneuropathy and mononeuropathy, has been reported with AUBAGIO. Age >60 years, concomitant neurotoxic medications, and diabetes may increase the risk. If peripheral neuropathy is suspected, consider discontinuing treatment and performing accelerated elimination. Transient acute renal failure and treatment-emergent hyperkalemia, as well as increased renal uric acid clearance, have been reported with AUBAGIO. Monitor renal function and potassium if symptoms of acute renal failure or hyperkalemia appear. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis have been reported rarely in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving leflunomide, with a similar risk expected for teriflunomide; therefore, stop treatment and use accelerated elimination if a severe skin reaction develops. 10 Please see Important Safety Information on pages 8-11 and accompanying Full Prescribing Information, including boxed WARNING regarding hepatotoxicity and use in pregnancy. AUBAGIO is available in 14 mg and 7 mg tablets. A GUIDE TO THE ACCELERATED ELIMINATION PROCEDURE FOR AUBAGIO® (teriflunomide) WARNING: HEPATOTOXICITY and RISK OF TERATOGENICITY Hepatotoxicity Severe liver injury including fatal liver failure has been reported in patients treated with leflunomide, which is indicated for rheumatoid arthritis. A similar risk would be expected for teriflunomide because recommended doses of teriflunomide and leflunomide result in a similar range of plasma concentrations of teriflunomide. Concomitant use of AUBAGIO with other potentially hepatotoxic drugs may increase the risk of severe liver injury. Obtain transaminase and bilirubin levels within 6 months before initiation of AUBAGIO therapy. Monitor ALT levels at least monthly for six months after starting AUBAGIO. If drug induced liver injury is suspected, discontinue AUBAGIO and start an accelerated elimination procedure with cholestyramine or charcoal. AUBAGIO is contraindicated in patients with severe hepatic impairment. Patients with pre-existing liver disease may be at increased risk of developing elevated serum transaminases when taking AUBAGIO. Risk of Teratogenicity Based on animal data, AUBAGIO may cause major birth defects if used during pregnancy. Pregnancy must be excluded before starting AUBAGIO. AUBAGIO is contraindicated in pregnant women or women of childbearing potential who are not using reliable contraception. Pregnancy must be avoided during AUBAGIO treatment or prior to the completion of an accelerated elimination procedure after AUBAGIO treatment. References: 1. AUBAGIO (teriflunomide) [package insert]. Cambridge, MA: Genzyme Corporation; September 2012. 2. Data on file, Sanofi/Genzyme. www.genzyme.com 11 © 2013 Genzyme Corporation, a Sanofi company. All rights reserved. MS.US.PO1245.0113 AUBAGIO is available in 14 mg and 7 mg tablets. Please see Important Safety Information on pages 8-11 and accompanying Full Prescribing Information, including boxed WARNING. AUBAGIO is available in 14 mg and 7 mg tablets. The safety and effectiveness of AUBAGIO have not been established in pediatric patients and in patients aged >65 years. The most frequent adverse reactions (≥10% and ≥2% greater than placebo) with AUBAGIO 7 mg and 14 mg and placebo, respectively, were ALT increased (12% and 14% vs 7%), alopecia (10% and 13% vs 3%), diarrhea (15% and 18% vs 9%), influenza (9% and 12% vs 10%), nausea (9% and 14% vs 7%), and paresthesia (9% and 10% vs 8%). The type or dose of oral contraceptives used in combination with teriflunomide should be considered because of increased ethinylestradiol and levonorgestrel levels following repeated doses of teriflunomide. A 25% decrease in peak international normalized ratio (INR) was observed when teriflunomide was coadministered with warfarin vs warfarin alone. Close INR follow-up and monitoring are recommended. Teriflunomide is an inhibitor of CYP2C8 and may be a weak inducer of CYP1A2. Monitor patients when teriflunomide is coadministered with drugs metabolized by these pathways. Interstitial lung disease and worsened preexisting interstitial lung disease have been reported with leflunomide, with a similar risk expected with teriflunomide. Increased blood pressure has occurred with AUBAGIO. Hypertension was reported in 4% of patients taking AUBAGIO vs 2% on placebo. Measure blood pressure at treatment initiation and manage appropriately during treatment. A GUIDE TO THE ACCELERATED ELIMINATION PROCEDURE FOR AUBAGIO® (teriflunomide) WARNING: HEPATOTOXICITY and RISK OF TERATOGENICITY AUBAGIO is available in 14 mg and 7 mg tablets. Hepatotoxicity Severe liver injury including fatal liver failure has been reported in patients treated with leflunomide, which is indicated for rheumatoid arthritis. A similar risk would be expected for teriflunomide because recommended doses of teriflunomide and leflunomide result in a similar range of plasma concentrations of teriflunomide. Concomitant use of AUBAGIO with other potentially hepatotoxic drugs may increase the risk of severe liver injury. Obtain transaminase and bilirubin levels within 6 months before initiation of AUBAGIO therapy. Monitor ALT levels at least monthly for six months after starting AUBAGIO. If drug induced liver injury is suspected, discontinue AUBAGIO and start an accelerated elimination procedure with cholestyramine or charcoal. AUBAGIO is contraindicated in patients with severe hepatic impairment. Patients with pre-existing liver disease may be at increased risk of developing elevated serum transaminases when taking AUBAGIO. Risk of Teratogenicity Based on animal data, AUBAGIO may cause major birth defects if used during pregnancy. Pregnancy must be excluded before starting AUBAGIO. AUBAGIO is contraindicated in pregnant women or women of childbearing potential who are not using reliable contraception. Pregnancy must be avoided during AUBAGIO treatment or prior to the completion of an accelerated elimination procedure after AUBAGIO treatment. References: 1. AUBAGIO (teriflunomide) [package insert]. Cambridge, MA: Genzyme Corporation; September 2012. 2. Data on file, Sanofi/Genzyme. www.genzyme.com © 2013 Genzyme Corporation, a Sanofi company. All rights reserved. MS.US.PO1245.0113 AUBAGIO is available in 14 mg and 7 mg tablets. Please see Important Safety Information on pages 8-11 and accompanying Full Prescribing Information, including boxed WARNING. AUBAGIO is available in 14 mg and 7 mg tablets. The safety and effectiveness of AUBAGIO have not been established in pediatric patients and in patients aged >65 years. The most frequent adverse reactions (≥10% and ≥2% greater than placebo) with AUBAGIO 7 mg and 14 mg and placebo, respectively, were ALT increased (12% and 14% vs 7%), alopecia (10% and 13% vs 3%), diarrhea (15% and 18% vs 9%), influenza (9% and 12% vs 10%), nausea (9% and 14% vs 7%), and paresthesia (9% and 10% vs 8%). The type or dose of oral contraceptives used in combination with teriflunomide should be considered because of increased ethinylestradiol and levonorgestrel levels following repeated doses of teriflunomide. A 25% decrease in peak international normalized ratio (INR) was observed when teriflunomide was coadministered with warfarin vs warfarin alone. Close INR follow-up and monitoring are recommended. Teriflunomide is an inhibitor of CYP2C8 and may be a weak inducer of CYP1A2. Monitor patients when teriflunomide is coadministered with drugs metabolized by these pathways. Interstitial lung disease and worsened preexisting interstitial lung disease have been reported with leflunomide, with a similar risk expected with teriflunomide. Increased blood pressure has occurred with AUBAGIO. Hypertension was reported in 4% of patients taking AUBAGIO vs 2% on placebo. Measure blood pressure at treatment initiation and manage appropriately during treatment. 11