* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Midterm Study Guide for 9th-Grade Ancient World History Chapter 1
Afrocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Black Egyptian hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Cradle of civilization wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek literature wikipedia , lookup
Repatriation (cultural heritage) wikipedia , lookup
Civilization wikipedia , lookup
History of Western civilization before AD 500 wikipedia , lookup
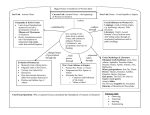
Midterm Study Guide for 9th-Grade Ancient World History Chapter 1: The First Humans Section 1: Early Humans 1. What is the difference between primary and secondary sources? AND Give an example of each. 2. What is meant by the term prehistoric? 3. What is the role of anthropology? 4. What do archeologists do? 5. Give three examples of artifacts. 6. Why is it important for archeologists to date artifacts? 7. List three methods of dating artifacts AND identify the dating method that can be used for the oldest artifacts. 8. Explain why anthropology is not considered an exact science. 9. Define the term hominid AND list three species of hominids in the order they developed. 10. Which hominid species was the first to a) use simple stone tools; b) use fire to keep warm; c) bury its dead. 11. To which hominid species do we, modern human beings, belong to? Be specific. 12. Describe the migratory routes of Homo Sapiens, starting in Eastern and Southern Africa. 13. What does the term Paleolithic mean AND from where did it get its name? 14. Describe the lives of prehistoric people: homes, jobs, clothing, and social life. 15. What was the significance of the discovery of fire for human life? 16. Why were hunting-gathering societies thought to be equal (men and women were equal)? 17. What does the term sympathetic magic mean? 18. What is Lascaux Cave in Southwest France famous of? Section 2: The Neolithic Revolution and the Rise of Civilization 1. What does the term Neolithic mean AND why is it a misnomer? 2. What revolution took place during the Neolithic Age? 3. Define the term systematic agriculture in AND provide another word for it. 4. What factors contributed to the development of systematic agriculture? 5. In what part of the world did systematic agriculture start? 6. What places do we call the Cradles of Civilization AND where was the 1st Cradle of Civilization? 7. What are Jericho and Catal Huyuk famous of? 8. Describe the consequences (results) of the Neolithic Revolution for humans, starting with the creation of permanent settlements (farming villages). 9. What types of materials did people use to make tools at the end of the Neolithic Age? 10. Define the term civilization AND explain what led to their development. 11. List the six characteristics of civilizations. 12. Describe the pyramid-like social structure of Neolithic civilizations. 13. Name a couple of reasons for the development of writing in the Neolithic Age (use textbook). 14. Provide a couple of examples for Neolithic architecture AND painting/sculptures (use textbook). Chapter 2: Western Asia and Egypt Section 1: Civilization Begins in Mesopotamia 1. Where was Mesopotamia located, what does the name “Mesopotamia” mean, AND why? 2. Explain why the land of Mesopotamia was able to sustain an early civilization? 3. Name the three main civilizations in Mesopotamia. 4. What were the basic (political) units of Sumer? AND Name three of them. 5. Describe the characteristics of Sumerian city-states (5 characteristics). 6. How did Sumerian make a living? 7. What was the social structure (classes) of Sumer? 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. What role did ziggurats play in the lives of city-states? Define and describe theocracy. Describe the writing system of Sumerians: name, process, purpose, an example. What group of people did the Akkadians belong to? AND Who was their leader? Define empire AND explain why the Akkadian Empire ultimately fell (collapsed)? Who was Hammurabi AND what was he famous of? Describe the main characteristics (5) of the Code of Hammurabi. Explain the principle behind Hammurabi’s code. What does it mean that Mesopotamians were polytheistic? List eight (8) inventions by Mesopotamians. Section 2: Egyptian Civilization: “The Gift of the Nile” 1. Describe the role of the Nile River in Egyptian Civilization. 2. What were Egypt’s natural barriers AND how did they contribute to the continuity of Egyptian Civilization? 3. What was ancient Egyptians’ primary concern in life? AND What does it mean that they were polytheistic? 4. What were the two main gods of ancient Egyptians? 5. What were the three major periods of Egyptian history AND what were their common characteristics (4)? 6. Who was Menes AND what role did he play in the history of Egypt? 7. In what period of Egyptian history was the age of the pharaohs and pyramids? 8. Who were the pharaohs AND where did they get their power from? 9. Who were the viziers? 10. What role did the pyramids play in Egyptian history, what were the parts of the pyramids, whose pyramid is the largest and where is it located (inside Egypt)? 11. Describe the reasoning behind AND the process of mummification. 12. How did the role of the pharaohs change during the Middle Kingdom? 13. What was the main characteristic of the New Kingdom? 14. Identify the following pharaohs: Hatshepsut, Tutankhamen, and Ramses II. 15. Describe the social structure (classes) of ancient Egypt. 16. Describe the writing system(s) of ancient Egyptians. 17. List five (5) achievements or inventions by ancient Egyptians. Section 3: New Centers of Civilization 1. Who were the pastoral nomads AND how did they affect the settled civilizations around them? 2. Define cultural diffusion. 3. Who were the Indo-Europeans? 4. What was the main achievement of the Hittites AND what happened to them (the Hittites)? 5. Describe the Phoenicians: where did they live, what was their source of livelihood, what was their most important colony, AND what did they contribute to humanity (that we still use today)? 6. Explain how the Phoenician alphabet differed from other ancient writing systems, e.g. hieroglyphics. 7. What group of people did the Israelites belong to AND what was their lifestyle? 8. According to the Hebrew Bible, where did the Israelites come from, how, AND why did they end up in Palestine? 9. Describe the United Kingdom of Israel: who founded it, what was its capital, and what was its main characteristic. 10. Why did the United Kingdom of Israel fall apart? 11. What are the ten lost tribes AND why are they considered “lost?” 12. Explain where today’s Jewish people and the Judaism come from. 13. Explain the concept of “stateless religion.” 14. How did monotheism affect the lives of Jews in the Middle East? AND Who is Yahweh? 15. Describe three ideas that are at the core of Jewish religious tradition. Section 4: The Rise of New Empires 1. Who were the Assyrians? 2. Describe how the Assyrians made transportation and communication efficient in their empire. 3. What was the attitude of the Assyrians toward their captives? 4. Who were the Persians? 5. Explain why Cyrus was considered the “Great King”? 6. Describe how the Persians run their empire (satrapies, satraps, Royal Road, way stations, Immortals). 7. What are the reasons for the collapse of the Persian Empire? Chapter 3: India and China Section 1: Early Civilization in India 1. What is a civilization? 2. What are the four core regions of India? 3. What were the first two civilizations in ancient India and where did they develop (location)? 4. What city characteristics made archeologists and historians think that Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro had highly organized city governments? 5. Who were the Aryans? 6. What was the Aryan way of life after settlement in India? 7. What was th Aryan’s writing system, and what did it make possible? 8. What was the caste system and what was it based on in ancient India? 9. Describe the five major castes in ancient India. 10.Where does Hinduism come from and what is its central idea? 11.Describe the process of reincarnation (rebirth, karma/dharma, Nirvana). 12.How did Hinduism help maintain the caste system of ancient Indian society? 13.What religion appeared as a rival to Hinduism and who was its founder? Why was he called Buddha? 14.Explain the basic principles (4) of Buddhism. 15.Explain what it means to follow the middle path. Section 2: New Empires in India 1. Describe the five major characteristics of the Mauryan Empire (when, emperor, location, political structure, and army). 2. Who was Asoka and what were his legacies (3)? 3. What was the most important contribution of the Kushan Kingdom to the development of India? 4. Describe the Silk Road (when, location, what was transported on it, and why)? 5. Where was the Kingdom of the Guptas established and by whom? 6. What were the characteristics (4) of the Kingdom of the Guptas? How do we know? 7. Why did the Kingdom of the Guptas ultimately collapse? 8. What were the Vedas? 9. Describe the three types of structures that were characteristic of ancient Indian architecture. 10. What were the contributions of ancient Indians to science? Section 3: Early Chinese Civilizations 1. Describe the geography of China. 2. What is a dynasty? Briefly describe the Shang Dynasty (ruler, capital, political structure, social structure, religion). 3. What was the role of oracle bones? How do we know that the Shang believed in the afterlife? 4. Why and how did the Zhou Dynasty come to rule ancient China? On what basis did the Zhou rule? 5. What were the legacies (3) of the Zhou Dynasty? 6. Describe the Mandate of Heaven. How was it similar to/different from the divine right of kings? 7. Define filial piety. What role did it play in ancient Chinese society? 8. What is the typical life cycle of dynasties? How did the Zhou Dynasty end? 9. Who was Confucius and around what question did his teachings center? What is the Dao? 10. What are the 2 main elements of Confucianism? 11. What is the merit system? 12. What are the central ideas of Daoism and Legalism? Section 4: Rise and Fall of Chinese Empires 1. What were the three parts of the central bureaucracy developed by the Quin dynasty? 2. What was the role of the Great Wall of China? 3. Describe the characteristics (5) of the Han Dynasty’s political structure. 5. What new technology developed during the Han Dynasty? 6. What was the purpose of the terra-cotta figures? Chapter 4: Ancient Greece Section 1: The First Greek Civilizations 1. Describe how Greece’s geography influenced its history. 2. What civilization was established on the island of Crete? 3. Why was the Minoan civilization considered advanced? What was its center called? 4. Why did the Minoan civilization collapse according to most historians? 5. What were the main values of Mycenaen civilization? 6. What type of poetry did Homer write? Name two of his works. 7. What was the significance of Homer’s writings in ancient Greece? 8. List the troubles affecting Mycenaen civilization before its collapse. 9. Why was the Dark Age of Greece considered “dark?” 10. What were some significant development that nevertheless occurred during the Dark Age of Greece? Section 2: The Greek City-States 1. Define polis. 2. What role did the acropolis play in the lives of city states? 3. What was the agora? 4. Describe the rights and responsibilities of people in the Greek city-states. 5. Who were the hoplites? 6. What was the phalanx? 7. What were the reasons behind Greek colonization of foreign lands? 8. Define tyranny as the ancient Greeks understood it. 9. What was the significance of tyranny in the development of Greek democracy? 10. How were the city-states of Sparta and Athens different? Similar? Section 3: Classical Greece 1. When and where did the Athenian army defeat the Persians? What was its significance? 2. Who was Pheidippides? Who was Xerxes? 3. What was the Delian League and why was it formed? 4. What is meant by the phase “The Age of Pericles.” 5. What does the word ostracism mean? 6. Identify which Greek city-states struggled for power after the Great Peloponnesian War? 7. What area to the north grew in power and threatened the freedom of the Greeks? Section 4: The Culture of Classical Greece 1. What was the role of religion in the lives of ancient Greeks? 2. What did they believe in? 3. What were rituals and festivities used for in ancient Greece? 4. What topics did Greek tragedies examine? 5. What was the philosopher Pythagoras’ view of the universe? 6. Who were the sophists? 7. What was Socrates’ view of education? What was his teaching method? 8. What three groups of people should make up the ideal state according to Plato? 9. What was Aristotle’s worldview? 10. Which government type did Aristotle think was the ideal one? 11. What was the role of the Parthenon? 12. Who was the greatest historian of the ancient world? What was his method? Section 5: Alexander and the Hellenistic Kingdoms 1. What does the word Hellenistic mean? 2. Describe the defining characteristics of the Hellenistic Age. 3. Why did King Philip II take control of all of Greece? 4. What were the goals of Alexander the Great? 5. How far did Alexander’s empire extend? 6. What was the legacy of Alexander the Great? 7. How did his worldview contribute to Alexander’s successes? 8. What happened to the empire after the death of Alexander? 9. What were three of the most important scientific developments of the Hellenistic Age? 10. How did the philosophers Epicurus and Zeno view happiness? 11. What is the name of Zeno’s philosophy?