* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download topics - no simpler
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Invention of the integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Printed circuit board wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
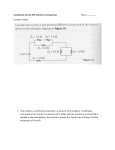
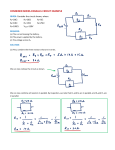
SECONDARY SCHOOL REFORM PROJECT CURRICULUM GUIDE ELECTRICITY/ELECTRONICS LEVEL 8 TOPICS METERS TEST METERS ENERGY METERS CONTENT Electro-meters (i) Volmeter (ii) Ammeter (iii) Ohmmeter (iv) Voltohmeter Energy or supply meters: (a) Mercury (b) Electrolytic (c) Induction SKILLS (i) Use instruments to measure voltage, current and resistance; power and energy (ii) Determine the instruments used in the measuring of electrical quantities voltage, current, resistance, power and energy. OBJECTIVES KNOWLEDGE List the instruments used to measure voltage,current, resistance power and energy. List the types of instruments. Identify the instrument used to measure each electrical quantity State the types of energy meters eg. mercury, induction and electrolytic. Electrometers are devices used to measure or record values and qualities such as voltages, current and resistance. Meters are named according to the quantity to be measured. A Voltmeter is used to measure the Voltage. An Ammeter is designed to measure the magnitude of an Electric current. STRATEGIES/ ATTITUDES Create an awareness of the need to identify the correct instrument to be used for measuring electrical quantities. Carefully measure electrical quantities and interpret the metre scale accurately EVALUATION METHODOLOGY (1) Discuss the mechanisms of eletrometers and their uses. (1) Help students to list the types of electrometers. (2) List the types of meters used to measure the various quantities. (2) State the types of metres used for the measurement of various electrical quantities. (3) Identify the instrument to be used to measure the respective quantity (3) State the unit of each quantity being measured. (4) List and describle the types of meter mechanisms AREAS OF INTEGRATION Mathematics, Physics, Social Studies. TOPICS CONTENT Types of Meter Mechanisms (i) Permament magnet moving coil. (ii) Moving Iron (a) attraction type (b) replusion type (iii) Electrostatic Mechanisms (iv) Taut-band Mechanism (v) Electrodynamic Mechanism (vi) Polarised Vane (vii) Thermocouple (viii) Induction. Scale:- SKILLS Interpret instrument scales accurately and read quantities measured OBJECTIVES KNOWLEDGE Explain the types of meter mechanisms. Describe each type of meter mechanism STRATEGIES/ ATTITUDES Understand the various mechanisms used in the construction of meters. (4) Describe the instrument used and how to connect it in circuits in order to measure the quantity. (5) Explain and demonstrate how to use the meter to measure the quantity and interpret the scales and record readings. Give students practice. Identify instrument scale and range. Determine the values measured by the instrument Meters are used with permanent magnet moving coil and moving iron attraction type and repulsion type. Instrument scales are calibrated in two scales (a) Linear (b) Non-Linear. Scales are either dial or face-plate. face-plate. 2 EVALUATION METHODOLOGY (5) Let student select the instrument scales to be used and measure any quantity and record values obtained. AREAS OF INTEGRATION History, Mathematics, Integreted Science, Physics, Social Studues. TOPICS RESISTORS CONTENT Types of resistors:Definition of a resistors (i) Fixed resistors (ii) Variable Resistors Fixed resistors:(a) Composition resistors (b) Film type resistors (c) Wire wound resistors (d) Photo resistors (e) Thermisters Variable resistors:(a) Potentiometers (b) Trimmers (c) Rheostats SKILLS - Demonstrate the use of each type of resistor. - draw diagram to show structure of resistors. - connect resistors in circuits as potentiometer s trimmers and rheostats - how to connect resistors to control current flow. - how to connect resistor to control vlotage across a component. - place resistors according to their uses. OBJECTIVES KNOWLEDGE List the types of resistors in common use - state their differences - list the uses of each type of resistor. Differentiate between fixed and variable resistors. - show the structure of a resistor. STRATEGIES/ ATTITUDES Develop an awareness of the types of resistors State the functions of the fixed and variable resistors. Show the operation of variable resistors. Resistance is measured in ohms. A resistor is a component which limits or opposes the current flow through a circuit. (1) Help the students to define a resistor. (1) Let students define a resistor (2) State the function of a resistor (2) List the types of resistors (3) List the types of resistors (3) Let students give example of functions of resistors. (4) Identify resistors which are classified as fixed resistors and variable resistors. (5) Describe the operation of variable resistors - as current controls and as voltage controls Resistors are classified according to their construction. Fixed Resistors: Fixed resistors are composition resistors, film - type resistors, wire wound resistors, photo-resistors and thermistors. 3 EVALUATION METHODOLOGY (4) Ask students to identify resistors fixed resistors and variable resistors. (5) Let students explain the operation of variable resistors as current controls and as voltage controls AREAS OF INTEGRATION TOPICS CONTENT Operation of Variable resistors in circuits as (a) a control for current through a circuit (b) a control for voltage across a component Classification of resistors Usage:(a) Power resistors (b) Instrument resistors (c) Resistors for electronic circuits. Resistor identification - Resistor colour code - Measurement of resistance using the ohmmeter SKILLS Connect variable resistors to control current flow. - connect resistor to control voltage across a component. - classify resistors accordung to uses - power resistors - instrument resistors - electronic circuits Identify resistor values - using the resistor colour code - measure resistance using the ohmmeter. OBJECTIVES KNOWLEDGE Determine resistor values using the colour code and measure the resistance using the ohmmeter. Variable resisors are potentiometers, trimmeters, rheostats. STRATEGIES/ ATTITUDES Classify resistors according to the uses. Measure resistance using the ohmmeter and calculate the resistance using the colour code. These are used to control the current flow in a circuit, or control the voltage across a component. Resistors are classified according to their uses:- as power resistors, as instrument resistors and in electronic circuits. Resistance can be determined by colour code or ohmmeter. 4 EVALUATION METHODOLOGY (6) Classify resistors according to use (7) Identify resstor values using the colour code and measure the values using an ohmmeter. (6) State the uses of the various types of resistors (7) Determine the resistance values of resistors given colours and using the ohmmeter. AREAS OF INTEGRATION Mathematics, Integreted Science, Physics. TOPICS CONTENT SKILLS OHM'S LAW Relationship of Voltage, Current and Resistance in circuits (i) Ohm's Law for Current - I = V R (ii) Ohm's Law for Voltage - V = IxR (iii) Ohm's Law Resistance V R= I Memorization Aid. - Demonstate the relationships in the formula between Voltage, current and resistance in circuits. - Identify the symbol for the ohm. (i) Apply ohm's law in calculating the current through a circuit. Use of V = IxR where - I= V R (ii) Apply ohm's law for voltage across a component - Calculate the voltage given the values of current and resistance V = IxR (iii) Apply ohm's law for Resistance in a circuit. - calculate the resistance of a circuit given the values of voltage and current. (iv) State formular for quantities. Draw the symbol for ohm. Measure voltage, current, resistance. OBJECTIVES KNOWLEDGE (1) The Voltage in any electrical resistance directly is proportional to the current flow through the resistance V = IxR providing R remains constant. (2) The current flow in a circuit is equal to the applied voltage V divided by the resistance R of the circuit:- I = V Amps. R (3) The voltage across a resistance is equal to the product of the current, I and the resistance R of circuit:- V = IxR. Volts. (4) The Resistance R in Ohm's is equal to the Voltage V divided by the current I and the resistance R of circuit:V R= ohm's I In memorizing:V = IxR. Volts I = VR Amps. R= STRATEGIES/ ATTITUDES Be aware that ohm's law shows the relationship between Voltage, Current and Resistance. Explain the symbols and Units of Voltage Current and Resistance as V Voltage in Volts. It current in Amperes R - Resistance in ohms. Explain the relationship between V and I when R is constant. Derive Ohm's Law and explain it using symbol V = IxR. Derive formula and give statement for Current I = V Amps. I Derive formula for and give statement for V Resistance R = ohm's. I Work examples using the laws V ohm's I 5 EVALUATION METHODOLOGY AREAS OF INTEGRATION In evaluating ask the student to name the Units of Voltage, Current and Resistance. State the Law for Curren, Voltage and Resistance. Give example by using typical values for Current and Resistance and calculate the Voltage usung ohm's law. V = IxR Similarly use values for Voltage and Resistance and calculate the Current using I = Give values for Voltage and Vurrent and calculate the value of the value of the resistance using V R= I Integreted Science Physics TOPICS ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC SYMBOLS CONTENT Graphical symbols are the drawings used to represent items. These items include:(i) Components (ii) Instruments (iii) Installative. Installation symbols describe Items and practices used to place or locate them in circuits. These include:(i) meters (ii) switches (iii) lamps (iv) wiring SKILLS Graphical Symbols: - sketch the symbol used to represent specific items components or instruments in a circuit diagram. Installation Symbols: - describe the symbols used to represent items or components in a circuit. - draw the symbol to represent a wiring proceduce in an installation circuit. OBJECTIVES KNOWLEDGE Identify the symbols that represent items, components or instrument in a circuit diagram. Identify alternative symbols for some components STRATEGIES/ ATTITUDES To become familiar with the symbols used to represent electrical and electronic components in schematic and wiring diagrams Describe the symbol used to represent an item on a diagram Draw a chart consisting of items and components in one columm and symbols in the opposite column. Describe the item in the item column and draw the symbols in the symbol column Describe a circuit using common items and draw the circuit using the symbols to represent the items or components. Interpret items for an installation as drawn in symbolic form: Also draw circuits using symbols only, then describe the items and circuitry. Electronic and Electrical symbols are universal expressions used to communicate, express design and interpret electronic and electrical circuitry and schematic deagram. deagrams 6 EVALUATION METHODOLOGY AREAS OF INTEGRATION In evaluatiing the lesson, describle items to be used in a circuit diagram and let students draw the circuit diagram using symbols to represent the items. Alternatively, draw a circuit diagram using signs and symbols and let the students descibe the symbols. Technical Drawing Physics Chemistry Social Studies TOPICS ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS. (SERIES) CONTENT Series Circuits: (i) Current flow in Series circuits - one path for current flow. electrons flow from negative to positive battery terminals through resistors. (ii) connection of components in series. - resistors, cells, capacitors etc (iii) Resistors in a Series circuit Formula RT = R1 + R2 + R3 + SKILLS - Identify a series circuit. - draw components in a series circuit. - trace the path of current flow in a series circuit - connect a battery and components in a series circuit. - connect resistors in series circuit. - calculate the total resistance when resistors are connected in series - using RT = R1 + R2 + R3 + … OBJECTIVES KNOWLEDGE -state how components are connected in series. - how current flows in a series circuit. - how to connect components in a series circuit. - Explain connection of resistors in a series circuit. - to calculate the total resistance when resistors are connected in series using formula. STRATEGIES/ ATTITUDES EVALUATION METHODOLOGY (1) Draw a series circuit and trace the path of current flow (2) Draw a circuit with resistors in series, using typical values, calculate the total resistance of the circuit using RT = R1 + R2 + R3 + Students will be asked to list the types of circuits. - connect items in series, parallel and series parallel. - trace the current flow through a series circuit. (2) Connected resistors in series and lit students calculate the total resistance using the formula. 7 AREAS OF INTEGRATION TOPICS CONTENT Voltage drop in series circuits VD = R x I (v) Application of Ohm's Law to series circuits (vi) Voltage in Series. (i) series aiding (ii) series opposing SKILLS - calculate voltage, current, and resistance in circuits. connect cells in series, as series aiding and as series opposing. OBJECTIVES KNOWLEDGE - Explain how voltage drops in a circuit. Calculate voltage, current and resistance using ohm's law - Methods of Connecting cells in series - series aiding and series opposing Resistors connected in series - total resistances RT = R1 + R2 + R3 + … STRATEGIES/ ATTITUDES (3) Draw a circuit consisting of a voltage supply, resistance and current flow. Using the law, find the voltage drop across the resistor (4) Connect cells in series circuits (a) series - aiding (b) series opposing. Voltage drop across a series circuit is given by VD = I x R. Cells may be connected in series aiding or series opposing. 8 EVALUATION METHODOLOGY (3) Give values gor current in a circuit and resistance, let students draw circuit diagram and calculate the voltage drop. (4) Use the formula to calculate Voltage, Current and Resistance in circuits. AREAS OF INTEGRATION Technical Drawing Physics Integreted Science TOPICS PARALLEL CIRCUITS CONTENT Connection of components in parallel circuits or branched circuits. Voltage in a parallel circuit. - examples of parallel circuit. (ii) Current in a parallel circuit IT = I1 + I2 + I3 +… - current varies in each branch (iii) Resistance in Parallel circuits – VT RT = IT V1 R1 = I1 R2 = V2 I2 SKILLS - Identity a parallel circuit - connect components in parallel eg cells, resistors. - identity the voltage in a parallel circuit. - Statement of current in various branches of the circuit - show that the total current entering the junction splits up through each resistor - calculate the total resistance using R – - calculate the resistance of each branch using V1 - R1 = I1 OBJECTIVES KNOWLEDGE Identification of a parallel circuit. How to connect cells, resistors etc in parallel. State the voltage in a parallel circuit. Explain the current flow in various branches of the circuit. The total current splits up through the various branch of the circuit. - Calculating the total resistance using 1 = R11 + R12 . RT Calculating the resistance of each branch using VT RT = IT STRATEGIES/ ATTITUDES Be aware that (I) components can be connected in parallel or branched circuit (2) The Voltage in a parallel circuit remains constant throughout the branches. (3) The current in a parallel circuit splits through each branch and the total current is the sum of the individual current through each branch - use IT = I 1 + I 2 + I 3+ … 9 EVALUATION METHODOLOGY (1) Draw diagram to show items in a parallel circuit. (2) Show the voltage across the circuit is same across each resistor. (3) Use typical values to find voltage across eachresistor and prove that the voltage supply is thed same as voltages across eachresistor. (4) Use values and prove that the total current in sum of the current in each branch. AREAS OF INTEGRATION (1) Students draw diagram to show cells, resistors in parallel. (2) Draw circuit diagram and calculate the voltage across each resistor in the branches (3) Give values of voltage supply and resistance of each resistor, and let students calculate the total currant and current through each resister. Also prove that the total the current splits in each resistor. Integreted Science Mathematics Physics TOPICS CONTENT (iv) Total Current and branch Currents. IT = I1 + I2 + I3 (v) Total Resistance in Parallel Circuits:1 = 1 + 1 RT R2 R1 + R13 +… (vi) Open Branch in Parallel circuits:- SKILLS - Calculate the total current in a parallel circuit using IT = I1 + I2 + I3. - Calculate the total resistance in parallel circuits using. 1 = 1 + RT R1 1 R2 + 1 R3 OBJECTIVES KNOWLEDGE Calculating the total current in a parallel circuit using using IT = I1 + I2 + I3. Calculating the total resistance in parallel using RT = R11 + R12 + 1 R3 STRATEGIES/ ATTITUDES (5) Use value to calculte the resistance of each branched item. (6) Calculate the total resistance in parallel circuits. +… (7) Show the effects of an open circuit. The effect of an open branch in an parallel circuit. +… - Show the effect of an open branch in a parallel circuit. 10 EVALUATION METHODOLOGY (4) Draw parallel circuits and let students calculate the resistance of each branch. (5) Give values of resistors in parallel and calculate the total resistance. AREAS OF INTEGRATION TOPICS CAPACITORS CONTENT Capacitor Symbol, uses and function. (i) Construction of Capacitors - shapes and sizes. - dielectric materials - air, paper, vacuum, oil, mica, ceramic etc. (ii) Types of Capacitors:(a) Fixed capacitors (b) Variable Capacitors. Fixed capacitors - nonelectrolytic. paper, mica ceramic, metallised. Electrolytic Capacitors. symbols. Types - air dielectric variable - trimmers. SKILLS - Draw the symbol of a capacitor. - state the function of a capacitor. - list uses of a capacitor (1) Show construction of a capacitor - list types of dielectric materials - list types of capacitors - identify fixed and variable capacitors - state dielectric materials in fixed capacitors. - list types of electrolytic capacitors - state symbol for variable capacitors. - use the capacitor code. OBJECTIVES KNOWLEDGE The symbol to represent a capacitor. List the functions of a capacitor. State the use of a capacitor. Draw a dagram and label the parts of a capacitor. STRATEGIES/ ATTITUDES Students must be able to draw the symbols for capacitors, state the function and used of capacitors List of the types of capacitor. Describe the structure of capacitors, name the plate and dielectric materials Identify fixed and variable capacitors. List the types of capacitors. List of types of slectrolytic capacitors Identify capacitors as fixed and variable. Draw symbols for variable capacitors. List types of variable capacitors State the dielectric materials of fixed and variable capacitors. 11 EVALUATION METHODOLOGY Show the class a capacitor draw symbols for each type, state the function and give uses of capacitors Show instruction of various types of capacitors. Flame firlrctric mstrial. Differentiate between fixed and variable capacitors. List dielectric materials for fixed and variable capacitors State the uses of fixed and variable capacitors. Let students draw symbols state uses and explain the functions of capacitors. List dielectric materials and describe shapes and sizes. Identify types of capacitors - fixed and variable State the uses of electrolytic and non-electrolytic capacitors. Use capacitor colour code to determine the capacitance. AREAS OF INTEGRATION TOPICS CONTENT (iii) Capacitor Codings (iv)Capacitor applications. (a) bypass and filtering (b) timming (c) coupling capacitor (v) Effect of capacitance - charging - discharging - energy (vi) Unit of capacitance (vii) Capacitors in combination (a) in parallrl (b) in series SKILLS -show the applications of capacitors. -Demonstrate the effects of capacitance. - charging a capacitor - discharging a capacitors -determine the energy stored in capacitors - state unit of capacitance - connect and calculate capacitance inparallel and series OBJECTIVES KNOWLEDGE Uses of variable capacitors. List the applications of capacitors. STRATEGIES/ ATTITUDES Use colour code to determine capacitor values State the effects of capacitance Explain the unit of capacitance The effects of capacitance in a circuit. Charging and discharging a capacitor. EVALUATION METHODOLOGY Connect circuit and calculate total capacitance in series and parallel. Explain the types of capacitors used as bypass, filtering, timing and coupling. How to charge and discharge a capacitor. State the unit of capacitance calculate total capacitance when capacitors are connected in series and in parallel. The energy stored in a capacitor connection of capacitors in series and parallel 12 AREAS OF INTEGRATION Integreted Science Mathematics Physics