* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Monocots vs - msamandakeller
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
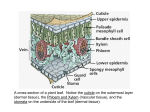
Monocots vs. Dicots Earlier in the unit, we learned that angiosperms can be divided into monocots and dicots. There are many differences between the two! Seeds Using figure 17.10 on pg. 562 in the text, draw a picture of a monocot seed and a dicot seed: (also check the chart on pg. 531) Monocot Dicot Make sure you have the following terms labeled on your diagrams above: Cotyledon: structure in the embryo of a seed plant that may form a ‘leaf’; also known as a seed leaf Endosperm: the nutritive tissue within seeds of flowering plants, surrounding and absorbed by the embro Seed coat: outer protective coating of the seed Plumule: terminal bud of a plant embryo Radicle: the part of a plant embryo which develops into a root What are the main differences between the seed of a monocot and dicot? ___________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ Lab portion: Obtain a pre-soaked corn and bean seed. Carefully slice each one lengthwise with a scalpel. Identify the cotyledons in each of the two types of seed. Keep these seeds for later. How they grow Monocot and dicot seeds grow very differently as well: 1. Using pg. 562, discuss the trigger for germination in both monocot and dicot plants. _________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Using figure 17.12 on pg. 563 as well as your own bean and corn plants. Draw a diagram to help explain the differences between how a monocot and dicot grow. (you may have to dig out your corn seed to see it) Monocots (corn) Dicots (bean) Stems and Roots The vascular bundles in the stems of monocots/dicots distribute differently. Using Figure 16.9, page 534 in the text, explain and draw the differences between the two: Monocots Dicots Using pg. 531, how do the roots compare between monocots and dicots? ___________________________ Leaves Using the chart on pg. 531 explain how leaves form differently on monocots and dicots. Draw a picture to help you: Monocots Dicots **Lab portion: Examine the leaves set aside in the classroom. Which ones are monocots and which are dicots? Draw their leaves under the appropriate heading below: Monocots Dicots Flowers How can you tell from the flower whether a plant is monocot or dicot? Use the chart on pg. 531 to assist you: _______________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ Label the pictures below as monocots or dicots: Chemical Composition **Lab portion: 1. Using your already pre-soaked and sliced seeds from the first section, add a few drops of Lugol’s solution to the exposed inner surfaces of each section. Recall from our first unit that Lugol’s solution turns black if there is starch present. 2. Make a labeled diagram of each section and indicate the location of starch: Monocot Dicot