* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download STUDY GUIDE – UNIT 3: EARTH IN SPACE
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
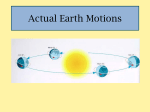
STUDY GUIDE – UNIT 3: EARTH IN SPACE DAILY APPARENT MOTION/DIAMETER objects appear to move E to W at 15/hr, due to Earth’s rotation, sunrise, sunset, star paths, circumpolar stars, object appears to get larger or smaller. larger = closer in orbit, smaller = farther in orbit SUN’S PATH seasonal change in sunrise, sunset, yearly altitude change, affects length of day, recognize path for different seasons, shadow direction and length, opposite, sun never at zenith in New York, insolation, duration and intensity of insolation, radiative balance MOON PHASES / MOTIONS apparent motion from E to W. correct order / positioning of phases, seeing same side rotation = revolution, cycle of phases: waxing/waning. sidereal month = one revolution 27 1/3 days, synodic month = one phases cycle, 29½ days, lunar / solar eclipses, positioning during phases/eclipses perigee = closest, largest apogee = farthest, smallest, ORBITS / CELESTIAL MODELS geocentric / heliocentric model, modern model, slightly eccentric ellipse, eccentricity, foci, formula e = d/L 0 = perfect circle, Kepler’s 3 Laws, 1. orbital velocity, KE / PE, faster, closer 2. orbital period, farther = longer revolution, 3. gravitation, closer = greater attraction EARTH’S ROTATION rotation rate = 15/hr, CCW, one rotation = 23 hrs, 56 min, 4 sec, rotation rate faster at equator Focault Pendulum- apparent change in swing, Coriolis Effect- apparent change in path of object right in Northern Hemisphere, left in Southern Hemisphere TIME AND EARTH MOTIONS time based on Earth motions, solar noon when sun reaches maximum altitude, sidereal day = 23 hrs, 56 min, 4 sec, apparent solar day = solar noon to solar noon, mean solar day = clock time determining local solar time, 4 min/degree + or EARTH’S REVOLUTION Earth orbits the sun, closest to sun = perihelion, Jan 3rd, farthest from sun = aphelion, July 4th, revolution = 365 1/4 days, tilt 23.5, partial cause of seasons, axis always points towards Polaris SEASONS / SUN’S PATH 3 reasons: tilt (23 ½) , parallelism (Polaris), revolution, WINTER: sun at zenith 23½ S, Tropic of Capricorn, tilted away from sun, winter solstice = Dec. 21st. short days, long nights, sun low in sky, sunrise S of E, sunset S of W, SUMMER: sun at zenith 23 1/2 N, Tropic of Cancer, tilt toward the sun, summer solstice = June 21st, long days, short nights, sun high in sky, sunrise N of E, sunset N of W, SPRING: sun at zenith at 0, equator , vernal equinox = Mar. 21st, equal day/night, sunrise due E, sunset due W, FALL: sun at zenith at 0, equator, autumnal equinox = Sept. 23rd , equal day/night, sunrise due E, sunset due W BEYOND EARTH Universe, light years, galaxies, galaxy shape, Milky Way, Our sun’s characteristics: size, temp, average, rotation, sunspots, solar system, Terrestrial vs. Jovian, comets, asteroids, meteors, origin of our universe (big bang), stars’ life cycle, nebula, main sequence, red giant, H-R diagram