* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 9: Elbow
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
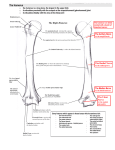
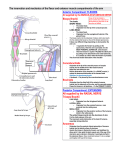
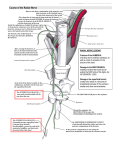
Chapter 9: Elbow Clinical Kinesiology for Physical Therapist Assistants, 3rd ed. Name For each question, choose the BEST answer. 1. 2. Which nerve innervates most of the elbow flexors? A. Axillary B. Musculocutaneous C. Radial D. Median What are the origins for the long head and the short head of the biceps brachii? A. Infraglenoid tubercle; coranoid process B. Supraglenoid tubercle; coracoid process C. Supraglenoid tubercle; coranoid process D. Supraglenoid tubercle; infraglenoid tubercle 3. What A. B. C. D. nerve innervates the triceps? Axillary N, C5-7 Radial N, C6-8 Radial N, C4-6 Suprascapular N, C5-6 4. , the lateral head from , The triceps long head originates on the and the medial head from the of the humerus. A. Infraglenoid tubercle; inferior to lesser tubercle on posterior humerus; posterior surface B. Supraglenoid tubercle; posterior surface of humerus; posterior surface C. Coracoid process; inferior to greater tubercle on posterior humerus; inferior surface D. Infraglenoid tubercle; inferior to greater tubercle on posterior humerus; posterior surface 5. What A. B. C. D. type of joint is the humeroradial joint? Ball and socket Pivot Gliding Hinge 6. What A. B. C. D. muscle attaches at the supraglenoid tubercle? Long head of triceps Long head of biceps Brachioradialis Anconeus 7. What A. B. C. D. articulates with the head of the radius? Coracoid process Trochlea Capitulum Olecranon fossa 8. What A. B. C. D. is the distal attachment for the brachioradialis? Radial styloid process Ulnar styloid process Ulnar tuberosity Radial tuberosity 9. What A. B. C. D. is the purpose of the medial collateral ligament? Protect against valgus stresses Protect against varus stresses Prevent posterior dislocations Keep the radius in proper alignment 10. Which structure holds the radial head against the ulna? A. Medial collateral ligament B. Lateral collateral ligament C. Annular ligament D. Interosseous membrane 11. Which is NOT a function of the interosseous membrane? A. Prevents radius and ulna from separating B. Surface area for muscle attachment C. Increases range of pronation and supination D. None of the above 12. Which muscle attaches from the distal half of humerus, anterior surface to the coronoid process and ulnar tuberosity? A. Biceps short head B. Brachialis C. Brachioradialis D. Coracobrachialis 13. When the biceps perform supination without elbow flexion, what muscle counteracts the elbow flexion? A. Triceps B. Supinator C. Pronator teres D. Anconeus 14. Which one-joint elbow flexor attaches most distally? A. Biceps B. Brachialis C. Brachioradialis D. Wrist flexors 15. Which muscle may prevent the annular ligament from being pinched in the olecranon fossa during elbow extension? A. Triceps B. Anconeus C. Supinator D. Pronator teres 16. What muscle arises from the medial epicondyle of the humerus and coronoid process of the ulna and inserts on the lateral aspect of the radius at its midpoint? A. Pronator teres B. Pronator quadratus C. Flexor carpi ulnaris D. Anconeus 17. Which muscle is deep and wraps around the elbow joint laterally from the posterior surface to the anterior surface? A. Pronator teres B. Pronator quadratus C. Anconeus D. Supinator 18. What A. B. C. D. nerve innervates the pronator quadratus? Musculocutaneous Radial Median Radial 19. The carrying angle of the elbow is greater in females. A. True B. False 20. The superior radioulnar joint is a uniaxial joint that allows for rotation. A. True B. False 21. Wrist extensors are assistant movers for elbow flexion. A. True B. False 22. There is a greater amount of pronation than supination in the forearm. A. True B. False