* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Origin of the Elements and the Earth
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Advanced Composition Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Planetary system wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Big Bang nucleosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Directed panspermia wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
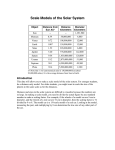
QUESTIONS 1. How do we form hypotheses about the formation of our Solar System? 2. In what ways can we scientifically test ideas about the Solar System’s formation and early events? 3. What is the Solar System’s destiny? BUILDING A SOLAR SYSTEM STEP 1. FUSE METALS ORIGIN OF MATTER • All matter originated at the Big Bang • Primordial nucleosynthesis • A few minutes after the big bang, protons were highly dense and very energetic, allowing fusion • For about 17 minutes, nucleosynthesis could occur BIG BANG NUCLEOSYNTHESIS • Discussed by Alpher-Bethe-Gamow in 1940s H+H D • Nearly all deuterium originated in the big bang • Also formed 3He, 4He, 7Li • ~10:1 H:He ratio • Beyond that energy required wasn’t amenable T=1000 s Lots of fusion Less fusion http://webhome.idirect.com/~rsnow/aboutstars.htg/H-RDIAGRAM.gif STARS AND FUSION NUCLEAR FUSION • The process of forming a new atomic nucleus by the fusing of two or more nuclei • Hydrogen is “burned” to form Helium, and further fusion leads to other elements • Fusion only occurs at high temperatures (core of the Sun, nuclear bomb, early big bang) Coulombic Barrier + + H HE 2H D 2H 4He D+H 3He 2 3He SYNTHESIS OF HEAVIER ELEMENTS • Requires bigger, hotter stars • High temperature means more energy to overcome coulomb barrier • Also means more frequent collisions between nuclei, so short-lived nuclei can act as intermediates MORE BURNING • 16O Triple alpha process 8Be 8Be 2 4He 12C 4He http://www.hacastronomy.com/sn/onion_skin_model.gif ORIGIN OF HEAVIER ELEMENTS From Stellar Nucleosynthesis HEAVIER ELEMENTS • Require energy to synthesize • No pay for their own nucleosynthesis • Supernova • Form new elements by proton/neutron capture • Result in the periodic table http://magic.mppmu.mpg.de/snr.jpg Anders and Grevasse 1989 Anders and Grevasse 1989 Most abundant elements easiest to synthesize Anders and Grevasse 1989 Heavy elements much rarer than light elements Anders and Grevasse 1989 Sawtooth pattern from addition of He nuclei Anders and Grevasse 1989 Iron peak- the dead end of nucleosynthesis Anders and Grevasse 1989 Easy to burn light elements so Li, Be, B are depleted STEP 2. DESTROY AN OLD STAR SUPERNOVA 1987A • Brightest Explosion since Kepler’s time • Guess the year it happened! • Ring of expelled gas from earlier • Bipolar filaments SUPERNOVA 1987A • Brightest Explosion since Kepler’s time • Guess the year it happened! • Ring of expelled gas from earlier • Bipolar filaments • Hubble has been watching… http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/2004/09/ PLANETARY NEBULA • Not actually planetary at all: Herschel thought they looked like planets, that they were new planetary systems forming. NEBULA • Orion Nebula • ~2000 Solar Masses STEP 3. CONDENSE A NEW STAR YOUNG STARS • Material condenses from “small” shock waves, perturbations in nebula • Spinning increases (Moment of Inertia) • Fusion begins when P/T is achieved • Materials fall into new star and are ejected • This modifies the solar system! STEP 4. GET A PROPLYD (PRO)TO(PL)ANETAR(Y D)ISK = PROPLYD • Material spins out like record, Earth • North and South of Sun, material is excavated by jets • Orion Nebula proplyds STEP 5. BUILD PARTICLES Anders and Grevasse 1989 Take a gas of this composition and cool it. What forms? FIRST THING TO FORM: • Ceramics • These are high temperature minerals • First condensates CALLED CALCIUM-ALUMINUM RICH INCLUSIONS THEN COME SILICATES AND METAL • Olivine and iron SILICATES MELTED • Formed chondrules VOLATILE MATERIALS • Phosphorus • Lower temeprature silicates (Na-, K-bearing) • Sulfides • Ices Where do they go? STEP 6. BUILD MASSES EARTH FORMED FROM SOLAR SYSTEM DEBRIS • Earth and other planets form from a mixture of rocky material • Meteorites • Asteroids • Comets Hoba- www.nmm.ac.uk ORIGINS OF THE EARTH’S CONSTITUENTS • Volatile components, including key biogenic elements, were in short supply on the early Earth • Earth was hot • Volatiles were lost or were not delivered • Not primordial ( 20Ne, 36Ar) LOSS OF VOLATILES ON INNER PLANETS Earth Si and SSAE Normalized Elemental Abundances vs. Condensation Temperature 1.800E+00 Elemental Abundance 1.600E+00 1.400E+00 1.200E+00 P 1.000E+00 H, C, N, O 8.000E-01 6.000E-01 4.000E-01 2.000E-01 0.000E+00 0 500 1000 Condensation Temperature (K) 1500 2000 DELIVERY OF VOLATILES TO THE EARTH Cometary Delivery • Comets, loaded with H 2O and organics, were the source of volatiles Late Veneer • • Loaded with water • Outgassing of volatiles led to hydro + atmosphere • High flux (possibly) to early Earth • D/H ratio is much higher than earth • What were early comets really like? Carbonaceous Chondrites, with hydrated minerals, were the last accreted constituent to the early earth • Consistent with D/H ratio • Something odd going on with PGEs STEP 7. “CRUSH THE MASSES” -Stalin PLANETARY ACCRETION • Dust grains and small particles collide and stick together • Accumulate, making larger and larger bodies • A miracle occurs • Planets form http://ircamera.as.arizona.edu/NatSci102/NatSci102/images/accretion.jpg http://blog.stackoverflow.com/wp-content/uploads/then-a-miracle-occurs-cartoon.png STEP 8. DIFFERENTIATE THE PLANETS PROCESSING OF PLANETS • Planets accreted and were warmed • Radioactive decay of short-lived elements? • Impact heating • Warming causes differentiation of planets STEP 9. REARRANGE AND WATCH OUT CREATING MOONS AND RINGS • From Robin Canup: • Gravity is hell • Earth-Moon formed from early collision • Jupiter kept eating its moons • Saturn’s Rings formed from destroyed ice moon? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Fwl_JBQtH9o THE LATE HEAVY BOMBARDMENT • Caused by a turbulent outer Solar System • 4.1 - 3.8 Ga http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6LzQfR-T5_A The Nice Model Gomes et al, Nature, 2005 • Giants were at 5-17 AU • Now at 5-30 AU http://physics.uoregon.edu/~jimbrau/astr121/notes/chapter15.html THE LATE HEAVY BOMBARDMENT • Caused by a turbulent outer Solar System • 4.1 - 3.8 Ga • Ended same time as life “?” showed up on Earth • Effects still seen nightly ANNOUNCEMENTS… MEET IN CHE313 NEXT WEEK! for METEORITICS HOMEWORK: DUE SEPT 12 IN CLASS • Uploaded to Canvas • Read Chapter 8, stopping at 8.8 for next week! • Homework: 1. Chapter 8, problems 1 & 2 2. Chelyabinsk Research Paper questions EXTRA CREDIT (2pts, due with HW2, 9/12) • We (The Solar System) is now in a cloud of gas probably blown to us by a group of super-giants. It is called the Local Interstellar Cloud(LIC) or the Local Fluff. • Assume: • T = 7000 K • 0.1 atoms/cubic cm • Using the Ideal Gas Law, Calculate its pressure. Give units. http://science1.nasa.gov/science-news/science-at-nasa/2003/06jan_bubble/