* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Which of the following organs is NOT used during digestion
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
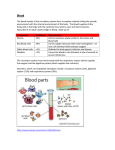
Body Systems and Disease Study Guide Skeletal system - To support the body; to give the body shape; to work with the muscles to move the body The skeletal system is made up of bones. Muscular system - To maintain body temperature; to help the body move; to maintain posture * Skeletal muscle – Voluntary; attached to the bones * Smooth muscle – Involuntary; controls movements within the body; makes up the stomach * Cardiac muscle - Involuntary; makes up the heart Integumentary system – To cover and protect the body * Skin - functions to cover the body, prevent water loss, and protect the body from infection. Circulatory System - transports oxygen and other nutrients to cells, circulates blood through the body * Heart - A muscular organ in the center of the chest that pushes blood throughout the circulatory system. * Blood vessels – tubes that carry blood throughout the body o Artery - A blood vessel with strong walls that carries blood away from the lungs. o Capillary - A narrow blood vessel that connects arteries with veins. o Vein - A blood vessel that carries blood back to the lungs. Respiratory System -exchanges gases between the body and the external environment (brings in oxygen, removes carbon dioxide) * Trachea - A tube that carries air from the throat to the lungs. * Lungs - Two large organs located in the chest and are the main organs of the respiratory system. * Bronchi - The two large air tubes leading from the trachea to the lungs that convey air to and from the lungs. * Diaphragm - A muscular wall that expands and contracts the chest when you breathe. Digestive System - breaks down food into nutrients the body can use and disposes of solid waste. * mouth – chemical and mechanical digestion take place here * esophagus – carries chewed food to the stomach * stomach – chemical and mechanical digestion take place here. * small intestine – most of the chemical digestion takes place here; where nutrients are absorbed * large intestine – Water is removed from the undigested food. * rectum – stores solid waste * liver – produces bile * gallbladder - stores bile * pancreas – produces digestive juices Urinary System - filters cellular wastes, toxins, and excess water from the body. * Kidney – Remove wastes and extra water from the blood to form urine. * Ureter – A tube that transports urine from a kidney to the bladder. * Bladder – A sac-like organ that stores urine. * Urethra – A tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. Nervous System - detects and responds to changes in the environment; transmits information throughout the body. * Brain – The main organ of the central nervous system. Controls and coordinates most of the body’s activities. * Spinal cord – A bundle of nerves that runs down the center of the back through the vertebrae which protects it. * Peripheral nerves – A network of nerves that branch out from the spinal cord and connect to the rest of the body. How the body systems work together: * The urinary and digestive systems work together to bring food into your body and remove waste. * The urinary and circulatory systems work together to clean blood and remove cellular waste. * The circulatory and respiratory systems work together to remove carbon dioxide and supply oxygen. * The digestive and circulatory systems work together to ensure that nutrients get to the cells of the body. * The skeletal and muscular systems work together to help the body move.