* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NAME Chapter 10: The Union in Peril Focus Sectional tensions
Missouri in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Missouri secession wikipedia , lookup
Secession in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
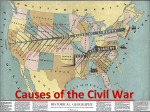
NAME ________________________________________________ Chapter 10: The Union in Peril Focus Sectional tensions caused by competing economic interests The industrial North favored high protective tariffs to protect Northern manufactured goods from foreign competition. The agricultural South opposed high tariffs that made the price of imports more expensive. Sectional tensions caused by westward expansion As new states entered the Union, compromises were reached that maintained the balance of power in Congress between “free” and “slave” states. – The Missouri Compromise (1820) drew an east-west line through the Louisiana Purchase, with slavery prohibited above the line and allowed below, except that slavery was allowed in Missouri, north of the line. – In the Compromise of 1850, California entered as a free state, while the new Southwestern territories acquired from Mexico would decide on their own. – The Kansas-Nebraska Act of 1854 repealed the Missouri Compromise line, giving people in Kansas and Nebraska the choice whether to allow slavery in their states or not (“popular sovereignty”). This law produced bloody fighting in Kansas as pro- and anti-slavery forces battled each other. It also led to the birth of the Republican Party that same year to oppose the spread of slavery. Sectional tensions caused by debates over the nature of the Union South Carolinians argued that sovereign states could nullify the Tariff of 1832 and other acts of Congress. A union that allowed state governments to invalidate acts of the national legislature could be dissolved by states seceding from the Union in defense of slavery (Nullification Crisis). President Jackson threatened to send federal troops to collect the tariff revenues. Sectional tensions caused by the institution of slavery Slave revolts in Virginia, led by Nat Turner and Gabriel Prosser, fed white Southerners’ fears about slave rebellions and led to harsh laws in the South against fugitive slaves. Southerners who favored abolition were intimidated into silence. Northerners, led by William Lloyd Garrison, publisher of The Liberator, increasingly viewed the institution of slavery as a violation of Christian principles and argued for its abolition. Southerners grew alarmed by the growing force of the Northern response to the abolitionists. Fugitive slave events pitted Southern slave owners against outraged Northerners who opposed returning escaped slaves to bondage. Causes of the Civil War Sectional disagreements and debates over tariffs, extension of slavery in the territories, and the nature of the Union (states’ rights) Northern abolitionists versus Southern defenders of slavery United States Supreme Court decision in the Dred Scott case Publication of Uncle Tom’s Cabin by Harriet Beecher Stowe Ineffective presidential leadership in the 1850s A series of failed compromises over the expansion of slavery in the territories President Lincoln’s call for federal troops in 1861 Vocab Secession Popular Sovereignty Compromise of 1850 Fugitive Slave Act Questions 1. What three issues divided America in the first half of the nineteenth century? 2. What were three causes of the Civil War? 3. Why did South Carolina begin the secession process? Choose the letter of the best answer. ____ 1. The Wilmot Proviso was favored by A. the North. B. the South. C. the North and the South. D. California alone. ____ 2. The formal withdrawal of a state from the Union is known as A. confederacy. B. compromise. C. secession. D. popular sovereignty. ____ 3. The Compromise of 1850 was supported by A. Clay and Calhoun. B. Clay and Webster. C. Calhoun and Webster but not Clay. D. Clay, Calhoun, and Webster. ____ 4. One of the most active conductors on the Underground Railroad was A. Harriet Beecher Stowe. B. Harriet Tubman. C. Horace Greeley. D. Abraham Lincoln. ____ 5. Uncle Tom's Cabin was written by A. Horace Greeley. B. John Brown. C. Harriet Beecher Stowe. D. Charlotte Forten. ____ 6. Members of the Know-Nothing Party were known for all of the following except their A. use of passwords. B. use of secret handshakes. C. support of the rights of immigrants. D. belief in nativism. ____ 7. One of the founders of the Republican Party was A. Franklin Pierce. B. Horace Greeley. C. James Buchanan. D. Millard Fillmore. ____ 8. The topic of the Lincoln-Douglas A. the Missouri Compromise. B. secession. C. the Wilmot Proviso. D. slavery in the territories. ____ 9. The Dred Scott decision did all of the following except A. please Southerners. B. rule that slaves did not have rights. C. declare the Missouri Compromise unconstitutional. D. guarantee that slavery would not be allowed in future states. ____ 10. The Confederacy included all of the following states except A. Maryland. B. Texas. C. Alabama. D. South Carolina. Using the exhibit, choose the letter of the best answer. A. Delaware B. Missouri C. Georgia D. Ohio E. Tennessee ____ 11. the state that seceded on January 19, 1861 ____ 12. the easternmost slave state that remained in the Union ____ 13. a state that prohibited slavery ____ 14. the state that seceded on June 8, 1861 ____ 15. a slave state that was bordered on three sides by states in the Union Using the Graph above, who do you think would have the advantage in the war…the North or South? Cite specific examples.