* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Seafloor spreading ws
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
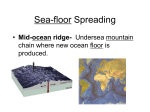
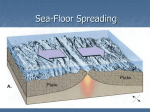
Sea-Floor Spreading On a separate sheet of paper, explain how the size and shape of oceans are continuously changing. 85D Name Date Class Sea-Floor Spreading Understanding Main Ideas Use the diagram below to answer Questions 1–5 on a separate sheet of paper. 1. Name and describe the feature of the ocean floor shown at A. 2. Name the process occurring at B, and explain what results from it. 3. What happens to old oceanic crust as new molten material rises from the mantle? 4. The arrows on the diagram show the ocean floor spreading from the ridge. What are three kinds of evidence scientists have found to support this idea? 5. What process is shown occurring at C, and why does it occur? Building Vocabulary Fill in the blank to complete each statement. 6. A canyon on the ocean floor at which the crust bends downward is called a(n) . 7. The process that continually adds new material to the ocean floor is called . 8. The process by which the ocean floor sinks into the mantle is known as . 9. A chain of underwater mountains along which sea-floor spreading occurs is a(n) . 85E Name Date Class Sea-Floor Spreading Study the map and read the passage. Then answer the questions that follow on a separate sheet of paper. The Birth of the Himalayas The greatest challenge for mountain climbers is Mt. Everest, whose peak rises 8,872 meters above sea level. This is the highest mountain in the world, though many mountains around it are almost as high. Mt. Everest is in the Himalayas, a series of massive ranges that extends 2,500 kilometers across South Asia north of India. The Himalayas cover all or part of the countries of Tibet, Nepal, and Bhutan. A climber on the high slopes of Mt. Everest would probably be surprised to learn that the region was relatively flat about 40 million years ago. It was then that two continental plates collided. The plate carrying India had been moving northwards for millions of years. The oceanic crust in front of it was slowly subducted under the Eurasian plate. But when the two continents collided, subduction stopped because India could not sink into the mantle. Instead, it pushed crust upward and downward. The Himalayas were one result. Thus, the Himalayas are actually pieces of plates broken and lifted up because of the collision. Another result of this collision was the movement of China eastward, as the movement of India northward pushed the Eurasian plate in front of it. The collision is still occurring today. In fact, the Himalayas are growing in elevation at a rate of about 1 centimeter per year. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. What are the Himalayas? What was the area of the Himalayas like 40 million years ago? How did the movement of plates create the Himalayas? What else resulted from the collision of those plates? What type of plate boundary exists today along the Himalayas? If the Himalayas continue to grow in elevation at their present rate, how tall will Mt. Everest be in another one million years? 85F Name Date Class Sea-Floor Spreading Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Which features form the longest mountain ranges on Earth? A the mid-ocean ridges B the deep-ocean trenches C the Rockies D the Andes 3. A B C D Where does subduction occur? along the middle of some ocean floors down the middle of mountain ranges on continents at deep-ocean trenches 2. Which process adds more crust to the ocean floor? A suction B sea-floor spreading C subduction D magnetic stripe 4. Which process or processes change the size and shape of the oceans? A subduction only B sea-floor spreading only C both subduction and sea-floor spreading D both drilling for samples and subduction If the statement is true, write true. If the statement is false, change the underlined word or words to make the statement true. 5. Sonar is a device that scientists use to map the ocean floor. 6. A deep-ocean trench is an underwater mountain. 7. Molten material erupts inside the central valley of mid-ocean ridges. 8. 9. 10. The farther from a mid-ocean ridge a rock sample is taken, the younger the rock is. Sea-floor spreading occurs at mid-ocean ridges. The pattern of magnetic stripes in rocks on either side of a mid-ocean ridge is the same.