* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Algebra II-B Unit 8: Day 1 Simplifying Square and Cube Roots Big
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
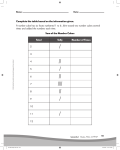
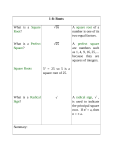
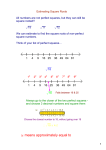
Algebra II-B Unit 8: Day 1 Simplifying Square and Cube Roots Big Ideas: Inverse operations “undo” each other. Vocabulary is used to help with explanations, memory and with decision making. Equivalent forms of an expression can be found by simplifying or expanding. I. Perfect Squares and Cubes To be proficient in square and cube roots, we need to recognize all types of each. Numeric One Term Perfect Perfect Squares Squares 12 _____ ( x) 2 ____ 2 2 _____ ( x 2 ) 2 ____ 3 2 _____ Perfect Square Numeric Perfect One Term Perfect Trinomials ( x 4) 2 Cubes Cubes 13 _____ ( x) 3 ____ 2 3 _____ ( x 2 ) 3 ____ ( x 3 ) 2 ____ 33 _____ ( x 3 ) 3 ____ 4 2 _____ ( x 4 ) 2 ____ 4 3 _____ ( x 4 ) 3 ____ 5 2 _____ ( x 5 ) 2 ____ 5 3 _____ ( x 5 ) 3 ____ 6 2 _____ ( x 6 ) 2 ____ 6 3 _____ ( x 6 ) 3 ____ 7 2 _____ ( x 7 ) 2 ____ 7 3 _____ ( x 7 ) 3 ____ 8 2 _____ ( x 8 ) 2 ____ ( x 8 ) 3 ____ 9 2 _____ ( x 9 ) 2 ____ ( x 9 ) 3 ____ 10 2 _____ ( x 10 ) 2 ____ (3 y 4) 2 10 3 _____ ( x 10 ) 3 ____ Topical Understanding #1 – Exponents on perfect squares and cubes _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ Topical Understanding #2 – Perfect Square Trinomials______________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ II. Simplifying Square Roots 1. Just like we should remove all factors that are perfect square (or any factor that appears in pairs) we should never leave an exponent inside that is greater than one. Problem Set 1: Simplify a. b. 250 49 x12 25 c. 9x 9 x 2 12x 36 d. 2. There are all kinds of considerations involving the signs of the quantities inside the square root and the answers we give. Problem Set 2: Simplify. If the quantity is not a real number, write “NO REALS”. a. 64 64 b. x 72 c. III. Cube Roots – 1. The cube root (k) of a number (N) is any solution to the equation: ___________ Topical Understanding #3 – Cube roots and positives and negatives________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ Problem Set 3: Simplify. a. 3 64 b. 3 27x 27 c. 3 40x 8 III. Formal Problem Solving – Special Right Triangles A. 45-45-90 Right Triangles (half a square) 1. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find side c. Give answer as a simplified radical. c 3 45o 2. In general, the sides of a 45-45-90 right triangle are related by the formulas in the diagram below. x 2 x 45o x B. 30-60-90 Right Triangles (half an equilateral triangle) 1. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the altitude (AE) of the equilateral triangle EQU. Give the answer in simplest radical form. E 6 o U 60 A Q 2. In general, the sides of a 30-60-90 right triangle are related by the formulas in the diagram below. 2x x 3 HW: p. 295 #1-23 odd o 60 x Name ________________________ Date ________________________ Unit 8 Day 1 Skills Practice 1. Circle the numbers or expressions that are prefect squares. Cross out those that are not. 121 x6 x 25 25 x 2 y 2 - 49 200 2. Circle the numbers or expressions that are prefect cubes. Cross out those that are not. y 12 144 125 8x 9 27 8 -1 Simplify. If the expressions do not represent real number, write “NO REALS” 3. 6. 3 108 4. x10 y 15 5. x10 y 15 7. 64 8. 3 3 32 64