* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plate tectonics note-taker - Tanque Verde Unified School District
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
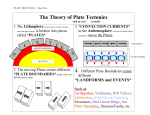
1. The Plate Tectonics Theory A. Outer part of Earth is made of up __________ and ____________ pieces called _____________, and these plates move ____________________and continually. B. There are 4 main pieces of evidence for plate tectonics: 1. ____________________________________________= fit together like a puzzle 2. Similarity of _____________________________________found on India, Australia and South Africa. 3. Similarity of _______________________________________found in South America and Africa. 4. Paleomagnetism – where _________________________that contain _______record Earth’s magnetic ______________________________at the time the rocks cooled. C. The Earth consists of ____ major plates and ___________________ minor plates. 1. Each plate is about _______ km thick. 2. Plates move between ___________ cm per year. 3. The average plate speed is ______ cm/year. D. Plate tectonics theory explains the _______________________ of mountain ranges, volcanoes, and __________________________________. 2. Earth’s layers A. Earth is composed of 3 main layers: 1. Core – Earth’s internal ________________________________. 2 sub-layers: a. Inner core is made of solid iron and ______________. b. Outer core is made of liquid _________. c. Heat in the core caused from remnant heat from Earth’s _____________& __________________________________________of elements. 2. Mantle – made of ____________________________ magma, 2 sub-layers: a. ______________sphere = lower mantle, made of iron and __________________________. The asthenosphere is semi-solid and can flow like ___________ ___________. b. ___________sphere = upper mantle and is rigid and stiff. Does __________________! c. Asthenosphere and Lithosphere separated by a change in _______________ and rock _______________________. The boundary between is called the ______________ discontinuity. 1 3. Crust – is the outer skin of the earth. ____ types of crust: a. Oceanic –thinner, ____________________, _______________ rock. b. ______________________– thicker, __________ dense, granite rock. B. Earth’s plates are made of either oceanic or continental crust and the ___________________. These tectonic plates “____________” on top of the plasticlike asthenosphere. 3. How Do Plates move? A. Answer: _______________________ currents in the mantle. B. Convection occurs when a liquid or gas is _______________, becomes _________ dense and ____________. When it cools, it gets ___________ dense and sinks, and the process _____________________. C. This cycle of ___________________ and ____________________ drives plate motion. D. Draw a simple convection current below. 4. Types of Plate Boundaries A. There are 3 types of plate boundaries. 1. Convergent = when 2 plates ____________________ into each other. Features such as mountains or subduction zones form. Draw a convergent plate boundary below. 2. Divergent = when 2 plates move __________ from each other. Volcanoes form at divergent boundaries. Draw a divergent plate boundary below. 3. Transform = when 2 plates __________ past each other. Earthquakes happen at transform boundaries. Draw a transform boundary below. 2 5. More about plate boundaries A. SUBDUCTION occurs when an oceanic plate (denser) is forced ______________ a continental (lighter) plate. 1. At the subduction zone a ________________________________ is formed where the plate is being forced downwards under the continental plate. 2. Subduction causes rocks to _____________, and magma _____________ to surface to form _____________________. 3. Example: ____________________ in US, ________________ Mountains in South America B. Mountains can be formed when 2 ____________________ plates collide into each other. 1. Because they both have the same density, neither one subducts under the other. They crumple together. 2. Classic examples are the _______________________, which are still going up at a rate of __________cm/year. C. When 2 plates move away from each other, magma _________ and _______ crust is formed. 1. This is happening along the mid-Atlantic ridge, which passes through ____________. 2. If continental crust pulls apart from continental crust then the same process occurs. As ______________ erupts to the surface to fill the gap, a ____________________ is created. D. When plates move past one another ___________________________ occur. 1. Plates are rigid so it is difficult for the plates to ________________ past each other. 2. The most famous conservative plate margin is the _______________________ Fault on the western coast of North America. 3