* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lab Worksheet - Flowers, For Me!
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
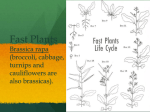
Name _____________________________________ Subject __________________, Period ____ Teacher __________________ Texas High School Date ____________ Lab Worksheet – Flowers, For Me! Part A: Stems Pour a small amount of the food coloring in water into your test tube. Snip off the bottom of the white flower your teacher has given you (you need a freshly cut surface on your stem for this part) and place the flower into the test tube. Let this sit until the end of class. What do you see? ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ Part B: A “Typical Flower” Flowering plants belong to the class angiospermae which is subdivided into two subclasses, ____________________________ and ____________________________. Monocots usually possess flower parts in multiples of _____________________. Dicots have flower parts in multiples of ______________________ or ____________________. Flowers specialize in sexual reproduction. They grow from a flower stalk called a pedicel. The floral parts are inserted in the receptacle. A complete flower has four rings of floral parts. The outer ring of floral parts if formed by several leaf-like structures called ______________________. These are usually, but not always, green. This ring of parts acts as a wrap which protects the developing bud. The next ring of parts are the ______________________ which are brightly colored to attract pollinators. The center of the flower contains the female reproductive structure, the ________________. Surrounded by the male reproductive structures, the ____________________________. Each stamen has a slender stalk or _________________________ with a sac at the top called an __________________________. The female flask-shaped carpel has a swollen base or _________________________ which contains _______________________, later to become seeds. Part C: Flower Variation Not all flowers are “typical”. Flowers with both male and female parts are ___________________ flowers. Flowers with only male parts are called _____________________ flowers. Flowers with only female parts are called _______________________________ flowers. Symmetry is a characteristic used by botanists to help identify flowers. Some flowers are radially symmetrical (can be cut in half many ways to will still produce two identical halves), other are bilateral (can only be cut one way to produce two identical halves). Name the kind of symmetry exhibited by each of the following. 1. ____________________________ 2. ____________________________ Flowers of plants in the Sunflower Family (Compositae Family) appear to be single blossoms, but are actually like a bouquet of flowers. If you examine a daisy closely, you would notice many small tube-shaped flowers in the center. These are called disc flowers. Along the margin of a daisy are strap-shaped ray flowers. Sometimes composite flowers have only ray or only disc flower types. A thistle is an example of a composite flower consisting of many disc flowers, but not ray flowers. Label each flower type. 1. _________________________________ 2. _________________________________ Part D: The seed. A seed is, in one sense a packaged plant. Everything a plant needs to begin growing is inside this “package”. Seeds typically consist of an embryo, stored food, and a seed coat. Angiosperms with two cotyledons are ___________________________ while those with one cotyledon are ________________________________. On the concave side of a bean is an oval scar called a hilium which is where the seed was attached to the ovary wall. A tiny pore found near one end of the hilium is the opening in the ovule wall where the pollen tube grew through called the microphyle. Inside the seed is the embryo plant. Label the seed. Part E: Examples 1. Draw and label your first flower here. Flower Leaf 2. What color are the petals? 3. How many petals does this flower have? 4. The flowers are (ray flowers, disk flowers, both ray and disk flowers). For questions 5 & 6, look at the information on the last page. 5. The veins in the leaves are (parallel, branching). 6. The leaf arrangement is ____________________________. 7. This flower is (complete, staminate, pistilate). 8. How many ovules does this flower have? 9. Is this flower a monocot or a dicot? Explain how you know. 10. Draw and label your second flower here. Flower 11. What color are the petals? 12. How many petals does this flower have? 13. The flowers are (ray flowers, disk flowers, both ray and disk flowers). Leaf For questions 14 & 15, look at the information shown below. 14. The veins in the leaves are (parallel, branching). 15. The leaf arrangement is ___________________________________. 16. This flower is (complete, staminate, pistilate). 17. How many ovules does this flower have? 18. Is this flower a monocot or a dicot? Explain. 19. Angiosperms are the most successful group of plants on Earth because of their many adaptations. List one adaptation of the plant parts observed in lab today and explain how it has made angiosperms so successful. Leaves: Stems: Seeds: Flowers: Veins: Leaf arrangement: