* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nutrition - Peda.net
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
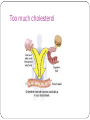
Nutrition Introduction to the nutrients Blanced diet maintains the homeostasis in the body by supporting the metabolism in the cells provides the energy needed contains fibre to aid the function of the gut the components are: carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, trace elements, dietary fibre (non-starch polysaccharide) and water Balanced diet Carbohydrates dietary carbohydrates originate mainly from plants mainly sugars and starches composed of carbon, oxygen and hydrogen are classified according to the complexity of the molecules from which they are formed glucose is the main form in which sugar is used by cells Carbohydrates Monosaccharide carbohydrates have to be broken into monosaccharides before they can be absorbed from the alimentary canal highly soluble in water the simplest form of carbohydrate glucose fructose lactose Disaccharide consists of two monosaccharides joined together sucrose (table sugar) = glucose + fructose lactose (milk sugar) = glucose + galactose maltose (malt sugar) = glucose + glucose highly soluble in water Polysaccharide consists of numerous monosaccharides joined together may be very large molecules poorly soluble in water glycogen is made of numerous glucose units, a means of storing glucose starch is equivalent storage polysaccharide (to glycogen) in plants Dietary fibre non-starch polysaccharide (NSP) indigestable part of the diet includes cellulose from plants important part of a healthy diet The structure of carbohydrates Main functions of carbohydrates provide energy and heat using carbohydrates saves proteins from being used as a source of energy act as energy reserves glycogen (liver and skeletal muscles) converted into fat and stored in fat depots Dietary fibre provides bulk to the diet slows the digestion rate stimulates peristalsis attracts water to faeces prevents constipation prevents some gastrointestinal disorders Dietary fiber Proteins made of amino acids joined together in different combinations composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen, some minerals can also be included 20 amino acids are used as the principal building blocks of protein may be in the form of animal or vegetable protein Proteins Amino acids Essential amino acids (9 in number) cannot be synthesised in the body but have to be included in the diet Non-essential amino acids (13 in number) can be synthesised in the body (liver) Most animal proteins have the full range of amino acids (= complete proteins). Vegetable proteins may lack adequate amounts of the essential amino acids. The structure Excess protein If the intake of protein exceeds the need the nitrogen part will be converted to urea and excreted by the kidneys the rest will be converted to fat and stored in the fat depots Functions of proteins growth and repair of body cells and tissues carrier molecules (e.g. haemoglobin) synthesis of enzymes, plasma proteins, antibodies, some hormones providing energy if needed Fats belong to lipids together with phospholipids, fat-soluble vitamins, cholesterol and prostaglandins composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, but in a different molecular structure from carbohydrates insoluble in water Fats Triglycerides • consist of one glycerol and three fatty acid molecules • make up the majority of all dietary fats The classification of fats Saturated fats solid at room temperature originate from animal sources Unsaturated fats fluid at room temperature usually originate from vegetables or plants Essential fatty acids 3 of the polyunsaturated fats are considered essential for life (linoleic, linolenic, arachadonic acid) Cholesterol a phospholipid a constiuent of the cell membrain and needed in the production of steroid hormones can be synthesised by the body (liver) full-fat dairy products, egg yolk and fatty meat contain cholesterol Too much cholesterol The functions of fats concentrated source of energy and heat storage of energy support some organs storage of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) insulation, reduces heat loss through the skin constituent of myelin sheat of the nerve cell formation of steroid hormones of cholesterol