* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Multiple-Choice Questions
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Rolling resistance wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
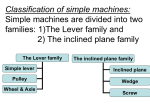
Name: Physics Section 1 Matching ___ 1. Speed ___ 2. Momentum ___ 3. Velocity ___ 4. Centripetal ___ 5. Uniform circular motion ___ 6. Acceleration ___ 7. g ___ 8. Centrifugal ___ 9. Deceleration ___ 10. Law of inertia a. an increase in velocity over time b. 9.8 meters per second per second c. away from the center d. a decrease in velocity over time e. 60 kilometers per hour west f. an apple sits motionless on a desk g. dependent on mass and velocity h. toward the center i. 25 miles per hour j. motion of a clothes dryer Multiple-Choice Questions ___ 11. A change in position relative to a body assumed to be at rest is called a. motion b. momentum c. inertia d. acceleration ___ 12. The average velocity can be determined from the formula a. time/distance c. distance/time b. time/acceleration d. distance x time ___ 13. The distance covered by a car traveling at an average velocity of 50 mph for 5 hours is a. 10 miles b. 250 miles c. 55 miles d. 45 miles ___ 14. The rate of change of velocity is called a. acceleration b. motion c. momentum d. inertia ___ 15. Consider a ball rolling down an inclined plane: The greatest acceleration occurs when the plane is at an angle of a. 60° b. 0° c. 90° d. 30° ___ 16. The acceleration due to gravity has been found to be a. 980 feet/second2 c. 32 centimeters/second2 b. 32 feet/second2 d. 32 feet/second ___ 17. The scientist who hypothesized that the acceleration produced by gravity is the same for all objects is a. Galileo b. Newton c. Copernicus d. Archimedes ___ 18. In a "coin and feather" jar, the feather falls at a slower rate than the coin because of a. inertia b. buoyant force c. momentum d. air resistance ___ 19. The symbol used to represent the gravitational constant for falling bodies is a. a b. v c. g d. t ___ 20. A body at rest tends to remain at rest and a body in motion tends to remain in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force is stated in the law of a. motion b. inertia c. momentum d. action and reaction ___ 21. A moving bus comes to a sudden stop and the passengers lurch forward. This is an example of a. velocity b. momentum c. acceleration d. deceleration ___ 22. As the force acting on an object decreases, the acceleration of the object a. increases c. remains the same b. decreases d. increases, then decreases ___ 23. As the mass of an object increases, the acceleration of that object a. increases c. remains the same b. decreases d. increases, then decreases ___ 24. The momentum of a body is the product of the mass of the body and its a. acceleration b. distance c. speed d. height ___ 25. The motion of a jet aircraft is primarily based on the law of a. action and reaction c. momentum b. inertia d. conservation of energy ___ 26. An inward force created by uniform circular motion is called a. buoyant force c. centripetal force b. centrifugal reaction d. gravity True (T) or False (F) ___ 27. The distance traveled by an object in a unit of time is called speed. ___ 28. The slowing down of a car in a given time is called velocity. ___ 29. Newton has 4 laws of motions. ___ 30. One of the first scientists to study the rate of gravitational acceleration was Newton. ___ 31. In the metric system, the gravitational acceleration has been found to be 9.8 meters per second2 ___ 32. The gravitational constant for acceleration varies for every object studied. ___ 33. The force acquired by a moving body because of its motion is called inertia ___ 34. Newton's third law is also known as the law of acceleration. ___ 35. A car can have a velocity of 50 miles per hour northeast. ___ 36. In a vacuum, all objects fall at the same rate. Testing Your Knowledge: Show all work to receive credit. 37. A stone that is dropped from the top of a building strikes the ground in 10 seconds. A. Compute the height of the building in feet. B. What is the velocity of the stone at the end of the 7th second? 38. Find the acceleration of an object, whose mass is 50 kilograms, that is being acted upon by an unbalanced force of 200 newtons. (Newton = 1 kg x m/sec.2) Find the scrambled term that matches each clue. Then unscramble it, and write it next to the clue. talicecerona trainie yolevict tommemun lateptricne crofe desep vragyti ____________ 39. the rate of change in velocity ____________ 40. describes the speed and direction of an object ____________ 41. the force of an object pulling towards the center of a circular path ____________ 42. the rate of change in position ____________ 43. property of a body that resists any change in velocity ____________ 44. mass of an object multiplied by its velocity ____________ 45. a push or pull exerted on one body by another ____________ 46. a force that acts on all objects on Earth Identify which of Newton’s law apply to each: First (1), Second (2) or Third (3)? _____ 47. A frog leaping upward off his lily pad is pulled downward by gravity and lands on another lily pad instead of continuing on in a straight line. _____ 48. As the fuel in a rocket ignites, the force of the gas expansion and explosion pushes out the back of the rocket and pushes the rocket forward. _____ 49. When you are standing up on a bus, and the bus suddenly stops, your body continues forward. _____ 50. A pitched baseball goes faster than one that is gently thrown. _____ 51. A swimmer pushes water back with her arms, but her body moves forward. _____ 52. As an ice skater pushes harder with her legs, she begins to move faster. _____ 53. When you paddle a canoe, the canoe goes forward. Name: Physics Section 2 Multiple-Choice ___1. Work is defined as the product of a. force and weight b. energy and height c. force and energy d. force and distance ___2. In the English system of measurement, the unit of work is the a. foot-pound b. pound-foot c. watt d. newton-meter ___3. In the metric system of measurement, the unit of work is the a. foot-pound b. pound-foot c. watt d. newton-meter ___4. In any machine a. some of the effort applied is lost to friction b. all the effort applied is lost to friction c. none of the effort applied is lost to friction ___5. When doing work, a reduction in effort is generally accompanied by a. no change in the distance b. a decrease in the distance covered by the effort c. a decrease in height d. an increase in the distance covered by the effort ___6. A machine that makes it possible to move a resistance faster is a a. wedge b. lever c. screw d. wheel-and-axle ___7. In an ideal machine, the work input a. is greater than the work output c. is equal to the work output b. is less than the work output d. never changes ___8. The product of the resistance and the distance through which the resistance is moved is called the a. law of machines b. work input c. work output d. effort ___9. When 30 pounds of effort are applied to a machine with a mechanical advantage of 3, the machine produces an effort of a. 10 pounds b. 30 pounds c. 90 pounds d. 15 pounds ___10. The ideal mechanical advantage refers to a machine that a. has no friction b. needs no effort c. produces large amounts of friction d. is easy to build ___11. Mechanical advantage is found by dividing the resistance by the a. effort b. resistance distance c. friction d. effort distance ___12. The amount by which a machine multiplies an effort force is called the a. mechanical advantage b. force ratio c. effort multiplier d. work input ___13. The rate of doing work is called a. power b. effort c. energy d. mechanical advantage ___14. One horsepower is equal to a. 700 foot-pounds c. 550 foot-pounds b. 500 watts d. 1 kilowatt Matching ___15. Ideal machine ___16. Watt ___17. MA ___18. Bernoulli’s Principle ___19. Lift a. metric unit of power b. resistance divided by the effort c. an upward force d. frictionless machine e. pressure exerted by a fluid in motion is less then when at rest True(T) or False(F) ___20. The force exerted when a person moves an object is called the resistance force. ___21. The actual work put into a machine is called work input. ___22. The equal nature of work input and work output of a machine is expressed in the law of power. ___23. In the metric system, power is expressed in a unit called a foot-pound. ___24. One thousand pounds are equal to a milliwatt. ___25. If a boy pushes a car and it does not move, he is still doing work. ___26. Work is equal to the applied force multiplied by the distance an object is moved. Testing Your Knowledge: Show all work to receive credit. 27. Compute the work performed by a man who exerts 600 newtons of force on a sled and moves it 6 meters. 28. 1000 foot-pounds of work are performed by a force of 50 pounds. Over what distance did the object move? 29. Find the power developed when a force of 1100 newtons moves an object a distance of 23 meters in 2 seconds. Name: Physics Section 3 Matching ___1. First-class lever ___2. Second-class lever ___3. Wedge ___4. Third-class lever ___5. Inclined plane ___6. Screw ___7. Wheel-and-axle a. axe b. spiral staircase c. doorknob d. pair of pliers e. sugar tongs f. ramp g. wheelbarrow Tell what simple machine is represented by each picture (Hint: look at the circled area) 8. A = ________________ 9. B = ________________ 10. C = ________________ 11. D = ________________ 12. E = ________________ 13. F = ________________ 14. G = ________________ 15. H = ________________ 16. I = ________________ 17. J = ________________ 18. K = ________________ 19. L = ________________ 20. M = ________________ 21. N = ________________ 22. O = ________________ True(T) or False(F) ___23. When a pulley is attached to the resistance and moves with it, it is known as a movable pulley. ___24. A modified double inclined plane describes a simple machine known as a screw. ___25. An inclined plane that is wrapped around a cylinder is called a wedge. ___26. The distance between two successive ridges of a screw is called the pitch. ___27. The mechanical advantage of the wedge depends on its slope (length) and thickness. Testing Your Knowledge: Show all work to receive credit. 28. Calculate the effort needed to raise a resistance of 150 pounds using a windlass. The radius of the wheel is 15 inches while the radius of the axle is 3 inches. 29. a. A 200-newton object is moved by a lever whose fulcrum is 1 meter from the object. The effort needed to move the object is exerted 2 meters on the other side of the fulcrum. Find the mechanical advantage of the lever. b. What effort force was needed to move the object? 30. a. What is the MA of an inclined plane 20 feet long with a height of 4 feet? b. Find the effort necessary to move a 100-pound object up the inclined plane. Multiple-Choice ___ 31. A device that consists of only one part that changes the size or direction of a force is a ___. a. force driver b. simple machine c. force mechanism d. reaction mechanism ___ 32. Two inclined planes put together form a simple machine called a a. lever b. winch c. screw d. wedge ___ 33. In an inclined plane, the distance through which the resistance moves a. is the same as the length of the plane b. is greater than the length of the plane c. is the height of the plane d. is less than the height of the plane ___ 34. A winding mountain road is an example of what kind of simple machine? a. lever b. wheel and axle c. pulley d. inclined plane ___ 35. An example of a first-class lever is a a. see-saw b. wheelbarrow c. nutcracker d. sugar tongs ___ 36. When the resistance in a lever lies somewhere between the effort and the fulcrum, it is a. a first-class lever c. a third-class lever b. a second-class lever d. none of these ___ 37. An example of a third-class lever is a a. wheel barrow b. sugar tongs c. pliers d. nutcracker ___ 38. Of the following, the simple machine that provides a mechanical advantage of 1is a a. second-class lever c. single fixed pulley b. single movable pulley d. screw ___ 39. An arrangement of pulleys designed to reduce the effort force is called a ____. a. fixed pulley b. trolley c. movable pulley d. block and tackle ___ 40. A simple machine used in a steering wheel and a bicycle is a a. lever b. wedge c. pulley d. wheel-and-axle ___ 41. The mechanical advantage of a wheel-and-axle equals a. the radius of the larger wheel divided by the radius of the axle b. the radius of the axle divided by the radius of the wheel c. the effort divided by the resistance d. the effort distance multiplied by the resistance distance Use the words in the box to fill in the blanks. What is a Simple Machine? into increase machine one force compound applied simple six more A job can be made easier by changing the size or direction of the force you must exert when using a (42)_____________. A simple machine is a machine consisting of only (43)______________ part. There are (44)______________ types of simple machines. A bicycle is a (45)_____________ machine. A bicycle is made of more than one (46)_____________ machine. Some machines make a job easier because they increase the amount of (47)_______________ you can exert. The resistance force is the force exerted by the machine. The effort force is the force (48)_____________ to the machine. The work put out by a machine is never (49)_____________ than the work put (50)_____________ it. A machine cannot (51)_____________ the amount of work done. The Lever longer applied force position acts fulcrum lever effort A bar that is free to pivot about a fixed point is called a (52)_____________. The point at which a lever pivots is called the (53)_______________. An effort force is applied to a lever on the (54)____________arm. The resistance arm exerts the resistance (55)_____________. The length of the effort arm is the distance from the fulcrum to the place where the effort force is (56)_____________. The length of the resistance arm is the distance from the fulcrum to the place where the resistance force (57)_______________. If the effort force is smaller than the resistance force, the effort arm must be (58)_______________ than the resistance arm. The three classes of levers differ in the (59)________________ of the fulcrum, effort force, and resistance force. Pulleys direction movable supporting raise simple block weight lever A pulley is a (60)____________ machine that acts like a (61)________________. A fixed pulley can be used to change the (62)________________ of the effort force. The pulley will act like a lever with an MA of one. By using the pulley, you can (63)_____________ an object while standing on the ground. To reduce the effort force needed for work, one can use a (64)_____________ pulley. For a movable pulley, the effort arm is equal to both ropes that support the resistance arm. With a movable pulley, the rope must be pulled up twice as far as the (65)_____________ rises. A person can lift heavy machinery with an arrangement of several pulleys called a (66)_______________ and tackle. The mechanical advantage of an ideal block and tackle is equal to the number of ropes (67)_______________ the resistance weight. The Wheel and Axle teeth resistance wheel larger axle effort gear A simple machine that consists of a large wheel fixed to a smaller wheel or shaft is called a (68)________________ and axle. The radius of the wheel is (69)_______________ than the radius of the axle. A crank used to lift a bucket of water from a well is a wheel and (70)______________. The force applied by your hand on the crank handle is the (71)______________ force. The force exerted on a rope wrapped around an axle is the (72) _______________ force. To prevent slippage, the wheel or axle can have (73)_____________ cut into it. It is then called a (74)______________. To transfer the force from one gear to the next, the two gears can touch each other, or a chain can be used. Inclined Plane, Screw, and Wedge raise friction inclined plane sloping wedge screw length A plank is a simple machine called an (75)__________ ____________. An inclined plane is a slanted surface used to (76)_____________ objects. The mechanical advantage of an inclined plane is the ratio of the (77)_______________ of the plane to the height. While the MA of an inclined plane can be used to predict the force needed to move objects, under actual conditions it takes more force to push an object up a ramp because the force of (78)______________ must be overcome. An inclined plane with either one or two sloping sides is called a (79)_____________. A knife blade is a wedge with two (80)_______________sides. An inclined plane wound around a cylinder is called a (81)_________________.