* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Answer Key Cloze
Eight Worlds wikipedia , lookup
Exploration of Jupiter wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Planet Nine wikipedia , lookup
Earth's rotation wikipedia , lookup
Space: 1889 wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
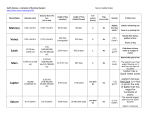
Answer Key – Cloze FIB Sheets Mercury Mercury is the planet closest to the Sun in our Solar System and the fastest moving planet in our Solar System. It is the second-hottest planet in our Solar System (only Venus is hotter). Mercury is so close to the Sun that from Earth, you can only see it near sunrise or sunset. Mercury has no moons. Mercury was named after Mercury, the mythical Roman winged messenger. This small, rocky planet has almost no atmosphere. Since the atmosphere is so slight, the sky would appear pitch black (except for the sun, stars, and other planets, when visible), even during the day. If you were on the surface of Mercury, the Sun would look almost three times as big as it does from Earth! Also, there is no "greenhouse effect" on Mercury. When the Sun sets, the temperature drops very quickly since the atmosphere does not help retain the heat. Mercury has a very elliptical orbit and a huge range in temperature. During the long daytime (which lasts 88 Earth days or an entire Mercurian year), the temperature is hotter than an oven; during the long night (the same length), the temperature is colder than a freezer. Mercury is about 3,031 miles (4,878 km) in diameter. It is the smallest planet in our Solar System (Pluto, now not considered to be a planet, is smaller). Mercury is only slightly larger than our moon. Mercury is a heavily cratered planet; its surface is similar to the surface of the Earth's moon. There are no seasons on Mercury. Seasons are caused by the tilt of the axis relative to the planet's orbit. Since Mercury's axis is directly perpendicular to its motion (it is not tilted), it has no seasons. Venus Venus is the second planet from the Sun in our Solar System. It is the hottest planet in our Solar System. This planet is covered with fast-moving sulphuric acid clouds which trap heat from the Sun. Its thick atmosphere is mostly carbon dioxide. Its cloud cover traps the heat of the sun (the greenhouse effect), giving Venus temperatures up to 480°C. Venus is a planet on which a person would asphyxiate in the poisonous atmosphere, be cooked in the extremely high heat, and be crushed by the enormous atmospheric pressure. Venus was named after the Roman goddess of love. Venus has an iron core but only a very weak magnetic field. It has no moons. Venus is about 7,521 miles (12,104 km) in diameter; this is about 95% of the diameter of the Earth. Venus is the closest to Earth in size and mass of any of the other planets in our Solar System. Venus' mass is about 4.87 x 1024 kg. The gravity on Venus is 91% of the gravity on Earth. A 100-pound person would weigh 91 pounds on Venus. Venus is also known as the "morning star" or the "evening star" since it is visible and quite bright at either dawn or dusk. It is only visible at dawn or dusk since it is closer to the Sun than we are. Like the moon, Venus' appearance from Earth changes as it orbits around the Sun. It goes from full to gibbous to crescent to new and back. Earth The Earth is the third planet from the Sun in our Solar System. It is the planet we evolved on and the only planet in our Solar System that is known to support life. The Earth is about 7,926 miles (12,756 km) in diameter; it is the fifth-largest planet in our Solar System. The Earth's mass is about 5.98 x 1024 kg. Earth is the densest planet in our Solar System. To escape the Earth's gravitational pull, an object must reach a velocity of 24,840 miles per hour (11,180 m/sec). The Earth's atmosphere is a thin layer of gases that surrounds the Earth. It composed of 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 0.9% argon, 0.03% carbon dioxide, and trace amounts of other gases. The Earth has one moon. The moon is about one quarter of the diameter of the Earth. The moon may have once been a part of the Earth; it may have been broken off the Earth during a catastrophic collision of a huge body with the Earth billions of years ago. On average, the Earth orbits at 93 million miles (149,600,000 km) from the Sun. The Earth is closest to the Sun (this is called perihelion) around January 2 each year (when we are 91.4 million miles = 147.1 million km from the Sun); it is farthest away from the Sun (this is called aphelion) around July 2 each year (when we are 94.8 million miles = 152.6 million km from the Sun). Each day on Earth takes 23.93 hours. Each year on Earth takes 365.26 Earth days (that is, it takes the Earth 365.26 days to orbit the Sun once). The Earth's rotation is slowing down very slightly over time, about one second every 10 years. The Earth's axis is tilted from perpendicular to the plane of the ecliptic by 23.45°. This tilting is what gives us the four seasons of the year: Summer, Spring, Winter and Autumn. Since the axis is tilted, different parts of the globe are oriented towards the Sun at different times of the year; this affects the amount of sunlight each receives. Mars Mars is the fourth planet from the sun and the most Earth-like planet in our Solar System. Mars was named after the Roman god of war. Mars is about 4,222 miles (6790 km) in diameter. This is 53% (a little over half) of the diameter of the Earth. Mars' mass is about 6.42 x 1023 kg. This is 1/9th of the mass of the Earth. A 100-pound person on Mars would weigh 38 pounds. This red planet has a very thin atmosphere that consists of 95% carbon dioxide (CO2), 3% nitrogen, and 1.6% argon (there is no oxygen). The surface of Mars is dry, rocky, and mostly covered with iron-rich dust. There are low-lying plains in the northern hemisphere, but the southern hemisphere is dotted with impact craters. The ground is frozen; this permafrost extends for several kilometers. The north and south poles of Mars are covered by ice caps composed of frozen water and carbon dioxide. Mars is much colder than the Earth. Mars' surface temperature ranges from a high of 68° F(20° C) to a low of -220° F(-140° C). Each day on Mars takes 1.03 Earth days (24.6 hours). A year on Mars takes 687 Earth days; it takes this long for Mars to orbit the Sun once. Mars has 2 tiny moons, Phobos and Deimos. They were probably asteroids that were pulled into orbit around Mars. Jupiter Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest planet in our Solar System. It is a gas giant planet that has a thick atmosphere, dozens of moons, and a dark, barely-visible ring. Jupiter's most prominent features are bands across its latitudes and a great red spot (which is a huge storm). Jupiter was named after the Roman primary god, Jupiter. Jupiter is composed mostly of gas. This enormous planet radiates twice as much heat as it absorbs from the Sun. It also has an extremely strong magnetic field. The planet is slightly flattened at its poles and it bulges out a bit at the equator. It takes Jupiter 9.8 Earth hours to revolve around its axis (this is a Jovian day). It takes 11.86 Earth years for Jupiter to orbit the Sun once (this is a Jovian year). Jupiter's diameter is 88,700 miles (142,800 km). This is a little more than 11 times the diameter of the Earth. Jupiter is so big that all the other planets in our Solar System could fit inside Jupiter (if it were hollow). Jupiter's mass is about 318 times the mass of the Earth, but the gravity on Jupiter is only about 2.54 times of the gravity on Earth. This is because Jupiter is such a large planet (and the gravitational force a planet exerts upon an object at the planet's surface is proportional to its mass and to the inverse of its radius squared). A 100-pound person would weigh 254 pounds on Jupiter. In 1610, Galileo first discovered the four largest moons of Jupiter, Io (which is volcanically active), Europa, Ganymede (the largest of Jupiter's moons), and Callisto; these moons are known as the Galilean moons. Ganymede is the largest moon in the Solar System. Saturn Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun in our Solar System. It is the second-largest planet in our Solar System (Jupiter is the largest) and is made mostly of hydrogen and helium gas (it is a gas giant planet). Saturn has beautiful rings. Although Saturn is visible without using a telescope, a low-power telescope is needed to see its rings. The rings were first observed by Galileo in the 17th century. Saturn's bright rings are made of ice chunks (and some rocks) that range in size from the size of a fingernail to the size of a car. Although the rings are extremely wide (almost 185,000 miles = 300,000 km in diameter), they are very thin (about 0.6 miles = 1 km thick). Saturn is about 74,898 miles = 120,536 km in diameter (at the equator at the cloud tops). This is about 9.4 times the diameter of the Earth. 764 Earths could fit inside a hollowed-out Saturn. Saturn's mass is about 5.69 x 1026 kg. Although this is 95 times the mass of the Earth, the gravity on Saturn is only 1.08 times the gravity on Earth. This is because Saturn is such a large planet (and the gravitational force a planet exerts upon an object at the planet's surface is proportional to its mass and to the inverse of its radius squared). A 100 pound person would only weigh 108 pounds on Saturn. Saturn is the only planet in our Solar System that is less dense than water. Saturn would float if there were a body of water large enough! Each day on Saturn takes 10.2 Earth hours. A year on Saturn takes 29.46 Earth years; it takes 29.46 Earth years for Saturn to orbit the Sun once. Saturn is the most oblate (flattened) planet in our Solar System. It has a equatorial diameter of 74,898 miles = 120,536 km (at the cloud tops) and a polar diameter of 67,560 miles =108,728 km. This is a difference of almost 10%. Saturn's flattened shape is probably caused by its fast rotation and its gaseous composition. Saturn has many moons. This planet was named for the Roman god of agriculture. Uranus Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun in our Solar System. This huge, icy gas-giant is covered with clouds and is encircled by a belt of 11 faint rings and 18 moons. Uranus' blue color is caused by the methane (CH4) in its atmosphere; this molecule absorbs red light. Uranus was discovered by the British astronomer William Herschel on March 13, 1781. It was named for the ancient Greek god of the sky. Uranus' 11 faint, narrow rings are composed of rock and dust. They circle Uranus is very elliptical orbits. These rings are only a fraction of the size of Saturn's rings, and were only discovered in 1977. Uranus is about 31,690 miles (51,118 km) in diameter. This is about 4 times the diameter of the Earth. This gas giant is the third-largest planet in our Solar System (after Jupiter and Saturn). Each day on Uranus takes 17.9 Earth hours. A year on Uranus takes 84.07 Earth years; it takes 84.07 Earth years for Uranus to orbit the Sun once. Uranus' rotational axis is strongly tilted on its side (97.9°). Instead of rotating with its axis roughly perpendicular to the plane of its orbit (like all the other planets in our Solar System), Uranus rotates on its side (along its orbital path). This tipped rotational axis gives rise to extreme seasons on Uranus. The mean temperature on the surface of Uranus' cloud layer is -350°F (59 K). Uranus radiates very little heat in comparison with the other gas giant planets. Uranus' mass is about 8.68 x 1025 kg. This is about 14 times the mass of the Earth, but the gravity on Uranus is only 91% of the gravity on Earth. This is because it is such a large planet (and the gravitational force a planet exerts upon an object at the planet's surface is proportional to its mass and to the inverse of its radius squared). A 100-pound person on Uranus would weigh 91 pounds. Neptune Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun in our Solar System. It is the fourth largest planet in our Solar System. This giant, frigid planet has a hazy atmosphere and strong winds. This gas giant is orbited by eight moons and narrow, faint rings arranged in clumps. Neptune's blue color is caused by the methane (CH4) in its atmosphere; this molecule absorbs red light. Neptune was visited by NASA's Voyager 2 in August, 1989. Before this visit, virtually nothing was known about Neptune. Neptune cannot be seen using the eyes alone. Neptune was the first planet whose existence was predicted mathematically in 1846 independently by J.C. Adams and Le Verrier (the planet Uranus's orbit was perturbed by an unknown object which turned our to be another gas giant, Neptune). Neptune was then observed by J.G. Galle and d'Arrest later that year. Neptune was named for the mythical Roman god of the seas. Neptune is about 30,775 miles (49,528 km) in diameter. This is 3.88 times the diameter of the Earth. If Neptune were hollow, it could hold almost 60 Earths. Neptune's mass is about 1.02 x 1026 kg. This is over 17 times the mass of the Earth, but the gravity on Neptune is only 1.19 times of the gravity on Earth. This is because it is such a large planet (and the gravitational force a planet exerts upon an object at the planet's surface is proportional to its mass and to the inverse of its radius squared). A 100-pound person would weigh 119 pounds on Neptune. Each day on Neptune takes 19.1 Earth hours. A year on Neptune takes 164.8 Earth years; it takes almost 165 Earth years for Neptune to orbit the Sun once. Since Neptune was discovered in 1846, it has not yet completed a single revolution around the Sun. Pluto Pluto is the ninth and usually the farthest planet (a dwarf planet) from the Sun in our Solar System; it is also the smallest planet in our Solar System. This cold, rocky planet was the last planet to be discovered (Pluto was considered to be a planet from its discovery until 2006, when it was reclassified as a dwarf planet). Clyde W. Tombaugh discovered Pluto in 1930. Unlike the 8 larger planets in our Solar System, Pluto has not been visited by our spacecraft yet. We only have blurry pictures of its surface. From Pluto, the Sun would look like a tiny dot in the sky. Pluto is about 1,413 miles (2274 km) in diameter. This is about 1/5 the diameter of the Earth. It is smaller than a lot of the other planets' moons, including our moon. Pluto's mass is about 1.29 x 1022 kg; it is the least massive planet in our Solar System. Pluto is about 1/500th of the mass of the Earth. The gravity on Pluto is only 8% of the gravity on Earth. A 100-pound person on Pluto would weigh only 8 pounds. Each day on Pluto takes 6.39 Earth days. Each year on Pluto takes 247.7 Earth years (that is, it takes 247.7 Earth years for Pluto to orbit the Sun once). Pluto has a very eccentric orbit; that means that its distance from the sun varies a lot during its orbit around the sun. Pluto also rotates about its axis in the opposite direction from most of the other planets. Pluto's orbit is tilted from the plane of the ecliptic. This angle, its orbital inclination, is 17.15°. This is the largest inclination of any of the planets. Pluto's unusual orbit makes some scientists think that Pluto is not a regular planet, but perhaps an asteroid. Pluto has one large moon, named Charon, that is almost as big as Pluto itself. Two minuscule moons were discovered in 2005. Charon was discovered by Jim Christy in 1978. Charon was named after the mythological demon who ferried people across the mythological river Styx into Hades.