* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Acetaminophen and Salicylates Toxicity and Management
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
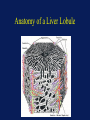
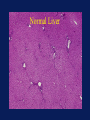
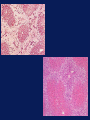
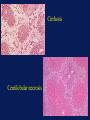
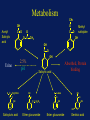
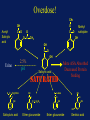
Acetaminophen and Salicylates Toxicity and Management Joseph Rella, MD Emergency Medicine NJMS Substances most frequently involved in Human exposures • • • • • Analgesics Cosmetics and personal care products Cleaning Substances Sedative-Hypnotics-Antipsychotics Foreign bodies 284,906 214,780 214,091 141,150 120,752 Bronstein AC, Spyker DA, Cantilena LR, et al 2006 Annual Report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers Toxic Exposure Surveillance System. ClinToxicol 2007;45:815-917 Categories with the largest number of deaths • • • • • • Sedatives-Hypnotics-Antipsychotics Opioids Cardiovascular drugs Antidepressants Stimulants and street drugs Acetaminophen (alone or combo) 382 307 252 210 203 352 Bronstein AC, Spyker DA, Cantilena LR, et al 2006 Annual Report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers Toxic Exposure Surveillance System. ClinToxicol 2007;45:815-917 American Association of Poison Control Centers 2006 Annual Report In the group Analgesics, Acetaminophen and Salicylate make up 40% of the cases reported. Acetaminophen N – acetyl – p – aminophenol (APAP) O H C N OH CH 3 Acetaminophen • First synthesized and used in the late 1800’s • “Rediscovered” in 1950 • A metabolite of phenacetin, it was not widely accepted in the medical community until the 1970’s Got Acetaminophen? Caplets: Arthritis Foundation Pain Reliever Aspirin Free Aspirin Free Pain Relief Aspirin Free Anacid Maximum Strength Atasol Atasol Forte Genapap Extra Strength Genebs Extra Strength Caplets Panadol Panadol Junior Strength Tapanol Extra Strength Tylenol Arthritis Extended Relief Tylenol Caplets Capsules: Dapacin Meda Cap Elixir: Aceta Genapap Children's Mapap Children's Oraphen-PD Ridenol Silapap Children's Tylenol Children's Gelcaps: Aspirin Free Anacid Maximum Strength Tapanol Extra Strength Tylenol Extra Strength Oral Liquid/Syrup: Atasol Children's Acetaminophen Elixir Drops Halenol Children's Panadol Children's Pediatrix Tempra Tempra 2 Syrup Tempra Children's Syrup Tylenol Extra Strength Oral Solution: Acetaminophen Drops Apacet Atasol Children's Acetaminophen Oral Solution Genapap Infants' Drops Mapap Infant Drops Panadol Infants' Drops Pediatrix PMS-Acetaminophen Silapap Infants Tempra 1 Tylenol Infants' Drops Uni-Ace Oral Suspension: Tylenol Children's Suspension Tylenol Infants' Suspension Sprinkle Capsules: Feverall Children's Feverall Junior Strength Suppositories: Abenol 120, 325, 650 mg Acephen Acetaminophen Uniserts Children's Feverall Infant's Feverall Junior Strength Feverall Neopap Tablets: Aceta A.F. Anacin A.F. Anacin Extra Strength Apo-Acetaminophen Aspirin Free Pain Relief Aspirin Free Anacin Maximum Strength Atasol Atasol Forte Extra Strength Acetaminophen Fem-Etts Genapap Genapap Extra Strength Genebs Genebs Extra Strength Mapap Regular Strength Mapap Extra Strength Maranox Meda Tab Panadol Redutemp Regular Strength Acetaminophen Tapanol Regular Strength Tapanol Extra Strength Tempra Tylenol Regular Strength Tylenol Extra Strength Tylenol Junior Strength Tylenol Tablets 325 mg, 500 mg Tablets, Chewable: Apacet Children's Chewable Acetaminophen Children's Genapap Children's Panadol Children's Tylenol Tempra Tempra 3 Tylenol Chewable Tablets Fruit Tylenol Junior Strength Chewable Tablets Fruit (OTC) Acetaminophen, buffered Acetaminophen, buffered (Bromo Seltzer) Acetaminophen, buffered O H Urine C N Metabolism O UDP-glucuronosyltransferase CH 3 H N CH3 50% <5% Acetaminophen O C6H8O6 CytoP450 - Acetaminophen glucuronide OH O H 5-15% C N CH 3 O O C C N C N CH3 CH3 O SO3 - Acetaminophen sulfate Glutathione (GSH) SG OH O N-acetylparabenzoquinoneimine Acetaminophen glutathione conjugate O H Urine C N Overdose! O UDP-glucuronosyltransferase CH 3 H C N CH3 <5% Acetaminophen O C6H8O6 OH O O H C CytoP450 N CH3 C N CH 3 SG O OH C N - CH3 Acetaminophen glutathione conjugate O SO3 - Acetaminophen sulfate NAPQI O N-acetylparabenzoquinoneimine Binding to cellular proteins leading to hepatic and renal injury NAPQI Toxicity • A highly reactive electrophile • Covalently binds to and arylates critical cell proteins leading to cell death • This process is not inevitable • This process may be prevented, interrupted, and reversed Organ Toxicity • NAPQI-derived – Liver – begins in zone 3 (centrilobular) – Renal – Acute Tubular Necrosis • Multiorgan failure – Heart, kidney • Poorly defined – Brain – Pancreas Anatomy of a Liver Lobule Normal Liver Cirrhosis Centilobular necrosis Number of people Most people took less than they say they did, except for those who took more. Clinical evidence of toxicity • Phase 1 – 0-24 hours – Nausea, vomiting, nothing • Phase 2 – 24-72 hours – RUQ pain, elevated liver enzymes, prolonged PT • Phase 3 – 72-96 hours – Hepatic necrosis, encephalopathy, coagulopathy, ATN • Phase 4 – 4 days- 2 weeks – If damage is not irreversible, complete resolution of hepatic dysfunction will occur Toxic Dose • Acute overdose is usually considered to be a single ingestion • Generally, 7.5 gm in an adult or 150 mg/kg in a child are the lowest threshold capable of toxicity Risk Assessment • Fatalities are relatively uncommon • The overwhelming majority of APAP exposures result in no toxicity • The antidote is very safe Risk Assessment • Plasma GSH is not related to hepatic GSH availability • Protein adducts (NAPQI bound to hepatic proteins) are measurable, but follow hepatic necrosis Rumack-Matthew Nomogram 500 200 Potential for Toxicity APAP concentration mcg/mL 150 100 50 Toxicity Unlikely 10 4 8 12 Time after ingestion 16 20 24 Validation of the Nomogram • Smilkstein, Knapp, Kulig, Rumack. Efficacy of oral NAcetylcysteine in the treatment of acetaminophen overdose: Analysis of the national multicenter study. N Engl J Med 1988;319:1557-1562 • 11,000 patients enrolled • 2,200 patients treated • 8 hour treatment window Laboratory predictors of poor prognosis: The King’s College Criteria • pH < 7.30 Or • PT > 100sec, Creatinine > 3.4 mg/dL, grade III+ Encephalopathy ( vitamin k vs. FFP) PPV= 98% NPV=82% Laboratory predictors of poor prognosis: The Clichy Criteria • • • • Factor V < 50% of normal Age Absence of HBsAg Α fetoprotein level PPV=90% NPV=94% Laboratory predictors of poor prognosis: Serum Phosphorus Chung PY, Sitrin MD, Te HS. Serum phosphorus level predict clinical outcome in fulminant hepatic failure. Liver Transplantation. 2003;9:248-253 GI Decontamination • Very rapid GI absorption • Activated Charcoal – Very early presentation – Co-ingestants – Adsorbs to NAC N-Acetylcysteine therapy • Prevents toxicity by limiting NAPQI formation • Increases capacity to detoxify formed NAPQI NAC-Good for what ails you O H Urine O C UDP-glucuronosyltransferase CH 3 N H CH3 O C6H8O6 CytoP450 - Acetaminophen glucuronide OH NAC O H 5-15% C N CH 3 O O C C N N 50% <5% Acetaminophen NAC C CH3 NAC N CH3 O SO3 - Acetaminophen sulfate Glutathione (GSH) O NAC SG OH Late NAC Therapy • Decreased hepatotoxicity when treatment begins 16-24 hours post ingestion Smilkstein, Knapp, Kulig, Rumack. N-Acetylcysteine in the treatment of acetaminophen overdose. N Engl J Med 1989;320:1418 • IV NAC begun after onset of fulminant hepatic failure decreased need for vasopressors, and decreased incidence of cerebral edema and death Keays, Harrison, Wendon, et al. Intravenous acetylcysteine in paracetamol induced fulminant hepatic failure: A prospective trial. Br Med J 1991;303:1026-1029 Other Benefits of NAC • Improved oxygen delivery and utilization in extrahepatic organs • Helps preserve cerebral blood flow • Possibly due to mediation of microvascular tone Treat everyone the Same? • Only the 17dose oral NAC regimen has been extensively studied – in the US – 140 mg/kg loading dose – 17 doses 70 mg/kg po • Shorter courses of therapy • Longer courses of therapy What about IV NAC? Con Pro • No vomiting • Consistent delivery • Only route studied for fulminant hepatic failure • Pregnancy? • • • • Anaphylactoid response No first-pass effect More costly No guarantee of sterility or pyrogen free The long-awaited… • 150 mg/kg in 200mL D5W over 15min • 50mg/kg in 500mL D5W over 4 hours • 100 mg/kg in 1L D5W over 16 hours Non-acute ingestions • Hepatotoxicity is rare • Usually seen in pediatric population – Poor label-reading – Mom & Dad… Case Examples • • • • • • Acute ingestion 4-hour level 155mcg/mL Acute ingestion 4-hour level 149mcg/mL Acute ingestion 1-hour presentation Acute ingestion 6-hour presentation Unknown time of ingestion Unknown time of ingestion, AST 2500 Salicylates OH C O O O C CH3 Acetyl salicylic acid Got Salicylates? Apo-Asa Asaphen Aspergum Aspirin Aspirin Regimen Bayer 81 mg with Calcium Bayer Children's Aspirin Easprin Ecotrin Caplets and Tablets Ecotrin Maximum Strength Caplets and Tablets Empirin Entrophen Excedrin Geltabs Genprin Genuine Bayer Aspirin Caplets and Tablets Halfprin 8-Hour Bayer Timed-Release Caplets Maximum Bayer Aspirin Caplets and Tablets MSD Enteric Coated ASA Norwich Extra Strength Novasen St. Joseph Adult Chewable Aspirin Therapy Bayer Caplets ZOR-prin (OTC) (Easprin and ZOR-prin are Rx) Acetylsalicylic acid, buffered Acetylsalicylic acid, buffered (Ascriptin Regular Strength, Bufferin) Acetylsalicylic acid, buffered Alka-Seltzer with Aspirin Alka-Seltzer with Aspirin (flavored) Alka-Seltzer Extra Strength with Aspirin Arthritis Pain Formula Ascriptin Regular Strength Ascriptin A/D Bayer Buffered Buffered Aspirin Bufferin Buffex Cama Arthritis Pain Reliever Magnaprin Magnaprin Arthritis Strength Captabs Tri-Buffered Bufferin Caplets and Tablets Pharmacokinetics • pKa of 3.5 • Peak serum levels in 30 minutes • Absorbed well in stomach and intestine Toxicokinetics • Above 30 mg/dL • Delayed absorption from pylorospasm, bezoar formation • Peak serum levels 4 – 6 or more hours • At toxic levels, elimination routes are saturated • Decreased fraction protein bound* Toxicity • • • • • • • • Primary respiratory stimulant Tinnitus Gastrointestinal upset and pylorospasm Diaphoresis Mental status changes Acute Lung Injury Increased brain utilization of glucose Metabolic acidosis Metabolism CH3 OH Acetyl Salicylic acid O C O O Methyl salicylate C O O C CH3 OH OH C O OH 2.5% pH Urine H N CH2COOH C O OH Absorbed, Protein binding Salicylic acid OH O C 6H 9O6 OH C O C O C O O C6H9O6 OH OH HO Salicyluric acid Ether glucuronide Ester glucuronide Gentisic acid Overdose! CH3 OH Acetyl Salicylic acid O C O O Methyl salicylate C O O C CH3 OH OH C O OH 2.5% pH Urine Salicylic acid SATURATED H N CH2COOH C O OH More ASA Absorbed Decreased Protein binding OH O C 6H 9O6 OH C O C O C O O C6H9O6 OH OH HO Salicyluric acid Ether glucuronide Ester glucuronide Gentisic acid Normal Energy Generation Glycolysis Glucose Pyruvate Pyruvate decarboxylase Kreb’s Cycle CO2 Oxidative Phosphorelation NADH2 H2O ATP Salicylate Uncoupling ATP Glycolysis Glucose Pyruvate Pyruvate decarboxylase Kreb’s Cycle CO2 Lactate Oxidative Phosphorelation NADH2 H2O SALICYLATES ATP MUDPILES • • • • • Methanol Uremia DKA, SKA, AKA Paraldehyde INH, Iron, Infection • Lactate • Ethylene glycol • Salicylates Does Serum Level Correlate with Acute Toxicity? • • • • Serum levels not tissue levels Done nomogram – 1960 Methylsalicylate – rapid deterioration Follow levels closely with: arterial pH, clinical condition • Serum levels > 100mg/dL Chronic Salicylism • Most common in the elderly-unintentional • May include any sign consistent with acute toxicity • May also present as: – – – – Delerium Dementia Encephalopathy of unknown origin Congestive heart failure Rapid ASA Confirmation OH OH C O C O OH + FeCl2 Salicylic Acid Fe OH (Purple colored complex) Management • Decontamination • Blood work – ABG – ASA level – mg/dL – Electrolytes – K+, BUN/Cr • Fluid resuscitation - a return to euvolemia • Electrolyte repletion • An appropriate cry for help? GI Decontamination • Activated Charcoal • Multiple Dose Activated Charcoal (MDAC) • Whole Bowel Irrigation (enteric coated) ABG Describes the Toxicity • Early – pure respiratory alkalosis – 7.50 / 30 7.60 / 20 • Later – add metabolic acidosis – 7.47 / 25 • Late – severe toxicity – 7.40 / 15 Urinary Alkalinization • Acidemia facilitates transfer of ASA into tissue • Acetazolamide creates alkyluria AND metabolic acidosis • NaBicarbonate – increases urinary elimination 10-20 times – – – – Bolus 1-2 mEq/kg followed by 3 amps (132-150mEq) in 1 L D5W at 1.5-2 times maintenance Urine pH 7.5-8.0 Serum pH not to exceed 7.55 Urinary Alkalinization • Alkalinizing urine from pH 5-8 increases renal elimination of ASA from 1.3 mL/min to 100 mL/min • Serum half-life decreases from 48 hours to 6 hours Morgan AG, Polak A. The excretion of salicylate in salicylate poisoning. Clin Sci 1971;41:475-484 Effects of Urinary Alkalinization Prior to Alkalinization Tissues pH 6.8 Plasma pH 7.1 Urine pH 6.5 HA HA HA H+ + A- H+ + A- H+ + A- Temple AR. Acute and chronic effects of aspirin toxicity and their treatment. Arch Intern Med 1981;141:367 Effects of Urinary Alkalinization After Alkalinization Tissues pH 6.8 Plasma pH 7.4 Urine pH 8 HA HA HA H+ + A- H+ + A- H+ + A- Temple AR. Acute and chronic effects of aspirin toxicity and their treatment. Arch Intern Med 1981;141:367 Problems with Alkalinization • Pre-existing Hypokalemia • Hypokalemia from serum alkalinization – Collecting tubule will excrete H+ – Urine pH remains low – Elimination remains limited • CHF • Poor Renal Function Extracorporeal Removal • • • • • • Very ill with salicylate poisoning Very high level Severe fluid and electrolyte disturbance Unable to eliminate salicylates Hemoperfusion has better clearance Hemodialysis allows for fluid, electrolyte, acid-base correction