* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Models of the sky—11 Sept Changes in the Sky
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Equation of time wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Armillary sphere wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
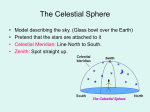
Models of the sky—11 Sept • Homework 1 is due Mon. Changes in the Sky • • • • • • The sun sets south of west in winter. Winter days are short. Stars move east to west over a night. The constellations change over the months. The sun (and moon and stars) rises & sets. The sun is higher in the sky in summer than winter. • Planets move with respect to the stars. • Comets appear irregularly. 1 Celestial sphere • Greek astronomers modeled the sky. – Earth is in the center. – Stars are pasted on a celestial sphere. – We will figure out what they did about the Sun and moon. • Our model has Earth, sun, stars on plastic celestial sphere. You may move the sun, turn the earth. Sun Earth Celestial sphere: sun • Our model has Earth, sun, stars on plastic celestial sphere. You may move the sun, turn the earth. Sun Earth 2 The Celestial Sphere 1. What explains observation A? a) b) c) 2. 3. 4. What explains observation B? Use same foils. What explains observation C? Use same foils. What do I move in the plastic model to demonstrate observations A & B? A. B. C. 5. The sun moves around the earth. The earth moves around the sun. The earth turns. What motions have you observed? A. Night & day. Sun rises & sets. B. Stars rise & set. C. Different stars are seen at different times of the year. Eg., Orion is seen in early evening in March. The “Summer Triangle” is seen in early evening in the summer. Move the sun only. Turn the earth only. Turn the whole works. What do I move in the plastic model to demonstrate observation C? Same foils. The Celestial Sphere • The sun “moves” into different constellations of the zodiac during the year. 4. At midnight tonight, which constellation of the zodiac will be high in the sky? A. B. C. D. Pisces Virgo Sagittarius Gemini 3 The Celestial Sphere 2. How do you explain day and night using the celestial sphere? Earth N E MI night day Sun This half of sky is not visible North pole Horizon for someone on equator Sun This half of sky is visible The Celestial Sphere 5. Which constellation is high in the sky at sunset tonight? A. B. C. D. • Pisces Virgo Sagittarius Gemini A star rises at 8 pm. When does it rise two months from now? You should be able to figure out this question from our model. 4