* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download English
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
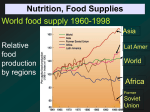
Health and nutrition of women in Afghanistan AAEP WIA Becky Ramsing, MPH, RD University of Maryland Outline Overview – state of nutrition and women The link – nutrition and health Immune system Nutrients Diseases Diarrhea, flu, etc. Bone health, overweight statistics Countries with the greatest number of rotavirus-related deaths Cycle of poor intake and malnutrition disease Worsened disease Weakened immunity Impaired food assimilation & intake Impaired nutrition status The cycle of poor nutrition Impaired disease resistance Immune tissue first impaired with nutrition deficiency or toxicity Not necessarily a severe deficiency (can be subclinical) Severity and speed of reaction vary Disease is more severe when immune system is weakened disease – nutrition cycle Who is at risk? Children Those with poor nutrition Elderly Malnutrition – most common cause of immunodeficiency in the world Deaths in children under 5 Poor nutrition Low disease resistance Impaired host defense Susceptible to illness Access to food Access to healthcare poverty Building blocks to health The immune system The immune system protects the body against infection and disease. It is a complex and integrated system of cells, tissues, and organs that have specialized roles in defending against foreign substances and pathogenic microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. The immune system Cells Tissues organs The Immune System Bacteria Parasite in red blood cell SARS virus Fungus Mounting an Immune Response Lymphokines Complement T cell Antibodies B cell Macrophage Killer cell Virus Effects of Protein-Energy Malnutrition on the Body’s Defense System System Effects of PEM Skin Skin becomes thinner with less connective tissue to serve as a barrier to protect underlying tissues Digestive Tract Antibody secretions and immune cell numbers are reduced Lymph tissues Immune system organs are reduced in size; cells of immune system are depleted General Invader kill time is prolonged; circulating immune cells are reduced; antibody response is impaired The Mucosal Immune System The variety of human pathogens is very large The vast majority of human pathogens enter the body at mucosal surfaces Nutrients and health Does nutrition really matter? o Your body is continually renewing its structure o o o Bone, skin, blood, tissue, fat Replacing old tissue with new requires energy and specific nutrients Food supports growth & maintenance by providing o o Energy (calories) Nutrients proteins Growth and maintenance Enzymes, hormones, compounds = reactions, messengers, responses, regulation Immune system – antibodies Fluid balance Acid-base balance energy Protein Quality Amino acids digestibiliy Protein deficiency Protein only Marasmus Young children Immunity decreased =>weakness/anemia => infections => diarrhea and illness Protein energy Kwashiorkor Newly weaned children Poor fluid balance Fatty liver => toxins Reddish hair Protein energy - marasmus Protein only - kwashiorkor Adult malnutrition carbohydrates Energy – calories Brain and nervous system Provide vitamins, minerals, fiber sources Grains & breads Fruits Vegetables Plant foods Carbohydrates deficiency Vitamin and mineral deficiencies Wasting Too much Overweight Diabetes Usually deficient in fat and protein fats Energy storage Essential functions Vision immunity Absorption of vitamins Insulation Cell membranes fat Too much Obesity Heart disease Too little Essential fatty acid deficiency Wasting dry scaly rash, decreased growth in infants and children, increased susceptibility to infection poor wound healing Specific nutrients - lipids Omega-3 Eicosanoids Some Omega 6 as well Vitamin A Normal functioning of immune system Maintains integrity and function of skin and mucosal cells Deficiency in children increases morbidity and mortality related to measles, and diarrheal infections may increase rates of certain infections Zinc Growth and immunity beans, nuts, certain types of seafood, whole grains, fortified breakfast cereals, and dairy products Vitamin D Bone turnover, immunity, muscle activity Sunlight Fortified foods Milk, yogurt Fish supplements Vitamin C and E Antioxidants – protect from cell damage Vitamin C also regenerates vitamin E B-vitamins Helps body use carbohydrates and protein to make energy Also needed for healthy skin, hair, eyes, liver Help nervous system function folate Required to make new cells Deficiencies affect blood cells and digestive tract first Anemia Abnormal digestive function Especially important in growth of fetus Nutrition and disease diarrhea Diarrhea Frequent passing of watery stools 3 or more times/day Causes dehydration and loss of nutrients Can also be vomiting blood in stools Fever Mucus Stomach pains causes Infection Poor sanitation Unclean Water Dirty hands – germs Dirty food Uncooked foods Contamination (meats) dehydration Eyes sunken Cheeks sunken Thirsty, dry mouth Skin pinch rehydration Water, tea, soup Small amounts every 5 minutes Oral rehydration solution – salt, sugar Treatment Rehydration Nutrition Yogurt nutrients Zinc supplements Medical – antibiotics Diarrhea and nutrition Worsened with poor nutrition Loss of nutrients in stools Loss of intake Acta Paediatr. 2003 May;92(5):531-6. Role of Zinc in reducing diarrheal morbidity in children 35 incidence of diarrhoea (%) 30.5 30 25 20 16.5 15.8 15 2 10 5 0 Daily zinc Weekly zinc Placebo Effect of zinc on time of recovery 7 6.2 6 Days 5 4.7 4 3 2 1 0 Zinc Arch Dis Child. 1997 Sep; 77(3):196-200 Control Zinc Control Lancet 2005; 366 (9490):999-1004 Iron Participates in energy production Transports oxygen to cells Low iron: Mental impairment Low performance in school Fatigue Poor development Iron deficiency Anemia (IDA) Iron deficiency Anemia Causes of anemia Major causes Iron deficiency (1300-2200 m) Hookworm (876 m) Vitamin A deficiency (300 m) Malaria infection (300 m) Other Important causes Chronic infections: TB, HIV Other vitamins Genetic defects Child Growth Defects Anemia may result in growth retardation which can be corrected by giving them iron supplements. Due to its implications on development, growth, health and work output of an individual there is an urgent need to control iron deficiency anemia. Treatment A good iron rich diet which should include a dark green leafy vegetables, dry fruits, enriched cereals, meats, beans and Vitamin C food. Supplement of iron. Prophylaxis: Anemia is common is third trimester of Pregnancy, iron and folate needs to be prescribed. Iron in food Two types of iron Heme iron (animal sources) Non-heme iron (plant sources) Absorption of heme iron is 20- 30% Absorption of non-heme iron varies between 1-10% and is much more affected by iron status and intraluminal factors Absorbing non-heme iron Enhancers : ascorbic acid, meat Inhibitors : phytates, phosphates,tanins, oxalates, soy protein Other nutrients: zinc, calcium The role of nutrition in healing Involves the activity of an intricate network of blood cells, tissues, and growth factors. Adequate dietary protein is absolutely essential for proper wound healing, and tissue levels of the amino acids arginine and glutamine may influence wound repair and immune function Important nutrients Greater demand for nutrients Glucose, fatty acids, proteins Vitamin A - collagen formation, proper immune function, and as a tissue antioxidant Vitamin C Vit E - major lipid-soluble antioxidant in the skin Bromelain reduces edema, bruising, pain, and healing time following trauma and surgical procedures. Glucosamine -for hyaluronic acid production in the wound From: Eplasty. 2009; 9: e9 Published online 2009 February 3. Skin health Nutritional status plays an important role in the maintenance of healthy skin. Macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids) and micronutrients (vitamins and nutritionally essential minerals) work together to maintain the barrier functions of skin. Changes in nutritional status that alter skin structure and function can also directly affect skin appearance Nutrition in bone health Calcium and vitamin D in bone building and strength Osteoporosis – decreased bone mass related to aging, poor diet, and hormonal changes Girls ages 12-14 building peak bone mass Loss with aging Food sources of calcium Milk, yougurt Dark greens - spinach Blood pressure and heart disease diabetes What is diabetes? Add Dari here