* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Women's Health History
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
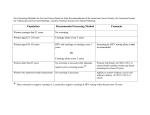
The Woman’s Health History University of Nebraska College of Medicine M3 OB/GYN Clerkship The Woman’s Health History • • • • • • • • • HPI Gynecologic History Obstetric History PMH PSH Medications/Allergies FH SH ROS Gynecologic History • LMP or FMP (if postmenopausal) • Age of menarche • Menstrual history ▫ Cycle length ▫ Duration of bleeding ▫ Amount of bleeding (heavy, light, clots) • Irregular bleeding ▫ Intermenstrual bleeding ▫ Postcoital bleeding Gynecologic History • If menopausal ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ Age of final menstrual period (FMP) Current of past HRT use Postmenopausal bleeding/spotting Menopausal sxs Hot flashes/night sweats Vaginal dryness Sleep or mood disturbances Are sxs affecting QOL? Gynecologic History • History of abnormal paps ▫ If yes When was abnormal pap What was the abnormality How was it evaluated (colposcopy?) Any treatment (cryotherapy, Leep, cone bx?) Results of subsequent paps Gynecologic History • History of STIs ▫ HPV, gonorrhea, Chlamydia, HSV, syphilis ▫ HIV, hepatitis B/C ▫ When was dx and how was infxn treated • Assessment of if STI risk factors2 ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ Hx of multiple sexual partners Partner with multiple sexual contacts Sexual contact with persons with culture proven STI Hx of repeated STIs STI clinic attendance Developmental disability Gynecologic History • Sexual history ▫ Age of coitarche ▫ Total lifetime partners ▫ Current relationship Single or multiple partners ▫ Sexual orientation ▫ History of sexual abuse ▫ Sexual satisfaction vs. concerns Gynecologic History • Current method of contraception ▫ Length of use ▫ Satisfaction with current method vs. problems ▫ Previous methods utilized • If no current method of contraception, ▫ Why? • Possibility of pregnancy exists in any sexually active female until 1 year from FMP! Obstetric History • Gravidity ▫ Total number of pregnancies regardless of outcome • Parity (TPAL) ▫ T = Number of term deliveries (>37 wks) ▫ P = Number of preterm deliveries (20-36 6/7 wks) ▫ A = Number of pregnancies ended <20 weeks (spontaneous and elective Abs, ectopics) ▫ L = Number of living children Obstetric History • Obtain specifics or each livebirth ▫ Term vs. preterm delivery ▫ Route of delivery SVD, CD, forceps/vacuum Complications of delivery 3rd/4th degree laceration; hemorrhage (PPH) ▫ Birth weight; gender ▫ Pregnancy complications Gestational DM (GDM) Hypertensive disorders (GHTN, preeclampsia, “toxemia”) Obstetric History • If gravida 0 ▫ By choice? ▫ History of infertility? Evaluation, if performed Treatment measures, if any Family History • Diabetes, HTN, CAD? • Cancer hx ▫ Breast, colon, ovarian • Genetic disorders ▫ Congenital/inherited defects ▫ Recurrent pregnancy losses/stillbirths ▫ Family members with clots during pregnancy or on OCPs/HRT • Osteoporosis Social History • • • • Tobacco/EtOH/drug use Intimate partner violence Sexual abuse (may have been covered in gyn hx) Nutrition/diet/exercise ▫ Folic acid ▫ Calcium Health Maintenance • Immunizations ▫ Chart with recommended vaccinations for women ▫ HPV vaccination Ages 9-26 years • Cervical cancer screening ▫ Pap screening ▫ Starting at age 21 • Breast Cancer screening ▫ Clinical breast exam/mammogram screening • Colorectal screening ▫ Starting at age 50 ▫ Colonoscopy, preferred method • Osteoporosis screening ▫ Assessment for risk factors (FH, Caucasian, smoker, poor nutrition, estrogen deficiency, low weight/low BMI, prior fracture, fall risk, inactivity) ▫ BMD assessment starting at age 65, younger for postmenopausal women with one risk factor for osteoporosis Recommended Vaccinations for Women Age: 13 to 18 Years DTaP Booster (once between ages 11 and 16) Hepatitis B One series if not previously immunized HPV One series for those not previously immunized Meningococcal Before entry into high school for individuals not previously immunized Influenza Annually For High-Risk Groups: One series if not already immunized Pneumococcal pneumonia Once if not already immunized* MMR Once series if not already immunized Varicella One series if not already immunized Age 19 to 39 Years DTaP booster Once every 10 years HPV For women age 26 and younger± not previously immunized. Given at 0, 2, and 6 months. Influenza Annually For High-Risk Groups: MMR Once Varicella One series Hepatitis A One series Hepatitis B One series Pneumococcal pneumonia Once* Meningococcal Once Age 40 to 64 Years DTaP booster Every 10 years Herpes zoster Once for women aged 60 years and older if not already immunized Influenza Annually For High-Risk Groups: MMR Once Varicella One series Hepatitis A One series Hepatitis B One series Pneumococcal vaccine Once* Meningococcal vaccine Once Age 65 Years and Older DTaP booster (every 10 years) Herpes zoster Once if not already immunized Influenza Annually Pneumococcal pneumonia Once* For High-Risk Groups: Hepatitis A One series Hepatitis B One series Pneumococcal vaccine Once* Meningococcal vaccine Once DTaP = diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis; HPV = human papillomavirus; MMR = measles, mumps rubella. * Based on risk factors, some women may need to have the vaccination repeated after 5 years. ± The “26” in “26 and younger” stems from the research population used to create the data in the first FDA application which was approved; its upper limit was 26 years. It is anticipated that the age for use will increase above 26 as more studies are reported with more robust study populations and that the vaccination of males will also be approved. Modified from American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Immunizations for Adolescents and Adults. Patient Education Pamphlet 117. Washington, DC: ACOG; 2008. Health Maintenance • STI screening ▫ HIV All reproductive age women should be screened at least once Annually for women with risk factors (IV drug users, have partners who are HIV+ or use IV drugs, dx of another STI within last year , >1 partner since last HIV test, exchange sex for drugs/money) ▫ Chlamydia Annually for women 25 yrs and younger who are sexually active >26 yrs should be screened annually if high risk ▫ Gonorrhea Similar recommendations to Chlamydia ▫ Syphilis Annual screening if at increased risk All pregnant women as early as possible Health Maintenance • Diabetes ▫ Screening fasting blood glucose starting at age 45 and every 3yrs thereafter ▫ Begin sooner if risk factors (BMI>25, FH, hx of GDM, HTN, habitual inactivity) • Thyroid disease ▫ TSH tested every 5 yrs starting at age 50 • HTN ▫ Screen BP annually • Lipid disorders ▫ No risk factors, screen every 5 yrs starting at age 45 ▫ Earlier screening if risk factors (FH of hyperlipidemia or premature CV disease, DM, multiple CAD risk factors) • Obesity ▫ BMI calculated annually Periodic Assessments • ACOG Committee Opinion No. 292 Presenting Patients in Clinic • Begin presentation with age, gravida, para, (LMP, if appropriate) and chief complaint ▫ 22yo G1 P1001 Caucasian female with LMP 6/30 who present for her annual exam ▫ 56 yo G3 P2012 AA postmenopausal female with 3 days of vaginal bleeding • Tailor history/information gathering to reason for visit… annual vs. problem visit vs. OB visit Pearls for Success in Clinic • Prepare for clinic ▫ Look up clinic pts (past hx, reason given for visit) • Be proactive in seeing patients! • If you asked about a subject in clinic and you don’t know… ▫ Look up the subject for next clinic day • Have fun learning! Physical Examination • Breast exam ▫ Reviewed in “Breast Disorders” lecture • Pelvic exam ▫ Video and pelvic model References • Beckman CRB., et al. The Woman’s Health Examination and The Obstetrician-Gynecologist’s Role in Screening and Preventative Care In: Obstetrics and Gynecology. 6th Edition. Philadelphia; 2010. • ACOG Committee Opinion No. 357 • ACOG Committee Opinion No. 292