* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Presentation file
Environmental impact of pharmaceuticals and personal care products wikipedia , lookup
Hotspot Ecosystem Research and Man's Impact On European Seas wikipedia , lookup
Water testing wikipedia , lookup
Water quality wikipedia , lookup
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
History of water supply and sanitation wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Eutrophication wikipedia , lookup
Camelford water pollution incident wikipedia , lookup
Wastewater discharge standards in Latin America wikipedia , lookup
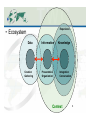
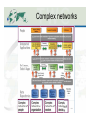
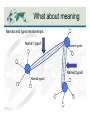
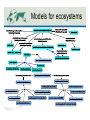
Knowledge Networks and Science Data Ecosystems December 7, 2012, AGU12 IN54A-02. Peter Fox (RPI/ Tetherless World Constellation and WHOI/AOP&E) [email protected] What’s ahead/pre-summary • Data ecosystems necessarily involve a variety of stakeholders • Complex relations require us to move beyond ‘simple’ networks • To do that, we: – Define the framework for a knowledge base, and populate it – Query and render the result Tetherless World Constellation 2 Experience •! Ecosystem Data Creation Gathering Information Presentation Organization Knowledge Integration Conversation Context 3 You mean, you want to know? What is a Knowledge Network? How does it work? Rendering of a network logd.tw.rpi.edu/demos Marine ecosystems Science ecosystem <$'$#12(9-"&"1&"4$/ New National Ocean Policy = Ecosystem Based Management =>"'$'()*(5%"$-%$ Regional Academic Consortia = PaCOOS + CINAR & CAMEO BCO - DMO !"#$%&$'()*(+,$-%*(.$$'/ NMFS / IEA 0-1)2$'()*(3#"41&$(5$%&6#(31#&-$#/7"8/( Packard Foundation + NCEAS + PISCO 9-(5$#4"%$(:6(0-'(;/$#/ Policy Professionals, Fisheries Management Councils, NMFS & Others (Center for Environmental Quality) CEQ + ESIP (Environmental Science Information Partners) 1$#/+.$+#&-+#(2.%+&7"3"8+,+3*&0&93*+8."*+4&'%(#)#*+,#&:##+##,+3* Figure Acknowledgement: Suzanne Lawrence 7".$3+&;(3#+.<"*$(3&0&7"3"8+,+3*&=((5#&>&?%+3".$(# '3<$.(3,+3*"5&@(5$%)&0&7"3"8+,+3*&@.(*(%(5#&A&93$*$"*$<+# !"#$%&'%(#)#*+,#&-+#+".%/&0&1234",+3*"5&'%(#)#*+,#&6)3",$%# Complex networks ‘Complex’ networks • Based on information content – Node count and number of links – Spanning height – ‘Width’ – Etc. • Or complexity metrics, cf. McCabe – number of linearly independent paths through the network • Open world networks lead to differing node relations… (or not) • Complex :== Meaning in context • Semantic networks are ones where the nodes and relations are ‘named and typed’ What about meaning Named and typed relationships Name1:type1 Namen:typen Name2:type2 Name2:type2 Framework - DPSIR forces and Pressures on the environment, the consequent State of the environment and its Impacts, and the Responses undertaken, and of the interlinkages between each of these elements. A generic DPSIR framework for water is shown in Figure 4. Figure 4: A generic DPSIR framework for water Responses Driving Forces ! Water use restrictions Alternative supplies Subsidised water prices Improved information Demand side management Voluntary agreements Regional conflicts Waste water treatment Ban on products Reservoirs Industry Energy Agriculture Aquaculture Households Tourism Climate Geology Pressures Climate change Point source pollution Diffuse source pollution Water abstraction Physical intrusions Water quantity Groundwater status Ecological status: chemical physical biological State Loss of habitats/species Ill health Droughts/floods Desertification Salinisation Loss of amenity Coastal erosion Non-indigenous species Eutrophication Acidification Impacts The state of water is determined by natural factors such as geology and climate and also by the pressures exerted by human activities. Many of the pressures and the underlying driving forces are common to all or a number of the issues. For example, agriculture is a significant storage reservoirs to safeguard supplies when other sources are stressed. Other measures are aimed at reducing or controlling the demand for water including water pricing, water-saving devices and reduction of water leakage in distribution systems. Figure 5: DPSIR conceptual framework for assessing water quantity resources Responses Driving Forces ! Industry Energy Agriculture Aquaculture Households Tourism Climate Overall reservoir stocks Water prices Water use efficiency Water leakage Pressures Climate change Total abstractions Sectoral water use: agriculture, industry households, tourism Available water State 3/9/12 Freshwater shortage, Modification of streamflows Saltwater instrusion Groundwater levels Impacts Water Quantity 14 Organic pollution and eutrophication The effects on the aquatic environment of organic pollution, caused by discharges from waste water treatment plants, industrial effluents and agricultural run-off, include reduced river Models for ecosystems Instances Network Scale(s) • Complex :== Meaning • Semantic networks are ones where the nodes and relations are ‘named and typed’ • Interesting property - scale-free – Citation networks – The Web – Semantic networks – Depend on super nodes Scale free? More likely – multi-scale with some hierarchy … Vision being implemented • “Our vision is to develop, facilitate, and maintain sustained multi-way engagement of natural and social scientists and many practitioners in multiscale local to global networks for Large Marine Ecosystems (LMEs)”. • Goal: Perform routine assessments of LMEs involving all (or as many) stakeholders and we want robust science data presented in forms that various end-users can consume… Discussion • We have the tools to explore these networks, collaboratively… • Now looking at network rendering, i.e. queries and visualizations • Current limit is: base information models upon which to develop the initial knowledge base(s) (i.e. ontologies) • Next: Compute deductive closure, iterate… ? • Thanks for listening. Questions?