* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Microbial growth
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
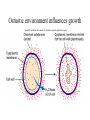
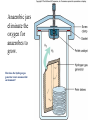
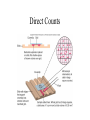
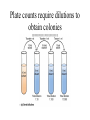
**Microbial Growth** • Growth= an increase in the number of cells, not an increase in size • Generation=growth by binary fission • Generation time=time it takes for a cell to divide and the population to double Bacteria divide by binary fission Generation times vary for each organism • E. coli • Mycobacterium tuberculosis **Bacterial growth curve** *Primary and Secondary metabolites I will ask you about secondary metabolites – know what they are, when they are produced and why. **Requirements for bacterial growth** • Environmental factors that influence – Temperature, pH, osmotic pressure, oxygen • Nutritional factors – Carbon, nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorous – Trace elements *Optimum Growth Temperatures • • • • Psychrophiles-optimum -5 to 15oC Psychrotrophs- range from 20-30oC Mesophiles- range from 25-45oC Thermophiles-range from 45-70oC Growth rates in different temperatures pH influences the growth • Bacteria-prefer a pH range of 6.5-7.5 • Molds prefer a pH range of 5.0-6.0 Osmotic environment influences growth **Oxygen preferences of organisms** • Obligate aerobes require oxygen for growth • Facultative anaerobes: can grow in aerobic or anaerobic environments • Obligate anaerobes: unable to grow in the presence of oxygen **Why can some organisms grow in the presence of oxygen?** • Because they have the ability to neutralize toxic oxygen molecules (superoxide, oxygen radicals) • Toxic forms of oxygen need to be neutralized by enzymes – Superoxide dismutase – Catalase *Oxygen Preferences of Bacteria Candle jars increase CO2 levels for growing capnophiles How does a candle jar create a CO2-enriched/O2-depleted environment? Is it an anaerobic environment? Anaerobic jars eliminate the oxygen for anaerobes to grow. How does the hydrogen gas generator create an anaerobic environment? Chemical requirements: Carbon • What are possible sources of carbon? • Bacteria are classified based on the source of carbon as either heterotrophs or autotrophs Classification based on Energy and Carbon sources Chemical Requirements: Nitrogen • Why do bacteria need nitrogen? Chemical requirements: Sulfur and Phosphorous • Why do bacteria need sulfur? • Why do bacteria need phosphorous? Chemical requirements: trace elements • Small amounts of minerals • Usually function as cofactors *Culture Media • Chemically defined – GSA A chemically defined medium is one where we know EXACTLY what the ingredients are. An undefined medium is one where we don’t know the exact chemical makeup (for instance, it may contain “protein digest” Chemically defined media Culture Media • Complex – Nutrient Agar – TSA – BHI *Culture Media • Selective • Differential • Selective and Differential *Ways to measure bacterial growth • Direct Count • Plate Count/Viable Cell Count • Measure Turbidity Direct Counts Plate counts require dilutions to obtain colonies Plate Counts: pour plate Plate Count-spread plate *Turbidity gives a rough estimate