* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Relocation Diffusion - Winston
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
History of geography wikipedia , lookup
Iberian cartography, 1400–1600 wikipedia , lookup
Diver navigation wikipedia , lookup
History of cartography wikipedia , lookup
Scale (map) wikipedia , lookup
Early world maps wikipedia , lookup
Counter-mapping wikipedia , lookup
Mercator 1569 world map wikipedia , lookup
Cartography wikipedia , lookup
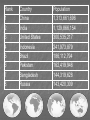
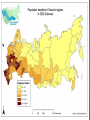
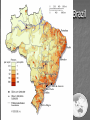
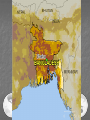
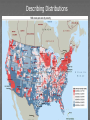
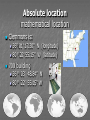
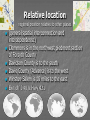
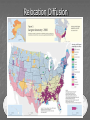
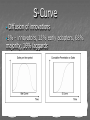
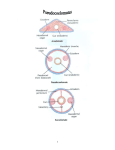
Three sources of map distortion Map scale – most maps are smaller than the reality they represent. Map scales tell us how much smaller. Map projection – this occurs because you must transform the curved surface of the earth on a flat plane. Map type – you can display the same information on different types of maps. Map scale – tells us relationship between distance on map and distance on earth’s surface Ratio scale = ratio of map distance to earth distance. 1:10,000 means that one inch on the map equals 10,000 inches earth’s surface; one centimeter represents 10,000 centimeters; or one foot equals 10,000 feet. Recall a small fraction has a large denominator so that 1:100,000 is a smaller scale than 1:25,000. A large-scale map depicts a small area with great detail. A small-scale map depicts a larger area with little detail. Distortion is especially severe here. A. B. C. D. Which is the largescale map? Which map scale shows the most detail? a. 1:250,000 b. 1:24,000 c. 1:100,000 d. 1:62,500 1. 2. a. b. c. d. e. A map with a large scale usually shows a large amount of land space a small amount of land space physical features only of a land space the local-global continuum political boundaries between countries only the other Scale Refers to at what scale a process occurs – For example, while the storm didn’t make the national news, at the local scale it was a major story. Distribution •Density •Concentration •Pattern Distribution definition The arrangement of something across earth’s surface Rank 1 Country China Population 1,313,661,696 2 India 1,129,866,154 3 United States 300,535,217 4 Indonesia 241,973,879 5 Brazil 186,112,794 6 Pakistan 162,419,946 7 Bangladesh 144,319,628 8 Russia 143,420,309 Rank Country Area – km2 1 Russia 17,098,242 3 China 9,640,821 4 United States 9,629,091 5 Brazil 8,514,877 7 India 3,287,263 16 Indonesia 1,904,569 36 Pakistan 880,254 94 Bangladesh 143,998 Population Density Population Density Asia Density of Population, 2005 Brazil Australia, 1997 1 dot = 1000 people India Population Density Spatial Distribution Definition: The regular arrangement of a phenomenon across Earth’s surface. Density: The frequency with which something exists within a given unit of area. Concentration: The spread of something over a given study area Pattern: The geometric or regular arrangement of something in a study area Describing Distributions Describing Distributions Land Ordinance of 1785 location, direction, distance site and situation Toponym Place Name! Some Vocab: Absolute Direction Absolute Distance Absolute Location Relative Direction Relative Distance Relative Location Absolute location mathematical location Clemmons is: 36⁰ 01’ 17.30” N (longitude) 80 ⁰ 22’ 55.15” W (latitude) 700 building 36 ⁰ 03’ 48.84” N 80 ⁰ 22’ 55.15“ W Site physical attributes (includes absolute location, but includes the physical setting; especially in urban geography) What are the relevant site features of Clemmons? Landforms Climate Soil quality Availability of water Vegetation Relative location regional position relative to other places (general spatial interconnection and interdependence) Clemmons is in the northwest piedmont section of Forsyth County Davidson County is to the south Davie County (Advance) is to the west Winston-Salem is 10 miles to the east Exit off I-40 & Hwy 421 Situation location attributes (external relations, a type of relation location that refers to items of significance, especially in urban geography) Suburb of Winston-Salem, a bedroom community for persons working in the medical, bio technical/medical and aeronautical businesses in the Triad I-40 and US 421, major transportation Absolute direction cardinal points N-S-E-W Clemmons is southwest of Winston-Salem. Relative direction culturally based, not necessarily an accurate cardinal point Clemmons is in the “South”. Clemmons is … Absolute distance mathematical space between 2 points Clemmons is 10 miles (16km) from Winston-Salem. Relative distance meaningful space measurement Clemmons is about 15 minutes from Winston-Salem. Clemmons is one hour from Mt. Airy. “City of 2 Million” article Vocabulary Time-Space Convergence Distance Decay Friction of Distance Use the terms… 1. Describe the absolute location, absolute direction and absolute distance of a place of your choice. 2. Describe the relative location, relative direction and relative distance of the same place. 3. Describe the site. 4. Describe the situation. Which of the following is not a measure of relative distance? a. 2,339 cm b. 35 seconds c. $2.50 cab ride d. 216 footsteps e. 15 minutes 1. 2. a. b. c. d. e. Relative location is an important geographic concept mainly because it locates places according to longitude and latitude defines a place in terms of how central or isolated it is to other places defines patterns of natural environment helps cartographers to develop more accurate maps illustrates how local, regional and global factors interact within the local-global continuum Homework for tonight is Subway Activity #3 Diffusion The process by which an idea or innovation is transmitted from one individual or group to another across space Fellman People move to a new area and take their culture with them – examples include- crops, culture, farming techniques, building styles Information about an innovation may spread through a society – examples include Hybrid corn, Cd’s, a religious creed. Possibly through mass media advertisement— Known as Known as Relocation Diffusion Expansion Diffusion Relocation Diffusion Type of Expansion Diffusion Contagious Diffusion Hierarchical Diffusion Stimulus Diffusion Contagious Diffusion Diffusion that spreads like a disease – but not necessarily applying only to diseases! Affects nearly uniformly all individuals and areas outward from the source region Examples – influenza, ideas on the world wide web; agriculture (like hybrid seeds), Buddhism (but not all religions), breaking news, Domino Theory Hierarchical Diffusion The spread of an idea from persons or nodes of authority or power to other persons or places Examples- Birkenstocks, Christianity, styles of clothing, music Stimulus Diffusion A fundamental idea, though not the trait itself, stimulates imitative behavior Examples – creation of a unique Cherokee written language, Beta vs. VHS, Macs, Siberians domesticated reindeers (after seeing domesticated cattle) Diffusion? http://www.youtube.com/user/samsungm obileusa?v=nf5-Prx19ZM Cultural Hearths •An area where cultural traits develop and from which the cultural traits diffuse. •Examples – Islam, agriculture, Time-Distance Decay •The farther the place is from the hearth, the less likely an innovation is to be adopted. •The acceptance of an innovation becomes less likely the longer it takes to reach its potential adopters. •Cultural barriers work against diffusion. Types of Diffusion are not speed specific – no type of diffusion is particularly fast or slow S-Curve Diffusion of innovations •3% - innovators, 13% early adopters, 68% majority, 16% laggards • • Which of the following type of diffusion spreads the quickest? a. b. c. d. e. Contagious Diffusion Hierarchical Diffusion Stimulus Diffusion Relocation Diffusion None of the answers Rap music first appeared in New York in the 1970’s. Later, it spread to large cities with vibrant AfricanAmerican populations – such as Los Angeles, Oakland, Chicago, and Detroit – without being absorbed by the smaller cities and rural areas in between. This type of spatial diffusion is called a. relocation potential b. hierarchical diffusion c. contagious diffusion d. cultural diffusion e. cascade diffusion Which of the following is not a good example of a barrier to spatial diffusion? a. A mountain range b. A different language c. A different dietary preference d. A highway system e. A strict religious system The Spanish-language concentration of Little Havana in Miami is an example of what type of diffusion? a. relocation diffusion b. expansion diffusion c. stimulus diffusion d. hierarchical diffusion FRQ Practice – NO Notes Define and Give an example of • – – – – Relocation Diffusion Hierarchical Diffusion Stimulus Diffusion Contagious Diffusion (diseases not allowed)