* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Discovering Our World - Mr. Cohen's English Village
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
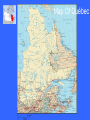
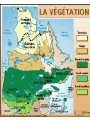
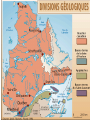
Discovering Our World Québec Continents and Oceans 4 Oceans 1. Atlantic Ocean 2. Pacific Ocean 3. Arctic Ocean 4. Indian Ocean 7 Continents 1. North America 2. South America 3. Europe 4. Asia 5. Africa 6. Australia (Oceania) 7. Antarctica World Map What did you notice? • 75% of the planet is Water • Most of the habitable land is in the Northern Hemisphere • Most people live in the Northern Hemisphere • As you move away from the equator to the poles, the temperature gets colder • Most large cities are close to water North America Made up of three countries 1. Canada 2. United States 3. Mexico Canada Made up of 10 Provinces 1. British Columbia 2. Alberta 3. Saskatchewan 4. Manitoba 5. Ontario 6. Québec 7. New Brunswick 8. Prince Edward Island 9. Nova Scotia 10. Labrador/Newfoundland And 3 Territories 1. Yukon 2. Northwest Territories 3. Nunavut Map of Canada Did you know…. • Canada is the 2nd largest country in the world • It is surrounded by three oceans • It was established on July 1st, 1867 with 4 provinces: Québec, Ontario, New Brunswick and Nova Scotia • The capital city is Ottawa • The population is 33,000,000 (approx.) • The three largest cities in order are Toronto (5.2 Million), Montreal (3.6 Million), and Vancouver • It has the largest undefended boarder with the United States Map Of Québec Did you know… • • • • • Québec is the largest Province in Canada Capital: Québec City Population: 7,600,000 (approx.) Largest City: Montreal (3,500,000 approx.) Québec (Kebec) is an Algonkian word for ‘where the river narrows’ • The Saint-Lawrence River is one of the most important waterways in North America Natural Resources • Anything we take or use from nature: trees, minerals, oil, soil, animals, water. Some are renewable, some are non-renewable. • Québec stands out notably in the mining sector by ranking among the top 10 producers in the world. • It also stands out with its notable development of forestry resources. Currently, 60% of the newsprint consumed in the north-eastern United States originates in Québec. • Québec's territory is one of the largest reservoirs of drinking water on the planet. Natural Forces • Events in nature that shaped and molded the earth’s surface over thousands of years. • Examples: earthquakes, volcanoes, glaciers, meteorites,water, wind, and fire. Vegetation Zones • In Québec, the main forest ecosystems correspond to the following 4 vegetation zones, running from south to north : • The mixed forest zone- containing deciduous and coniferous trees in southern Québec where we live. Deciduous - Ex. maple, birch, oak (trees that lose their leaves) • The boreal forest zone, made up primarily of coniferous trees- Ex. evergreens, Pine, fir (needle trees that stay green all year) • The taiga (short conifers spread around a large territory) • The tundra (subarctic and arctic regions, mosses, lichens, weeds, bushes, low growing plants) Vegetation Zones • The boreal forest of conifers, accounts for 73.7 % of Québec forests. It is made up almost entirely of balsam fir, black and white spruce, jack pine and larch. The only hardwoods that grow there are white birch, trembling aspen and balsam poplar. • South of the boreal forest lies the southern forest of hardwoods, of which the most abundant species are sugar maple, yellow birch and beech. Other species include black cherry, linden, three species of oak, three species of ash, two species of hickory, three other species of maple, and two species of poplar. • The southern forests also include certain softwood species such as white and red pine, hemlock and cedar. The species found in this zone live longer than those found in the boreal forest and grow to a bigger size. Climate and Weather • The Climate of a region is constant (doesn’t change) from year to year and season to season when looking at a place in the world. It means that the temperature in August each year will have similar warm summer weather. The temperature in February each year will also have similar cold winter weather. The climate is predictable based on the trends in the past. • The Weather of a region changes daily from clear to precipitation (what falls from the clouds); rain, snow, sleet, hail… Climate Zones • One feature of a land area as vast as Québec's is striking variations in temperature and precipitation in various regions. Québec has a mild spring, an often hot summer, a colourful but sometimes chilly fall, and a cold snowy winter which Quebecers have mastered. • Québec has three types of climates : (From South to North) 1. Continental Humid, Where we live. south of the 50th parallel (a hot summer, especially in July, a cold winter and abundant precipitation) 2. Subarctic, between the 50th and 58th parallels (colder, longer winters, shorter, cooler summers, less precipitation) 3. Arctic, in the far north (rigorous winter, brief annual thaw, continuous permafrost) Agriculture • Using the soil for farming. • dairy farmers, pig farmers, maple syrop, fruit(berries), vegetables (corn). • Organic Water By harnessing water resources, Québec has made hydroelectricity a key to economic growth. Saint Lawrence River • The Saint Lawrence River is one of the most important rivers in North America. From its source in the Great Lakes, it flows to the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the Atlantic. • It is one of the leading navigable waterways of the world and the main river route in North America. • It links the Atlantic Ocean and the huge Great Lakes basin, it makes it possible to reach the Prairies in the west and leading industrial centres in Canada and the United States. • The Saint Lawrence is a lifeline for flora, fauna and human life. • The river was the focal point of the lives of the continent's first inhabitants. They established their villages on its shores, lived on fish, hunted the birds and mammals that inhabited the river's shores, and travelled on its waters. Fishing Québec waters are brimming with a number of species of highly sought-after fish, crustaceans and molluscs. Forestry • Much of Québec is covered by forests, which are of prime economic, social and environmental importance. Mining • Québec has extensive deposits of gold, copper, zinc, nickel, iron and ilmenite • (a mineral containing titanium). Future Well integrated into the environment, wind turbines are a key component of sustainable development and promise clean, renewable energy. Canadian Shield • 95% of the land •Oldest rock in the world • Formed thousands of years ago by glaciers that eroded the land and formed plateaus and valleys. •Includes millions of lakes and waterways.. the largest lakes (Mistassini) and rivers (La Grande) for hydroelectricity. •Not much will grow on the soil, but under it you will find rich mineral deposits of gold, copper, and iron ore. •Area is rich in wood from all the forests. •Includes the tourist areas of the Laurentian mountains..Mt.Tremblant, Mt.Saint-Sauveur. Appalachians • Chain of rolling mountains covering the eastern townships and the Gaspé. • Area that covers parts of Newfoundland and stretches all the way to Georgia in the U.S.A. • Farming in the valleys, trees on the hills and minerals under the ground. St. Lawrence Lowlands • Where we live • Where most people live in the area along the St. Lawrence River. • Flat land in the valley between the two mountainous regions. • Rich and fertile land for agriculture…fruit, vegetables, dairy, meat.