* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download OSPF
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
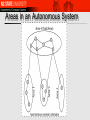
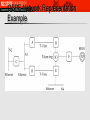
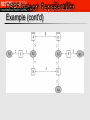
OSPF CSC/ECE 573, Sections 001 Fall, 2012 Introduction 1-1 OSPF: Open (= non-proprietary) SPF RFC 2328 (OSPF version 2) Recommended interior (intra-domain) routing protocol for TCP/IP – Goals – – link state routing using Dijkstra's algorithm converge faster than RIP exchange less information than RIP Runs directly over IP (not UDP or TCP); protocol number 89 OSPF “advanced” features (not in RIP) Network Layer security: all OSPF messages authenticated (to prevent malicious intrusion) multiple same-cost paths allowed (only one path in RIP) For each link, multiple cost metrics for different TOS (e.g., satellite link cost set “low” for best effort; high for real time) integrated uni- and multicast support: – Multicast OSPF (MOSPF) uses same topology data base as OSPF hierarchical OSPF in large domains. 4-3 OSPF (cont’d) Optimization metrics – hop-count – delay – throughput, etc. When several equal-cost routes exist, can send traffic along each of them – for load-balancing Reliability – – – – flooding, with neighbor acknowledgments reoriginate LSAs at 30 minute intervals all LSAs are checksummed can withdraw state using LSA with maximum age OSPF (cont’d) Subnetting – designed to work with variable-length subnets and CIDR Security – – simple cleartext password MD5 message digest, based on shared secret key Area Routing Routing domain is split into areas – – – Area = generalization of a subnet – – – “backbone” and attached areas areas do not overlap 2-level hierarchy; each area must attach directly to backbone its topology and details are not visible outside the area each area runs a copy of the link-state protocol smaller link-state databases Routers at boundaries intercommunicate – summarize (aggregate) routing prefixes and advertise fewer routes Areas in an Autonomous System OSPF Areas (cont’d) Exchange of summary LSA’s across the backbone: Distance Vector! – But using flooding as method of distribution Virtual links to handle connections of border routers to the backbone area – – Result: border routers do not have to be physically directly connected to each other “tunnels” through non-border routers virtual link OSPF Classes of Routers Internal routers: wholly within an area Area border routers: connect two or more areas Backbone routers: on the backbone AS boundary routers: talk to routers in other AS The classes are allowed to overlap OSPF Classes of Routers (cont'd) Connections And Networks OSPF supports three types of connections and networks – – – Point-to-point lines between exactly two routers Multiaccess networks with broadcasting (e.g., most LANs) Multiaccess networks without broadcasting (e.g., most WANs) OSPF abstracts the collection of actual networks, routers, and lines into a directed graph (hosts do not play a role in OSPF) LAN Abstraction N routers connected to a broadcast LAN Model as N*(N-1)/2 point-to-point connections expensive! – – Instead, create one LSA for the LAN, containing links to all routers – size of link-state database (N routers, O(N2) links) # of messages exchanged (O(N2) for N routers in LAN) N+1 nodes, N links, N messages on LAN A “Designated Router” is responsible for originating the LSA representing the LAN – there may also be a “backup designated router” LAN Abstraction Example OSPF Network Representation Example OSPF Network Representation Example (cont'd) Message Types Hello – Link state update – at boot time, used to discover who the neighbors are; also used to periodically test reachability flooded to the whole network; provides the sender's cost to its neighbors Link state ACK – ACKs link state update reliable flooding Message Types (cont’d) Database description – when a line between routers is brought up, gives sequence # of all link state entries a sender has Link state request – after exchanging database description messages, sender requests link state information for links for which the other router has more recent info LSA Types: Router LSA Lists router's interfaces, their cost, the network/router they connect to, the range of IP addresses directly accessible via the interfaces LSA Types: Network LSA Performs the LAN abstraction: lists all routers connected to the network LSA Types: Summary Link Link to border router, advertises IP addresses between areas External Link LSA Link to another site, imports routing information from other AS