* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Efficient Mobility Management for Vertical Handoff between WWAN
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.11 wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
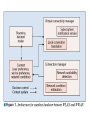
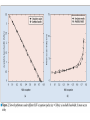
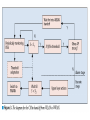
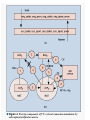
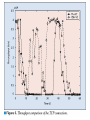
Efficient Mobility Management for Vertical Handoff between WWAN and WLAN IEEE Communications Magazine November 2003 Authors Qian Zhang Chuanxiong Guo Zihua Guo Wenwu Zhu All come from Wireless and Networking Group, Microsoft Research Asia Teammates 資工所 廖翊均 692410001 資工所 林世敏 692410035 資工所 陳崇凱 692410078 Outline Introduction Connection manager Virtual connectivity manager Performance evaluation conclusions Introduction WLAN vs. WWAN Horizontal handoff vs. Vertical handoff Mobile IP IEEE 802.11 vs. GPRS HA, FA, CoA Routing, scalability Migrate Reference [8], Proc. Mobicom 2000 End-to-end Two limitations Cannot make mobility transparent to application Cannot maintain connection under NAT & simultaneous movement Introduction Proposed approach IP-centric Connection Manager (CM) Virtual Connectivity Manager (VC) Detect conditions and availability of networks Maintain connection’s continuity Local Connection Translation (LCT) subscription/notification service (S/N) Roaming decision maker Context database Connection Manager Handoff from WWAN to WLAN Physical Layer Sensing Detect the available of the stable WLAN signal MAC Layer Sensing NAV (Network Allocation Vector) Traffic load vs. NAV occupation Network-condition-aware handoff Adaptation of upper layers Best QoS selected Connection Manager Handoff from WLAN to WWAN FFT-Based Decay Detection FFT:Fast Fourier Transform To detect signal decay X(1)/N:threshold N:RSSI sampled number Connection Manager Adaptive Threshold Configuration To set an appropriate RSSI threshold RSSI:Received Signal Strength Indication S1 = S2 + Δ Virtual Connectivity Manager Problems caused by mobility Transparency to application Especially important for UDP applications Transparency to NAT Simultaneous movements The VC protocol Peer negotiation Connection maintenance S/N protocol Virtual Connectivity Manager Local Connection Translation (LCT) Mapping relationship between the original and the current connection information Solve “transparency to application” problem Subscription/Notification service (S/N) To bridge the two communication parties so that they can exchange address information S/N server is publicly addressed and never moves Solve “transparency to NAT” & “simultaneous movement” problems Performance Evaluation OS:Windows 2000 CM:manipulates and monitors all wireless network interfaces via the NDIS device interface, and provides related information to the roaming decision maker, which runs in the system as a background service. VC:implemented in the system together with the TCP/IP stack, and is located naturally between the network and transport layers. Conclusions In this article a novel mobility management system is proposed for vertical handoff between WWAN and WLAN. The system integrates a CM and a VC. Collaboration between the CM and VC accomplishes seamless handoff between WWAN and WLAN. Conclusions CM:detect the wireless network changes MAC sensing FFT detection adaptive threshold configuration VC:maintain connectivity using the end-to-end principle LCT:support application transparency S/N: support working under NAT and handling of simultaneous movement