* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reliable multi-media services for NGNs
Policies promoting wireless broadband in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
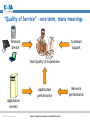
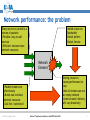
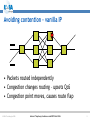
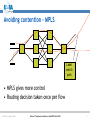
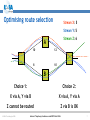
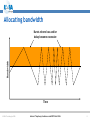
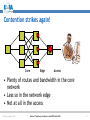
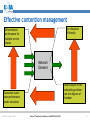
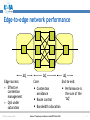
An Overview of QoS for Multi-Service IP Networks Peter Thompson Chief Scientist U4EA Technologies Ltd. Internet Telephony Conference and EXPO East 2006 1 Overview • Understand the reasons for performance variability in IP networks • Examine the techniques to control this in the network core • See why these techniques are less useful in the access part of the network • Explore how QoS can be achieved in parts of the network where contention is likely © U4EA Technologies 2006 Internet Telephony Conference and EXPO East 2006 2 “Quality of Service” – one term, many meanings Terminal device Customer support User Quality of Experience Application performance Network performance Application servers © U4EA Technologies 2006 Internet Telephony Conference and EXPO East 2006 3 Network performance: the problem Every service is carried in a stream of packets: •Flexible: easy to add services •Efficient: streams share network resources Limited resources: •Bandwidth •Packet buffers •Packet Service Network Element Sharing resources causes performance to vary: •Not all streams can see an empty network •Some streams’ delivery will vary drastically •Packet streams are often bursty •Bursts can overload network resources •Call this ‘contention’ © U4EA Technologies 2006 Internet Telephony Conference and EXPO East 2006 4 Avoiding contention – vanilla IP • Packets routed independently • Congestion changes routing – upsets QoS • Congestion point moves, causes route flap © U4EA Technologies 2006 Internet Telephony Conference and EXPO East 2006 5 Avoiding contention - MPLS Label switch path • MPLS gives more control • Routing decision taken once per flow © U4EA Technologies 2006 Internet Telephony Conference and EXPO East 2006 6 Optimising route selection Stream X: 5 Stream Y: 5 Stream Z: 6 A 10 12 8 10 B Choice 1: Choice 2: X via A, Y via B X via A, Y via A Z cannot be routed Z via B is OK © U4EA Technologies 2006 Internet Telephony Conference and EXPO East 2006 7 Allocating bandwidth Bandwidth Bursts where loss and/or delay become excessive Time © U4EA Technologies 2006 Internet Telephony Conference and EXPO East 2006 8 Allocating bandwidth Bandwidth Bursts for which loss and delay are tolerable Allocation above average to get acceptable performance Time © U4EA Technologies 2006 Internet Telephony Conference and EXPO East 2006 9 Contention strikes again! Core Edge Access • Plenty of routes and bandwidth in the core network • Less so in the network edge • Not at all in the access © U4EA Technologies 2006 Internet Telephony Conference and EXPO East 2006 10 Contention management Use resources efficiently Differentiate performance for multiple types of service Keep average Network load below Element 30-40% Various mechanisms: •Policing •Shaping •Queuing •Scheduling Maintain consistent performance under saturation © U4EA Technologies 2006 Internet Telephony Conference and EXPO East 2006 11 Effective contention management Use resources efficiently Differentiated performance for multiple service classes Network Element Deep analysis of the scheduling problem – use the degrees of freedom Guarantee worstcase performance under saturation © U4EA Technologies 2006 Internet Telephony Conference and EXPO East 2006 12 Edge-to-edge network performance ∆Q Edge/access: • Effective contention management • QoS under saturation © U4EA Technologies 2006 ∆Q ∆Q Core: End-to-end: • Contention • Performance is avoidance the sum of the ‘∆Q’ • Route control • Bandwidth allocation Internet Telephony Conference and EXPO East 2006 13 Thank you! Any questions? Peter Thompson U4EA Technologies Limited [email protected] www.u4eatech.com © U4EA Technologies 2006 Internet Telephony Conference and EXPO East 2006 14