* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Internet Telephony
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
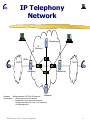
Internet Telephony Introduction What is it? History IP Telephony v. PSTN DCE Project 1999 - Internet Telephony 1 IP Telephony v PSTN Data Packet Switched Circuit Switched Calls broken to pieces and sent to Dedicated circuit for destination Better use of network capacity Data Network 80% reliable Downtime is 4 hours per month (Data Communications) DCE Project 1999 - Internet Telephony each call Telephone Network 99.999% reliable Downtime measured in seconds per year Regulation 2 Voice Gateways Physical interface Placed between PSTN and IP Network Handles signaling to and from telephone network reception of telephone numbers conversion of tel nos to IP addresses voice processing reception of voice signal compression(to reduce bandwidth and delay impact from Network) and packetization echo cancellation silence suppression No of gateways crucial - around 500 in existence DCE Project 1999 - Internet Telephony 3 IP Telephony Network Gatekeeper IP Network R T ISDN PSTN PSTN R T Gateway R T R T Gateway Gateway Gateway : Bridge between PSTN & IP Networks Gatekeeper : Admission control for network Bandwidth control and management Address translation (E.164 <-> IP address) Call Management DCE Project 1999 - Internet Telephony 4 IP Telephony Services Encompasses phone-to-phone phone-to-PC PC-to-PC fax-to-fax video conferencing desktop collaboration Software such as Microsoft NetMeeting DeltaThree’s DotDialer IDT’s Net2Phone DCE Project 1999 - Internet Telephony 5 Standards Why do we need them? The benefits of standardisation • • • • Interoperability billing, settlement and reconciliation uniformity for carriers marketability Currently • no standards for signaling • no standard agreement on accounting records or billing These issues being handled through maturing standards such as ITU’s • H.323 • Tiphon DCE Project 1999 - Internet Telephony 6 H.323-The Vendors Choice? H.323 recommends G.723 • compresses voice to 5.3 or 6.3 kbit/s Some using GSM algorithm • compresses to 13.3 kbit/s, appears to provide superior quality to G.723 Tiphon • based on H.323 • specifies network architecture, numbering, supplementary services integration DCE Project 1999 - Internet Telephony 7 Security Initially somewhat overlooked, now being raised by carriers and business users Security Issues • • • • User and data authentication Data privacy (integrity, confidentiality) Access control Policy management Security Measures • Encryption – SSL (secure sockets layer) – TLS (transport layer security) • Tunnelling – Layer 2 Tunnelling Protocol (L2TP) – establish a secure tunnel between gateways or gatekeepers DCE Project 1999 - Internet Telephony 8 Encryption SSL, TLS on transport level, suitable for Gatekeeper-to-gatekeeper, but not if unreliable, connectionless UDP transports the voice IETF IPsec working group describes security architecture for IP protocol that makes it suitable for secure VPN authenticates users encrypts payload tracks who has changed packet Incorporated in H.323 V2 via H.235 also called H Secure Encryption Problems Political/military issues (limits on keys etc) Hardware issues (processing power) Dealing with security issues US Chamber of commerce announced automatic approvals for financial institutions Therefore encryption more readily available?? DCE Project 1999 - Internet Telephony 9 Effect on the Traditional Communications Companies Telecommunications or information service? Telecommunications Act 1996 promote competition facilitate new telecommunications technologies DCE Project 1999 - Internet Telephony 10 Economics Cost savings dependent on the provider and location Calls between London and Tokyo around 30 cents per minute ($1 per minute for POTS) DCE Project 1999 - Internet Telephony 11 The Future Market predicted to grow to $560 million by end of 1999 By 2002, 3% of US long-distance traffic, 5% of European long-distance traffic, 14% of US international traffic and 11% of European international traffic Not economic but service benefit Used with video and data sharing for multi-media communications DCE Project 1999 - Internet Telephony 12