* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Group 13 and 14 Summary of Threats and Defenses Honeynets and
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Remote Desktop Services wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
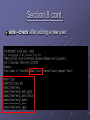
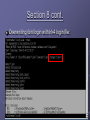
ECE4112 Lab 7: Honeypots and Network Monitoring and Forensics Group 13 + Group 14 Allen Brewer Jiayue (Simon) Chen Daniel Chu Chinmay Patel Background Honeypot Definition in lab: system whose value lies in being probed, attacked, or otherwise taken advantage of by blackhat. Responds to the user informing hacker has attempted an attack on system Two types: Production Honeypots: alerts user of an attack Research Honeypots: tracks hacker’s actions Background Intrusion Detection System (IDS) Monitors traffic and suspicious activities Alerts the network administrator May respond to malicious traffic by blocking user or source IP address from accessing the network Section 1: BackOfficerFriendly Known for its ability to attract and trap hackers For exercise, attempted a connection from RH 4.0 to windows using telnet Outcome? Source IP Address, username and passwords attempted Why use BOF? Prevent hackers Section 2: Homemade Honeypot using Netcat as a Port Sniffer Offers more options than BOF Monitored and stored sent data Data was sent from RH 4.0 to RH 7.2 machine Should be able to see the file Section 3: Capturing Packets using Ethereal Packets observed using Telnet: TCP telnet packets to port 23 Content of packets They contained single characters. Packets observed using IMAP: SMB packets Content of packets The commands from the imapd client Section 4: Set up and use Snort to capture packets Snort: Similar to Ethereal Three modes: Sniffer, Packet Logger, Network Intrusion Detection How –l option organizes logging of network traffic? A new directory was created for each IP, with subdirectories for each type of packet sent. Section 5: Scan of the Month Challenge Challenge is to determine hacker’s activity and how it was accomplished: Hacker’s IP: 203.173.144.80 Hacker’s first activity: Initializes the backdoor to respond to one specific IP Purpose of ‘foo’: To gather email address and send them via UDP to particular host How ‘foo’ will be used? : To spam, sell addresses, create havoc Section 6: Using SNORT to act as an IDS Create rules to generate alerts and logs of suspicious packets. Rule syntax: ACTION PROTOCOL IP[/mask] PORT -> IP[/mask] PORT (OPTIONS) Rule to detect the imapd-ex attack: “alert tcp any any -> 57.35.6.147 143” Section 6: Using SNORT to act as an IDS How to evade detection by SNORT? Send packets out of sequence Retransmit different byte ranges of data Content inspection of packets is expensive. Can be easily overloaded with bogus alerts Solution? Support modules: portscan and stream4 preprocessors Section 7: Advanced Uses of Ethereal Conducted forensic analysis of real honeynet data [email protected] Source IP : 219.166.103.235, 130.160.86.86, 128.61.252.112 Target IP: 192.168.1.10 , 192.168.1.20, etc. Duration: approximately 8 hours Hacker Activities: ARP broadcast for specific internal IP Spoofs this IP Attempts to connect to the corresponding IP with various methods/services: ARP, FTP, http, ICMP (ping), and SNMP. Section 7 cont. [email protected] Duration: approximately 15 hours Hacker Activities: ARP broadcast to find legitimate active IP on network. Attempts to establish ssh connection http request to execute command on webserver. Script calls windows command line to run a TFTP (trivial FTP) client to retrieve remote files such as Kill.exe and .ini files on 199.203.162.200 victim webserver copies file from server script performs other operations such as: deleting, copying, moving files, etc. Section 7 cont. Security Methods for Prevention Limit the number of ARP broadcasts within a time interval Packets with destination port value of 80 should only be connecting to network’s web server Secure neighboring routers, own router, neighboring subnets to prevent hackers from compromising a system and sending ARP broadcasts. Section 8 Introduction to AIDE Used AIDE (Advanced Intrusion Detection Environment) to detect system changes Creates checksums of files for later comparison Drawback: AIDE must be run before an attack Where should the clean copy be stored? Section 8 cont. aide –check after adding a new user: Section 8 cont. Overwriting /bin/login with lrk4 login file: Section 9: Snare for Windows System iNtrusion Analysis & Reporting Environment View specific details of system events How is Snare useful for our purposes? What’s the benefit in having remote control functionality? Section 10: Forensics Investigation the Penguin Sleuth Kit Bootable Linux distribution based on KNOPPIX. Using Penguin Sleuth for “postmortem” forensic investigation Using Autopsy to analyze hard drive image Generate time line of what happened on a system Is there a Windows Alternative? Questions? ?