* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download midterm
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
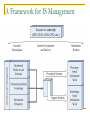
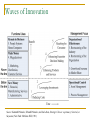
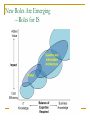
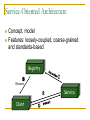
Midterm Review Chapter 1. IS Management Overview The Internet Economy From APARTNET to today’s Internet WWW has evolved from a graphical layer of the Internet to a cyberspace for business eRetailers, eMarkets, eAggregators, Informediaries, Exchanges, Portals Dot-com crash Pure Internet economy VS. the hybrid model Business Ecosystems An ecosystem is a web of relationships surrounding one or a few companies They appear to follow biological rules Various players in one's business ecosystem Suppliers, distributors, retailers, competitors, banks, advertising agencies etc. From Supply-Push to Demand-Pull Supply-push Companies did their best to figure out what customers wanted Organized to build a supply of products or services and then ‘push’ them out to end customers on stores shelves, in catalogs etc. Demand-pull Allows much closer and ‘one-to-one’ contact between customer and seller Offer customers the components of a product/service then the customer creates their own version by ‘pulling’ what they want Outsourcing and Strategic Alliances To become more competitive, organizations are examining types of work that should be done internally or externally by others The thinking is: We should focus on what we do best and outsource the other functions to people who specialize in them Ranges from a simple contract for services to a long-term strategic alliance Demise of Hierarchy Hierarchical structures cannot cope with rapid change Communications up and down the chain of command takes too much time for today’s environment Self-managed groups produce higher performance IT enables team-based organizational structures by facilitating rapid and far-flung communication The Mission of Information Systems Early days: "paperwork factories" to pay employees, bill customers, ship products etc. MIS era: producing reports all levels of management “Get the right information to the right person at the right time.” Today: Improve the performance of people in organizations through the use of information technology. A Framework for IS Management Chapter 2. The Top IS Job Waves of Innovation Source: Kenneth Primozic, Edward Primozic, and Joe Leben, Strategic Choices: supremacy, Survival, or Sayonara (New York: McGraw-Hill, 1991) Traditional Functions Are Being Nibbled Away (1) The traditional set of responsibilities for IS : Managing operations of data centers, remote systems, and networks Managing corporate data Performing systems analysis and design, and constructing new systems Systems planning Identifying opportunities for new systems Traditional Functions Are Being Nibbled Away (2) Distributed systems Ever more knowledgeable users Better application packages Outsourcing New Roles Are Emerging ---The Squeeze on Traditional IS Activities New Roles Are Emerging ---Roles for IS Toward IS Lite Major IT Eras Four Aspects of the CIO Role Leading Governing Establishing an IS Governance structure Investing Creating a vision by understanding the business Shaping the IT portfolio Managing Establishing credibility and fostering change Leading: Creating a Vision by Understanding the Business Seven approaches to understanding the business and its environment: Encourage project teams to study the marketplace Concentrate on lines of business Sponsor weekly briefings Attend industry meetings with line executives Read industry publications Hold informal listening sessions Partner with a line executive Investing: Shaping the IT Portfolio IT investments has gained increased attention Two key IT investment topics CIOs were usually falsely blamed for making poor IT investment What to invest in (strategic) How to make investment decision (tactical) IT portfolio management Systematic management of large classes of planned IT initiatives, projects, and ongoing IT services etc. Chapter 3. Strategic Use of IT Strategic Use of Information Systems "Working inward" "Working outward" Improving a firm's internal processes and structure Improving the firm's products and relationships with customers "Working across" Improving its processes and relationships with its business partners Whither the Internet Revolution? British Railway Revolution – the mania started in 1830s and experienced a crash in 1845 10 fold increase in 1910, 65 years after the crash During boom, great excitement and small companies flourished After crash, glamour gone, business became serious and full of hard work Industry became orderly and profits began to reflect real returns Investment frenzy for connection technology: "race for space" Does IT Still Matter? "IT Doesn't Matter" – article by Nicholas Carr in Harvard Business Review May 2003 What makes a resource truly strategic is not ubiquity but scarcity As information technology's power and ubiquity have grown, its strategic importance has diminished. Being now available and affordable to all, IT has evolved from potentially strategic resources into commodity factors of production. Jumping to a New Experience Curve (1) Strategically using IT to work outward is highly competitive and innovative Technology updates occur frequently, forming a set of connected experience curves Each curve represents a new technology or combination thereof in a product or service as well as in its manufacture and/or support Moving to a new curve requires substantial investment in a new technology Establishing Close and Tight Relationships (2) 3 level of systems integration between companies Loose: provide ad hoc access to internal information Close: two parties exchange information in a formal manner Business processes remain distinct Processes are distinct, but some tasks are handled jointly Tight: two parties share at least one business process High volumes of possibly confidential data are exchanged Chapter 4. IS Planning Tradition Strategy Making Step 1 Business Strategy Where is the •Business decision business •Objectives and direction going and •Change why? Supports business Step 2 What is required? Direction For IS System Strategy •Business-based •Demand-oriented •Application-focused Infrastructure and services Assumptions: Needs and priorities IT Strategy Step 3 How can it •Activity-based be delivered? •Supply-oriented •Technology-focused The future can be predicted Time is available to do these 3 parts IS supports and follows the business Top management knows best (broadest view of firm) Company: like an "Army" Today's Sense-and-Response Approach (1) Let strategies unfold rather than plan them: A sense-and-respond approach when predictions are risky Sense a new opportunity and immediately respond by testing it Myriad of small experiments Old-era strategy One big choice, long commitment Time New-era strategy Many small choices, short commitments Time Strategic envelop Stages of Growth Richard Nolan et al observed four stages in the introduction and assimilations of a new technology Early Successes Contagion Interest grows rapidly; growth is uncontrolled; learning period for the field Control Increased interest and experimentation Efforts begun toward cost reduction and standardization Integration Dominant design mastered; setting the stage for newer technology Five Forces Analysis of the Internet The Internet tends to dampen the profitability of industries Increases the bargaining power of buyers Decreases barriers to entry Increases the bargaining power of suppliers Increases the threat of substitute products and services Intensifies rivalry among competitors Success depends on offering distinct value Firms should focus on their strategic position in an industry and how they will maintain profitability Chapter 5. Distributed Systems Definition: IT Architecture VS. IT Infrastructure An IT architecture is a blueprint showing how the parts will interact and interrelate. System, information, departments... Multiplicity of structures and views An IT infrastructure is the implementation of an architecture. processors, software, databases, electronic links, data centers, standards, skills, electronic processes... We now tend to divide computing into applications and infrastructures Open Standards Open standards provide foundations for Interconnectivity Interoperability Open standards after 1990s OSI Reference Model SQL API: standardized interface TCP/IP Internet---Topology and Reliability Internet is a scale-free network A small number of nodes have a large number of links while the majority of nodes only have a small number of links Internet is robust to random failures, but vulnerable to targeted attacks Client-Server Systems (2) ---Distribution of Processing Distributed Presentation Remote Presentation Distributed Function Remote Data Management Distributed Database Data Management Data Management Data Management Data Management Data Management Application Function Application Function Application Function Presentation Server Client Presentation Data Management Presentation Application Function Application Function Application Function Presentation Presentation Presentation Client-Server Systems (7) ---Three-tier Client-Server Style Server (usually DB server) connected to the network via one or more servers, and sometimes directly as well Multiple specialized servers, some possibly dedicated to middleware (application servers) Internet or LANs Clients, some of which may be portable Peer-to-Peer Computing Concept How does P2P computing adapt to Internet computing environment, especially in content distributation Web Services Concept Foundations for Web Services Service directory: UDDI Service description: WSDL Service interaction: SOAP Format description: XML Schema Data format: XML Communication Protocol: HTTP Communication Network: Internet Service-Oriented Architecture Concept, model Features: loosely-coupled, coarse-grained and standards-based Registry ② Discover Service Client Grid Computing A computational grid is a hardware and software infrastructure that provides dependable, consistent, pervasive, and inexpensive access to high-end computational capabilities Grid is a generalized network computing system that is supposed to scale to Internet levels and handle data and computation seamlessly Chapter 6. Managing Telecomms Transformation of Telecom Industry AT&T deregulation in 1984 The last mile problem for RBOCs in 1990s Divest it LECs (RBOCs) in return for a chance in Internet services industry A Fire-hose-to-straw gap tbps (1012) in backbones VS. 56k or 1.2m in the last mile RBOCs then became ILECs, and there came new competitors CLECs (competitive LECS) ILECs bundled local phone access with Internet access CLECs came up with new connection options Cable modems, optical fiber, wireless, satellite… Telecom Technologies and Their Speeds Bits Per Second Technologies 1011-1012 Optical fiber 1010 Optical wireless local loop(20G), WMAN (100G) 109 Microwave LANs (1.5G-2.0G), Gigabit Ethernet (1G), WMAN (24g) 108 ATM (155-622M), Faster Ethernet (100M) 107 Frame relay (10M), Ethernet (10M), WLANs(10M), cable modem (10M), Wi-Fi (11-54M) 106 Stationary 3G (2M), DSL(1.5-7M), WiMax (1.5-10M) 105 Mobile 3G (384k), ISDN (128k) 104 Modems (56k), 2.5G(57k) 103 2G (9.6-14.4k) The Internet is the Network of Choice (4) Intranet Internet technology used inside an enterprise Extranet Internet technology used to connect trading partners, customers, suppliers etc. Public Website Extranet E Intranet OSI Reference Model Important protocols 7 Application Layer HTTP 6 Presentation Layer NetBIOS 5 Session Layer SSL 4 Transport Layer TCP 3 Network Layer IP, X.25 2 Data Link Layer Ethernet, Token ring, FDDI, ISDN, ATM, Frame relay Physical Layer 10BaseT, twisted pair, fiberoptic cable 1 Wireless Networks Licensed VS. Unlicensed Frequencies Some frequencies of the radio spectrum are licensed by governments for specific purposes; others are not Devices that tap unlicensed frequencies are cheaper No big licensing fees Greater competition, more innovation and faster changes Possibility of collision between signals "Telecoms Crash" Auctions of the 3g radio spectrum in Germany and Britain at the beginning of 2000. The nature of the auctions, was to offer a limited number of licenses Although one similar auction in the USA had failed disastrously the year before. 3G also requires an infrastructure development measured in billions of dollars This put the telephone operators in a difficult position, as diabetics being forced to bid for insulin. The stock market lost confidence (dot-com crash), influencing the credit rating of the operators Within a year 100,000 jobs were lost in telecoms in Europe (30,000 in UK) Subsequent government auctions of the 3g spectrum were met with low bids The Role of the IS Department Three roles of IS department Create the telecom architecture Connectivity Interoperability Operate the network Stay current with the technology