* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CDMA Network
TV Everywhere wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
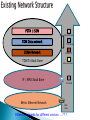
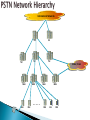
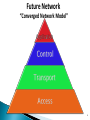
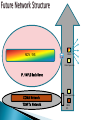
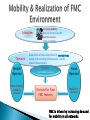
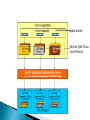
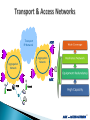
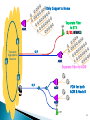
By Tilak de Silva Chief Global & Network Officer Sri Lanka Telecom Ltd. Overall functional architecture of an implementable NGN Functional architecture for supporting mobility & realization of FMC environment Architectural point view of “QoS” & “network performance” to meet NGN service requirement from users & providers Relevance of IPv6 for NGN transportation NGN Access networks Underline network support capabilities essential for successful NGN GSM Network WiMAX Network DSL Network MPLS Network MEN Network DATA Network CDMA Network PSTN Network Multiple Platform based Vertical Network Architecture Services 3 PSTN / ISDN MSU/RSU/ELU TDM Data network CDMA Network TDM Tx Back Bone IP / MPLS Back Bone Metro Ethernet Network Data Node CDMA BTS Other Operators IP-DSLAM MEN Node Different networks for different services … ? ? ? International Networks TSC ISC TSC TSC CDMA/ PLMN MSU RSU ISC MSU RSU ..... MSU RSU MSU ELU RSU Future Network “Converged Network Model” 6 Migration & Limitations No vendor support Un repairable hardware/ software faults Expansion/ Upgrading not possible Large customer base Limited VAS capacity End of Life Time No/ Limited CLI capacity Frequent failures Supports only R2 signaling Technology already obsolete CDR not properly generated for Value Added Services Customer demand for new features 7 Why NGN…….. Pave the path to fixed Mobile convergence Cost effective Operation and Maintenance by means of High system centralized capabilities (Call network handling, management Rapid subscriber Less cost for system capacity, traffic transport network deployment of handling, etc…..) (MPLS backbone) new third party applications due due to Availability of new transportation of to open services. (Unified architecture packets messaging, IP Centrex/Hosted PBX, etc…) High One network competitiveness for all services due to large (Voice, Video Less OPEX number of & Data) manufactures Less CAPEX …???? 8 NGN /IMS MSAN Other Operators IP / MPLS Back Bone CDMA Network TDM Tx Network Other Operators CDMA BTS ALL IP + Voice TDM → ALL IP Control Layer ALL IP → FMC Softswitch ALL IP + Multimedia ALL IP + FMC IMS PSTN Transport Layer MPLS IP OSS / BSS Convergence Servicebased IP QoS Access Layer Database Convergence MSAN + DSLAM MSAN + DSLAM + HGW IAD / SIP Phone Time of maturity and popularity Industry Chain Ready NGN architecture defined in ITU-T Rec. Y.2012 IMS Functional Architecture Model NGN architecture supports the delivery of: PSTN and ISDN replacement Multimedia services Content delivery services Video streaming Broadcasting etc. ITU-T Rec. Y.2012 Service Stratum ◦ Application Support Function and Service Support Function Gateway Authentication & Authorization ◦ Service Control Function Resource Control Registration Authentication & Authorization Transport Stratum ◦ Transport Control Function IP connectivity services to NGN users Network Attachment Control Functions (NACF) Resource and Admission Control Functions (RACF) To get desired QoS for communication To get permission to access certain resources ◦ Transport Function Core Transport Functions Access Transport Functions Management Function ◦ Manage the NGN network in order to provide NGN services with the expected Quality, Security and Reliability. Subscriber Operator Mobile Operator Home location in Mobile network Increasing mobility Only one contract /one bill Seamless services home zone billing Acquisition of new subscribers by new services mainly with existing infrastructure / partly shared infrastructure Operator Fixed & Mobile services Fixed Operator Demand for New FMC features Mobility in network FMC is driven by increasing demand for mobility in all networks Is concerned with the provision of network and service capabilities which are independent of the access technique Does not necessarily imply physical convergence of networks Is concerned with the development of converged network capabilities and supporting standards to offer consistent services, that may be used via fixed or mobile access to fixed or mobile, public or private networks. An important feature of FMC is the separation of the subscriptions and services from individual access points and terminals and The possibility of internetwork roaming using the same consistent set of services An Operator will regard the “Customer‘s view“ as essential; (e.g. will take into account QoS classification) Classes: BEST HIGH MEDIUM BEST EFFORT : : : : Better than today‘s PSTN/ISDN Equivalent to today‘s PSTN/ISDN Equivalent to today‘s wireless Networks Significantly impaired but usable Applications Service QoS Class and Priority PSTN to NGN Migration Services Session Control Transport Access Session Control Platform with Enriched Features Reliable Transport Network in Higher Capacities Widely Spreaded Access Networks 20 Transport & Access Networks Transport IP Network Aggregation Network Aggregation Network PON NodeB WiMAX 21 Only Copper to Home Separate Fiber to BTS (2/3G,WiMAX) O/F Transport / Aggregation Network Separate Fiber to AGW O/F PON OLT PON for both AGW & Node B 22 IP V6 IPv6 is emerging to form the basis of the NGNs and well-defined IPv6 suite will provides considerable flexibility to NGN by ◦ Improving network provisioning and operations, as well as Services to be offered to the NGN providers and users. IP-based networks relevant to NGN can be classified into ◦ ‘IPv6-based NGN’, ‘IPv4-based NGN’, ‘IPv6-based non-NGN’, ‘IPv4-based non-NGN’ Addressing schemes, QoS, Security and Mobility are the key features of IPv6 which may significantly impact on NGN Overview of IPv6-based NGN IP V6 IPv6 to NGN ◦ Enhanced service capabilities Enables congestion/flow control using additional QoS information such as flow label, etc. The flow label field of IPv6 header enables IPv6 flow identification independently of transport layer protocols ◦ Any-to-any IP connectivity IPv6 offers the advantages of localizing traffic with unique local addresses, while making some devices globally reachable by assigning addresses which are scoped globally ◦ Self-organization and service discovery using autoconfiguration Address auto-configuration of IPv6 protocol will facilitate NGNs to support dynamic address assignments and multiple user/network identities ◦ Multi-homing using IPv6 addressing IPv6 can handle multiple heterogeneous access interfaces and/or multiple IPv6 addresses through single or multiple access interfaces. Multi-homing can provide redundancy and fault tolerance