* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 22 Bootstrap and Auto configuration (DHCP)
Survey
Document related concepts
Server Message Block wikipedia , lookup
SIP extensions for the IP Multimedia Subsystem wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Remote Desktop Services wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
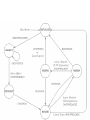
Chapter 22 Bootstrap and Auto configuration (DHCP) History of Bootstrap -Bootstrap is used to assign IP address to the computer. -Constant changes in the protocols for assignment of IP address has made tremendous changes in network administration. -Changes are : RARP BOOTP DHCP -As far as DHCP is concern, it uses UDP and IP both as DHCP follows client server architecture. In CS architecture, client starts communication by sending “bootstrap request” to the server and server will respond which includes IP address, router address and name server address. DHCP includes “options” field in reply to the request. Using IP to determine an IP address Any limited broadcast IP address (all 1’s) is used for providing IP address to the computer. UDP protocol is used to carry message from one terminal to another terminal. HOW? DHCP UDP IP Any terminal which doesn’t know its IP address, so for the IP address it sends DHCP request to Broadcast Address. Any destination will not get the IP address on request than it broadcast the request again within the network. DHCP Retransmission Policy In any client server architecture, DHCP has major responsibilities regarding client. For sending any request UDP will use IP. So to remove delay of message, lost of message, remove duplication, client includes checksum. Checksum is useful to avoid any bit corruption in message. Request and Reply both sent with “do not fragment” fields to reduce the occupancy of memory. - Timeout and Retransmission are two major policies which will take care of any datagram and avoid datagram loss. Timer starts when request is sent and if there will not be any reply from destination the sender sends the request again and starts the timer. So timer and retransmission are two policies which are used to send request from one sender to destination and vice versa. Resulting collisions are avoided with the help of random delay of request. The DHCP Message Format Type of message will be known from OP field by 1 for request and 2 for reply. HTYPE for hardware type and HLEN hardware address length. HOPS field include 0, when client receives request and pass it to another client. DHCP increment the HOPS count. Transaction ID, where client match the response with request. Whenever the client start, the SECOND field counts the number of seconds. Client IP address: - Gives client computer IP address. Server IP address: This information is filled by the client computer. If it is zero, any server will reply to the client request. If non zero, than some specify server will reply to the request. Server’s reply to the client comes in YOUR IP ADDRESS field. FLAG field will control every request and reply. It is of 16 bits. 0 B MUST BE ZERO 15 B is a broadcast request. It is a broadcast request as the client doesn’t have any IP address when it boots… Anytime the IP address of destination doesn’t match with the IP address which is broadcasted by any client, than the datagram which was sent will be discarded. DHCP is having features like BOOT FILE NAME.(it is for diskless systems). Here no need to encode any specific files as to do in other diskless client machines.. OPTIONS : - uses Type – Length – Value (TLV) Need for Dynamic Configuration For address assignment, DHCP will allow any computer to obtain the IP address dynamically. Any request from the client to server for IP address, the server will assign the IP address to that client. Assignment of IP address is of three types: - •Manual Configuration •Auto Configuration •Dynamic Configuration. In Manual Configuration, the manager configures a specific address for a computer. In auto configuration, the IP address is permanently assign to any computer when it connects to the network. In Dynamic Configuration, the assignment of an IP address is for limited period of time. DHCP Lease Concept DHCP server will lease the address to the client for finite period of time is called DHCP Lease. The time of lease will be allocated by the server. This allocation will be done at the time of assignment of address by the server to the client. When the lease period will finished, there are two ways for client to proceed further. 1. Renew the lease period and 2. Stop to use the address. Optimal time is depend on particular network and needs of particular host. Multiple Addresses And Relays Relay agent is a router, it receives a broadcast request from client and forward it to the server. When a client sends multiple request to the server, the server will identify the client by “client identifier”. Server is able to differentiate the request from the client and also from reply agent. ADDRESS ACQUISITION STATES There are six states, around which the client always present… •After booting client enters in to the INITIALIZE state, and client connect to all available DHCP servers. For connection with the DHCP server, client will broadcast DHCPDISCOVER message and moves to the SELECT state. This DHCPDISCOVER message go in UDP datagram and in response to this message particular server will respond to the client by sending DHCPOFFER response, All the DHCPOFFER are collect by SELECT state. The DHCPOFFER stores all the configuration information of the client including the IP address which was requested by the client. Client will select the one of the response for a lease, so for that client sends the server a DHCPREQUEST message and enters in to the REQUEST state. DHCPACK will send the acknowledgement of the receipt of the request. Once the acknowledgement arrives the client moves to the BOUND state, where the client uses the address. Early Lease Termination Client is always in BOUND state. Client stores its IP address (assignment by DHCP server) in secondary storage device. This storage of IP address is used at the next booting process by the client (for sending the same IP address request to the server) When the address is not needed, DHCP permits the client to terminate the lease without waiting for the lease to terminate. To terminate the lease the client DHCPRELEASE message to the server. sends Once release message is send, other datagram will not be sent further. After sending DHCPRELEASE the client will leave the BOUND state. Lease Renewal State Client in BOUND state will set three different timers. Timer helps for renewal, rebinding and expiration. The allotment of timer is done at the time of assignment of IP address to the client. Default timer time is one-half of the total lease time. When ever the first timer expires the client will process for renewal of the lease. DHCPREQUEST message send from the server to the client who needs the lease to be renewed. Now client moves to RENEW state. RENEWAL is accepted in two different ways, one is to stop using address and second is it approved for continuous use of it. Once it is approved that client sends DHCPACK and moves to BOUND state & If it is not approved than client will send DHCPNACK, which will stop the client to use it and moves to the INITIALIZE state. Client always wait for the response in RENEW state. When the client enters in the BOUND state the second timers starts, this second timer will expire after 87.5% timer period of lease time and moves the client from RENEW state to REBIND state. DHCP Options and Message Type DHCP always kept the message in BOOTP format, and use the OPTIONS field to identify the message. (in DHCP) CODE (53) LENGTH (1) TYPE (1-7) Type field from 1 to 7 will describe DHCP message type…