* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ground Shaking Criteria 1997 Codes and Beyond
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Wireless USB wikipedia , lookup
Policies promoting wireless broadband in the United States wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.11 wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
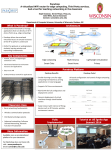
Field Testing & Monitoring of Structural Performance High Performance Mobile Network Steve Kang, Systems Administrator University of California, Los Angeles NSF Site Visit June 17-18, 2002 High Performance Mobile Network 2 Mobile Command Center [Gantt tasks 41-44] Originally data acquisition trailer – 8’ x 16’ Upgraded to self propelled vehicle – 2003 Chevy Crew cab – 8’ x 15’ van body 3 Mobile Command Center Self propelled vehicle – Maneuverability – Faster deployment (aftershock monitoring) – Lower operation cost vs. renting a pickup (~$12k/yr) – Storage cabinets for data loggers 4 Overhead View Rear Entry Rack Mount 5 Streetside View 6 Curbside View 7 Pictures (June 11, 2003) 8 LAN & Telepresence System [Gantt tasks 48-62] Comprised of two separate networks – Field-LAN Mobile command center Wireless telemetry – Campus-LAN Connection to NEESgrid services via the campus backbone and Internet2 at Gbps 9 Networking Equipment Wireless Equipment – Enterasys RoamAbout wireless bundle including access points, wireless adapters and antennas Routers/Switches – Cisco 2651XM router – Cisco 3550-12T gigabit switches – 1000Base-T network cards for Sun and PCbased servers 10 Field-LAN 11 Wireless Network Data Concentrator Sensor stations Wireless Backbone Workgroup Access points 12 Field-LAN Throughput Wireless Network – Nominally 54 Mbps Intra-Mobile Command Center – Server to server 1 Gbps – MCC network can be connected to Campus-LAN (hardwired) for Gbps connectivity Satellite uplink – ~1.544 Mbps 13 Satellite time costs Desired throughput 1.28 Mbps up Low end solution (Hughes/DirectPC) – Hardware costs - < $3000 – Operations ~$100/month – Shared bandwidth, w/ nominal 56k up Medium end solution (Tachyon, Inc.) – Hardware costs - $20k to 100k – Operations - $2000/month – Shared bandwidth, w/ nominal 256k up & 1.544 Mbps down 14 Satellite time costs High end solution – Stratos Hardware costs - $200k Operations – $19k/month for unlimited minutes Dedicated bandwidth of 1.544 Mbps up, purchase FCC license Stratos developing new pricing model – April 03 – Globecast North America Hardware costs - ~$150k-200k Operations - $5k/month for 2500 minutes Dedicated bandwidth of 1.544 Mbps up & 512 kbps down 15 Telepresence Equipment Digital video camera (2x) Axis 2400 video server (2x) Axis 2191 audio server Telepresence server 16 Appendix Wireless Networking Benefits – Eliminates high cost of wiring and rewiring – Network access in places that are difficult or impossible to wire – Easier installation than wired networks – Flexibility and mobility of clients – Potential range of 1500’ line-of-sight 18 Wireless Networking Disadvantages – Interference cuts down on throughput, range and reliability – Many forms of interference Fog, rain, dust storms, concrete, mirrors, lead, other wireless devices, other wireless networks – Security issues – Networks not properly secured pose potential threats from hackers 19 Wireless Networking Overcoming the disadvantages – Throughput Although 802.11b has a maximum of 11Mbps throughput (5-6Mbps actual), 802.11a provides for increased throughput, 4-5 times as much actual Increased throughput should allow for multimedia applications like streaming video 20 Wireless Networking IEEE 802.11b IEEE 802.11a Frequency range 2.40 GHz (ISM band) 5.15 to 5.35 GHz (UNII band) Data rate 1 to 11 Mbps 6 to 54 Mbps Range in free space (dependent on the data rate) 120 meters (11 Mbit) to 460 meters (1 Mbit) 30 (54 Mbit) to 300 meters (6 Mbit) Range in rooms (dependent on the data rate) 30 (11 Mbit) to 90 meters (1 Mbit) 12 meters (54 Mbit) to 90 meters (6 Mbit) Number of independent channels 3 8 Number of users supported per Access Point 192 512 Application Data Multimedia Protocol TCP/IP 21 Wireless Networking Overcoming the disadvantages – Interference Bridges and signal boosters can be used to strengthen the signal at various points throughout the network SOHO retail devices can boost signals around 20-30%, although commercial devices can boost the signal to range of 5 miles 802.11a transmits at a higher frequency, making it incompatible (therefore, non-interfering) with 802.11b and other wireless devices 22 Wireless Networking – Bridge Used to extend the distance of an access point It communicates wirelessly with both access points and wireless adapters, and is used to connect wireless segments to wireless segments It takes the communication from access points and rebroadcasts it to wireless adapters, and vice versa 23 Wireless Networking Overcoming the disadvantages – Security WEP (Wired-Equivalent Protection) can be used to secure the network using a minimum 64bit128bit encryption for 802.11b and up to 256bit encryption for 802.11a devices 24 Wireless Networking – WEP (Wired-Equivalent Protection) WEP is the security component of basic wireless networking WEP prevents unauthorized users from gaining access to your network via wireless connection by encrypting transmitted data For WEP to work, it must be configured on both the access point and on the wireless adapter(s) and the settings must match Both 64bit and 128bit WEP encryption are typically offered on 802.11b wireless products 25 Cisco Catalyst 3550-12T 12 port Multilayer Switch The Catalyst 3550-12T Switch features ten 10/100/1000BaseT ports and two Gigabit Interface Converter (GBIC)-based 1000BaseX ports for connectivity to other media ($10,000) Gigabit speeds over category 5e copper wire makes for simple integration to any existing network 26 Cisco 2651XM High Performance 10/100 Modular Router 10/100BASE-TX Modular access router with one Network Module (NM) slot, two WAN Interface Card (WIC) slots, and one Advanced Integration Module (AIM) slot ($3,300) 2 - Ethernet 10BaseT/100Base-TX - RJ-45 ports Serial WAN interface card ($300-500) 27 Cisco 2651XM High Performance 10/100 Modular Router 1 x Motorola MPC860 80 MHz RISC processor 64MB RAM (installed) / 128MB RAM (maximum) 16MB Flash memory (installed) / 48MB Flash memory (maximum) 40 kpps maximum throughput 28 Intel® PRO/1000 XT PCI Server Adapter Intel® PRO/1000 XT PCI Server Adapter reduces bottlenecks and increases bandwidth ($200) 10/100/1000 autonegotiation lets you automatically run at the speed of the network Gigabit over cat 5 cables allows for simple scalability 29 Sun GigaSwift Ethernet UTP Adapter The Sun GigaSwift Ethernet UTP PCI Adapter provides high bandwidth connections through copper media at gigabit speed ($1500) Works with 10/100 networks as well Compatible with all Ultra and Blade workstations as well as Enterprise and Netra servers 30 Enterasys RoamAbout The RoamAbout family is based on two key components: the Access Point 2000 and an 11 Mbps 2.4 GHz Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) wireless Ethernet PC Card Yagi and omnidirectional antennas are used to shoot the signal from the building to the MCC 31