* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 4 PowerPoint
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Policies promoting wireless broadband in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
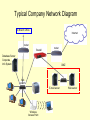
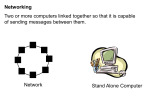
Chapter 4 Highlights – Computer Networks Why network or connect computers? Share Data/Files Share Hardware e.g. Printers, Scanners Access Company Information Systems Share Internet Connection Communicate e.g. Telephone (VOIP), Chat, E-mail, Video Conference) In the home, you can share entertainment devices LAN = Local Area Network In the 1980’s companies began networking their computers. Various topologies and LAN protocols were used. The star topology using Ethernet has become the standard today. Star Topology Typical of 10BaseT Ethernet 100BaseT Ethernet Gigabit Ethernet Categories of Networks Local area network (LAN): covers a relatively small geographical area, such as a home, office building, or school. Most popular LAN protocol is Ethernet running in a star configuration. Wide area network (WAN): covers a large geographical area. A WAN is often used to connect two or more LANS. Popular WAN protocols are T1 and T3 lines, ATM, and frame relay Metropolitan area network (MAN): Some cities offer public networks for police, fire, or WiFi for all residents. Personal area network (PAN): A term that is sometimes used for an individual's network of personal devices such their PC, phone, headset, and printer. Intranet: A private network for a company that is set up like the Internet. This term often refers to web sites that are only accessible internally at a company. VPN: A private secure network that uses the Internet for data communication. Branch offices for a large company may set up an VPN over the Internet to communicate to the parent office. This is cheaper than purchasing expensive private data lines. Security and encryption is essential since the Internet is a public network. Data Transmission Analog versus Digital – In analog transmission, information is in the form of waves. In digital transmission, information is sent as binary 1’s and 0’s. Television broadcasts are currently converting from analog to digital (HDTV). Vinyl records stored music as analog sound waves. CD’s store music digitally. Bandwidth – Is the speed of data communication. It is usually measured in bits/second. Q: If your Internet connection is 2 Mbps, how long would it take to download a 2 MB file? A: We need to convert bytes to bits: 2 Million Bytes = 16 Million Bits. At 2 Million bits/second, it would take 8 seconds to xfer 16 Million bits. Q: If your Internet connection is 256 Kbps, how long would it take to download a 1 MB file? Circuit-Switched vs. Packet-Switched The telephone network is a circuit-switched network – you have a dedicated path between you and the person you are talking to. The Internet is packetswitched. Everything sent over the Internet is broken up into small packets of data and sent on their way. Protocols A protocol is the set of rules that defines how devices communicate in a network. For Internet communication, TCP/IP is used. This protocol is how you open web sites, send e-mail, etc. Other protocols define how data travels around a LAN (e.g. Ethernet), WAN, or a wireless network (e.g. WiFi). Ethernet - LANs Ethernet is most popular LAN protocol. It is used to connect computers at businesses as well as at your home. In the 1980’s, Ethernet LANs used coax cable in a bus configuration, but now they use twisted pair wire in a star configuration. Each network adapter has a hard-coded MAC address. To see this address on the Ethernet adapter on a PC, open a command prompt and type ipconfig /all Windows lists this as the “physical address”. Cell Phone Transmission 1G – The original cell phones (1980’s) were analog transmission 2G – Cell phones switched to digital transmission (1990’s). This added data support such as txt messages. 3G – We are now switching to 3G cell phone service which offers high-speed Internet. WiFi – (802.11) WiFi can be used to create an entirely wireless network, or to add wireless capabilities to an existing wired Ethernet network. WiFi Hotspots refer to public places that users can connect their laptops. For example Starbucks, or at Eastfield. Limitations: A WiFi network is designed for no more than 300 feet in distance and no roaming (like cell phones). WiFi Standards: 802.11b = original WiFi standard at 11 Mbps 802.11g = current WiFi standard at 54 Mbps 802.11n = newest WiFi standard at 300 Mbps Wireless Access Point Wireless - BlueTooth Bluetooth was designed for wirelessly connecting personal consumer devices and peripherals. Bluetooth works over short distances, typically less than 30 feet. Communication speed is less than 1 Mbps. Pairs of devices establish a trusted relationship by the user entering a shared passkey or PIN. Trusted devices may encrypt the data that they exchange over the air so that no one can listen in. Growing in popularity is using bluetooth equipped phones to make payments. Summary of Wireless Protocols Typical Company Network Diagram To Branch Office Internet router firewall router Database Server Corporate Info System DMZ hub switch E-mail server Wireless Access Point Web server