* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download IT 601: Mobile Computing
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Policies promoting wireless broadband in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.11 wikipedia , lookup
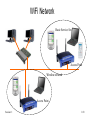
IT 601: Mobile Computing Session 1 Introduction Prof. Anirudha Sahoo IIT Bombay Session: 1 0.1 Course Evaluation •Home assignment – 10% •Pop Quizzes – 5% •MidSem – 25% •Project – 25% •EndSem – 35% Session: 1 0.2 Course Evaluation •Academic dishonesty (in any form) will not be tolerated – will result in FF grade •Attendance : as per Institute rules •Audit Requirements – attendance : as per Institute rules – must appear midsem and endsem exams – may exchange endsem with project – take quiz/homework – at least CC grade in the evaluation Session: 1 0.3 Prerequisite • Basic Computer Networks –Sound knowledge in traditional MAC protocols –IP routing protocols –TCP • Basics of Probability theory and queuing theory Session: 1 0.4 References • Mobile Communications – J. Schiller, Pearson education publishing 2003 • Wireless Communications and Networks – W. Stallings, Pearson education publishing 2002 •Technical papers – will be given out throughout the course Session: 1 0.5 Introduction • What is different in wireless network? – Bandwidth – Error rate – Media – Signal strength (fading) – MAC – Mobility – Security Session: 1 0.6 Wireless networks • Two types – Voice network • Cellular systems (GSM, CDMA etc.) – Data network • WiFi, HiperLAN • Networks are moving towards an integrated network – GPRS – Voice over WiFi Session: 1 0.7 Physical Layer (PHY) • Binary (digital) data transmitted over airwave • Requires antenna • characterized by transmission range, power, modulation scheme, frequency range Session: 1 0.8 MAC Layer • How wireless stations share the air medium and avoid contention to transmit data successfully • “listen before you speak” or “speak at predetermined interval” • Unique problems – Hidden node – Exposed node Session: 1 0.9 Network Layer • • • • Responsible for facilitating multihop communication Need to run some routing protocol Traditional routing protocols may not work efficiently Mobility at IP layer Session: 1 0.10 Transport Layer • Reliable Transport such as TCP may not work well in wireless medium – TCP inherently assumes that packet loss is due to congestion – Needs modification for wireless network Session: 1 0.11 802.16 120Mbps Source: Matt Welsh, Harvard University Session: 1 0.12 WiFi Network Basic Service Set Access Point Wireline network g Access Point Session: 1 0.13 WiFi Network • • • • 802.11b and 802.11g Use 2.4 GHz ISM band 802.11b : 11 Mbps 802.11g : 54 Mbps 802.11a : uses 5 GHz band: 54Mbps Session: 1 0.14 Bluetooth • Short range (10m),moderate data rate (720kbps) for creating an adhoc network between personal devices • One master and upto 7 slaves in a piconet • Master controls the transmission schedules of all the devices – TDMA scheduling • Frequency hopping used to avoid interference with other piconets PICONET – 79 channels in the 2.4GHz ISM band, with 1 MHz spacing – Frequency hopping at 1600 hops/s Session: 1 0.15