* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download LAB1-Overview
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
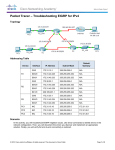
NETW905 – Introduction Lab Network Fundamentals – Chapter 6 [6.4 & 6.5] Network Fundamentals – Chapter 11 Version 4.0 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 1 Objectives Determine the network portion of the host address and explain the role of the subnet mask in dividing networks (Basic Subnetting). Define the role of the Internetwork Operating System (IOS). Use Cisco CLI commands to perform basic router and switch configuration and verification. Given a network addressing scheme, select, apply, and verify appropriate addressing parameters to a host. Use common utilities to verify network connectivity between hosts. Use common utilities to establish a relative performance baseline for the network. © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 2 Classify and Define IPv4 Addresses Name the three types of addresses in the network and describe the purpose of each type © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 3 Classify and Define IPv4 Addresses Determine the network, broadcast and host addresses for a given address and prefix combination © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 4 Classify and Define IPv4 Addresses Name the three types of communication in the Network Layer and describe the characteristics of each type © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 5 Classify and Define IPv4 Addresses Identify the historic method for assigning addresses and the issues associated with the method © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 6 Determine the network portion of the host address and the role of the subnet mask Describe how the subnet mask is used to create and specify the network and host portions of an IP address © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 7 Determine the network portion of the host address and the role of the subnet mask Use the subnet mask and ANDing process to extract the network address from the IP address © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 8 Determine the network portion of the host address and the role of the subnet mask Use ANDing logic to determine an outcome © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 9 Determine the network portion of the host address and the role of the subnet mask Observe the steps in the ANDing of an IPv4 host address and subnet mask © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 10 Calculating Addresses Use the subnet mask to divide a network into smaller networks and describe the implications of dividing networks for network planners © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 11 Calculating Addresses Extract network addresses from host addresses using the subnet mask © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 12 Calculating Addresses Calculate the number of hosts in a network range given an address and subnet mask © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 13 Calculating Addresses Given a subnet address and subnet mask, calculate the network address, host addresses and broadcast address © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 14 Calculating Addresses Given a pool of addresses and masks, assign a host parameter with address, mask and gateway © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 15 Calculating Addresses Given a diagram of a multi-layered network, address range, number of hosts in each network and the ranges for each network, create a network scheme that assigns addressing ranges to each network © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 16 Role of Internetwork Operating System (IOS) Identify several classes of devices that have IOS embedded © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 17 Role of Internetwork Operating System (IOS) Define the purpose of startup config © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 18 Role of Internetwork Operating System (IOS) Identify the relationship between IOS and config © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 19 Role of Internetwork Operating System (IOS) Recognize that Cisco IOS is modal and describe the implications of modes © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 20 Role of Internetwork Operating System (IOS) Define the different modes and identify the mode prompts in the CLI © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 21 Role of Internetwork Operating System (IOS) Identify the basic command structure for IOS commands © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 22 Role of Internetwork Operating System (IOS) Identify the types of help and feedback available while using IOS and use these features to get help, take shortcuts and ascertain success © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 23 Role of Internetwork Operating System (IOS) Identify the purpose of the show command and several of its variations © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 24 Role of Internetwork Operating System (IOS) Identify several of the configuration modes, their purpose and their associated prompt © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 25 Role of Internetwork Operating System (IOS) Use the CLI to access various IOS configuration modes on a device © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 26 Use Cisco CLI Commands to Perform Basic Router & Switch Configuration and Verification Explain the reasons for naming devices © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 27 Use Cisco CLI Commands to Perform Basic Router & Switch Configuration and Verification Describe two common approaches to establishing naming conventions © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 28 Use Cisco CLI Commands to Perform Basic Router & Switch Configuration and Verification Based on a diagram, configure host names using the CLI © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 29 Use Cisco CLI Commands to Perform Basic Router & Switch Configuration and Verification Describe the role of passwords in limiting access to device configurations © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 30 Use Cisco CLI Commands to Perform Basic Router & Switch Configuration and Verification Describe several ways in which access to a device configuration can be limited © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 31 Use Cisco CLI Commands to Perform Basic Router & Switch Configuration and Verification Use the CLI to set passwords and add banners to a device © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 32 Use Cisco CLI Commands to Perform Basic Router & Switch Configuration and Verification Trace the steps used to examine the startup config, make changes to config, and replace the startup config with the running config © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 33 Use Cisco CLI Commands to Perform Basic Router & Switch Configuration and Verification Use basic IOS config commands to manage a device. © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 34 Use Cisco CLI Commands to Perform Basic Router & Switch Configuration and Verification Use a text file to backup and restore config settings © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 35 Use Cisco CLI Commands to Perform Basic Router & Switch Configuration and Verification Identify the role of a router in a network. © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 36 Use Cisco CLI Commands to Perform Basic Router & Switch Configuration and Verification Describe the purpose of having multiple interfaces in one router © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 37 Use Cisco CLI Commands to Perform Basic Router & Switch Configuration and Verification Explain the purpose of assigning interface descriptions to a router © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 38 Use Cisco CLI Commands to Perform Basic Router & Switch Configuration and Verification Assign a router interface, assign a meaningful interface description, and enable the interface © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 39 Select, Apply, and Verify Appropriate Addressing Parameters to a Host Given a type of host and a master addressing scheme, trace the steps for assigning host parameters to a host © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 40 Select, Apply, and Verify Appropriate Addressing Parameters to a Host Trace the steps for using ipconfig/ifconfig to verify host parameter assignments and for using ping to test assignments © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 41 Select, Apply, and Verify Appropriate Addressing Parameters to a Host Identify two ways parameters can be assigned to hosts © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 42 Use Common Utilities to Verify Network Connectivity Between Hosts Use the ping command in the CLI to determine if the IP protocol is operational on a local host © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 43 Use Common Utilities to Verify Network Connectivity Between Hosts Use the ping command to determine if the IP protocol is properly bound to an NIC © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 44 Use Common Utilities to Verify Network Connectivity Between Hosts Use the ping command to determine if a host can actively communicate across the local network © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 45 Use Common Utilities to Verify Network Connectivity Between Hosts Use the ping command to verify that the local host can communicate across the internetwork to a given remote host. © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 46 Use Common Utilities to Verify Network Connectivity Between Hosts Identify several conditions that might cause the test to fail © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 47 Use Common Utilities to Verify Network Connectivity Between Hosts Use trace commands to identify network connectivity problem © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 48 Use Common Utilities to Establish a Relative Performance Baseline for the Network Use the output of the ping command, saved into logs, and repeated over time, to establish relative network performance © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 49 Use Common Utilities to Establish a Relative Performance Baseline for the Network Use the output of the traceroute command, saved into logs, and repeated over time, to establish relative network performance © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 50 Use Common Utilities to Establish a Relative Performance Baseline for the Network Trace the steps for verifying the physical addresses of the hosts © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 51 Summary © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 52 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Cisco Public 53