* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Wireless Ethernet ()
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Wireless USB wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.11 wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Policies promoting wireless broadband in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
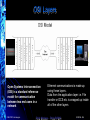
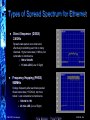
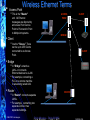
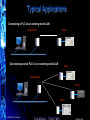
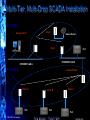
Industrial Wireless Ethernet The New Era of Data Transmission © ELPRO Technologies Think Wireless…Think ELRPO NORCAL ISA OSI Layers Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) is a standard reference model for communication between two end users in a network © ELPRO Technologies Ethernet communications is made up using these layers. Data from the application layer i.e. File transfer or DCS etc. is wrapped up inside all of the other layers Think Wireless…Think ELRPO NORCAL ISA Types of Spread Spectrum for Ethernet Direct Sequence (DSSS) 2.4GHz Spreads data packet over wide band, effectively transmitting each bit on many channels. Higher data rates (>1Mb/s), but vulnerable to interference. 100 to 500mW 1-5 mile LOS (Line of Sight) Frequency Hopping (FHSS) 900MHz Change frequency after each data packet. Slower data rates (115.2Kbd), but more robust. Less vulnerable to interference. 100mW to 1W © ELPRO Technologies 20 mile LOS (Line of Sight) Think Wireless…Think ELRPO NORCAL ISA Power and Antenna’s Under FCC regulations, the Effective Isotropic Radiated Power (EIRP) must be less than 4W. Radio power level of 1Watt, 100mW or 300mW allows the use of gained antennas, which results in greater distances. The drawback of using higher gain antennas is that a radio will pick up more background interference, and is only recommended in interference free areas. 900Mhz, (1W) + 6dB gain antenna = 4W EIRP 900Mhz, (250mW) + 12dB gain antenna = 4W EIRP 2.4 GHz, (100mW) + 16dB gain antenna = 4W EIRP 2.4GHz, (300mW) + 11dB gain antenna = 4W EIRP © ELPRO Technologies Think Wireless…Think ELRPO Main Groups for Wireless Ethernet • 5.8Ghz 802.11a WiFi, Higher performan with more bandwidth, less interference, distance is shorter than 802.11b or g • 2.4GHz WiFi (also known as “802.11b or g”) very high data rates but very short distance • 2.4GHz frequency hopping spread spectrum high data rates but short distance • 900MHz frequency hopping spread spectrum lower data rates but longer distance © ELPRO Technologies Think Wireless…Think ELRPO NORCAL ISA The Common Security Concerns Hacking Industrial Espionage Most common occurrence is when an intruder uses the same modulation or spread spectrum as the target system For protection utilize an AES system with WEP, WPA or WPA2 Make sure products include an embedded or physical firewall Systems should have a data format that has a unique structure with added security features, including network and address validation Data can be encrypted using a high-security encryption algorithm Send messages on an Exception Reporting protocol instead of continuous transmission Jamming With enough resources any wireless system can be jammed. To decrease this be sure the system utilizes wider channels, exception reporting, Frequency Hopping techniques, or with Direct Sequence proper encryption and powerful radios © ELPRO Technologies Think Wireless…Think ELRPO Security • Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) – Lowest level of encrypting data wirelessly with a 64 or 128 bit encryption key. • WiFi Protected Access (WPA) - uses a series of mathematical algorithms to authenticate users. If a user sends unauthorized data in short bursts the system shuts down. • WiFi Protected Access(WPA2) - provides government grade security by implementing the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) FIPS 140-2 compliant Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) encryption algorithm and 802.1x-based authentication. © ELPRO Technologies Think Wireless…Think ELRPO MAC Address Filtering A MAC (Media Access Control) address is a unique identifiers for all Ethernet hardware devices Mac addresses are factory set and are expressed as a 6 bytes string eg. xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx Blacklist is a list of nominated MAC addresses you don’t want to have access to your network Whitelist is a list of nominated MAC addresses that you want to allow access to your network Cannot have both Blacklist and Whitelist © ELPRO Technologies Think Wireless…Think ELRPO Wireless Ethernet Terms • Access Point • This is the “Master” ACCESS POINT unit. All Ethernet messages are directed by an Access Point Can be Point to Point and/or Point to Multipoint systems. BRIDGE • Client • Are the “Slaves.” There can be up to 255 Clients connected to an Access Point. CLIENT • Bridge • A “Bridge” extends a LAN – or connects Ethernet devices to a LAN. • For example, connecting a PLC on a remote machine to an existing wired LAN. • Router • A “Router” connects separate LAN’s. • For example, connecting two separate LAN’s in two separate buildings. © ELPRO Technologies CLIENT Think Wireless…Think ELRPO ROUTER How Is A Connection Established? Access Point - On start-up begins sending “Beacons” (Link messages) Client Scans for messages from AP and attempts to establish a link with the strongest radio signal Access Point PC Client 1 Client 2 PC Client 3 Client Link Establishment Checks Authentication (System address and Encryption) Request a link (Association), Link LED AP Link LED, Acts as a Master and controls flow of messages © ELPRO Technologies Think Wireless…Think ELRPO … Client N Why Wireless Ethernet? • Massive growth of Wired Ethernet in the last 5 years • Wireless Ethernet is an extension of this growth • Ethernet is well-known, carries multiple applications • Simple IP programming compared I/O Telemetry programming and mapping © ELPRO Technologies Think Wireless…Think ELRPO NORCAL ISA Uses for Wireless Ethernet • Developed for industrial customers & Factory Automation • Process control and automation applications - PLCs, DCS, SCADA, data acquisition, wireless video • Can handle multiple applications simultaneously © ELPRO Technologies Think Wireless…Think ELRPO NORCAL ISA Typical Applications Connecting a PLC to an existing wired LAN Access Point Connecting several PLC’s to an existing wired LAN Client Client Access Point Client Client © ELPRO Technologies Think Wireless…Think ELRPO Applications Most are PLC connections PLC to PLC or PLC to computer Automation industries Pharmaceutical, Manufacturing, Ethernet Enabled Transmitters, Video Security Process Control – Data Loggers, RTU’s, Digital Recorders, Video Security SCADA market Oil & Gas, Water/Waste Water, Irrigation © ELPRO Technologies Think Wireless…Think ELRPO NORCAL ISA Multi-Tier, Multi-Drop SCADA Installation SYSTEM A Access Point 1 Client Device Server Client PLC ETHERNET LAN B ETHERNET LAN A SYSTEM B Access Point 2 Client A PLC © ELPRO Technologies Client B PLC Think Wireless…Think ELRPO Client C PLC Wireless Ethernet Spanning Tree • • The “Spanning Tree Algorithm” function is able to handle network loops and provide redundant paths in networks. Blocks redundant paths until needed. • Each Wireless Bridge OR WIRED ETHERNET has a priority which determines where the node sits in the tree. • When the highest connection point (255) fails the lowest connection point (0) instantly activates to become the main node connection on the network. • There is some overhead in maintaining a network utilizing the Spanning Tree Algorithm. © ELPRO Technologies Think Wireless…Think ELRPO Configuration and Diagnostics Configuration and diagnostics via Web browser (Internet Explorer) – Typically there is an Easy Quick Start Configuration Password protected Configuration and diagnostics accessed remotely via radio link Radio signal, Background noise, and connection diagnostics Most have default configuration by DIP switch Firmware easily upgraded © ELPRO Technologies Think Wireless…Think ELRPO Sample Quick Start Page Quick Start Configuration Menu Item © ELPRO Technologies Think Wireless…Think ELRPO Ethernet Modems in the Real World © ELPRO Technologies Can I browse the internet? 900Mhz, Yes, but expect to get web browsing speeds slightly faster than a 56k dial up modem. 2.4Ghz Yes, used in many commercial applications, Hotels, Airports, etc. Can it do video? 900Mhz - is not designed for that purpose unless utilizing very high compression MPEG 3 or 4. 2.4Ghz – Can display realtime live video, more reliable at 802.11b Think Wireless…Think ELRPO Key To Wireless Ethernet 1. Long Range 900Mhz - Provides much greater distances (up to 60 miles) 2.4Ghz - High power WiFi 802.11 and FHSS. 2. Security 900Mhz - 128 bit AES or 64 bit proprietary encryption 2.4Ghz - 40 or 104 bit WEP, WPA1 or WPA2 (128 bit AES) 3. Reliability 900Mhz - less prone to interference provides better penetration of signal and reflection off of surfaces. 2.4Ghz – Standard 802.11b WiFi, Proven Technology 4. Repeater 900Mhz & 2.4Ghz – Most can double as a Repeater 5. Configuration 900Mhz & 2.4Ghz – Configuration done via embedded web pages that can be accessed remotely. Installation Installation is simple. AP automatically sends out a beacon to detect available clients and establish the link. 6. © ELPRO Technologies Think Wireless…Think ELRPO THANK YOU Wireless Ethernet The New Era of Data Transmission Tim Gross ELPRO Technologies [email protected] 858-822-8818 © ELPRO Technologies Think Wireless…Think ELRPO NORCAL ISA