* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CommunicationsBetwee.. - Home (www.dginter.net)
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Routing in delay-tolerant networking wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
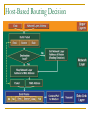
Communication Between Networks How the Internet Got Its Name Addressing to get Out of Town MAC Addresses used for Local Traffic Hierarchical Addressing Needed for internetwork traffic. (Think Zip Codes or Phone #). Network Layer Protocols: IP: Early 1980s, ARPANet, used with TCP IPX: Late 1980s to 90s. 32-bits for network + MAC Routing Layer in DECnet: 1975 – Path Control Layer in SNA Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4) What’s in a Name? All Internet Names (i.e. alllinksvt.com) convert IP Address (using Domain Name Service) 32-bit address, divided into 4 8-bit sections A.B.C.D (i.e. 68.178.232.99) Numbers can be between 0 and 255 (8-bits) Part of the address identifies the Network, the other part identifies the host. Networks and Hosts IP Network Addresses are assigned using IP Address and Subnet mask. Subnet mask defines network and host portions. Example: IP Addr 10 24 250 12 Netmask 255 255 0 O Network 10 24 0 0 0 0 250 12 Host Special IP Addresses Private IP Addresses: Do not Route on Internet 10.0.0.0/8 (i.e. netmask=255.0.0.0) 172.16-32.0.0/16 (i.e. netmask=255.255.0.0) 192.168.x.x/24 (i.e. netmask=255.255.255.0) These Addresses are used on LANS. Routers translate these to routable IP Addresses using Network Address Translation Without Private Address we would be out of IP Addr. Network Address Translation Router translates internal (private) address to external (public) IP Address. Typically this is a many to one translation. All external communication uses Routers WAN Address. Router keeps a table of connections in order to route correctly. Helps security by obscuring LAN IP Addresses You can’t attack what you can’t see. Where do IP Addresses Come From? Globally: Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) Regional: American Registry for Internet Numbers (ARIN) for North America and parts of the Caribbean RIPE Network Coordination Centre (RIPE NCC) for Europe, the Middle East and Central Asia Asia-Pacific Network Information Centre (APNIC) for Asia and the Pacific region Latin American and Caribbean Internet Addresses Registry (LACNIC) for Latin America and parts of the Caribbean region African Network Information Centre (AfriNIC) for Africa Configuring IP Addresses Can be Set Manually IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway DNS 1, DNS2 Can be set by Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Server. A range of LAN addresses is set aside DHCP Server “Leases” these out. Host-Based Routing Decision Routers: Getting There from Here Hop by Hop Routing Routers Build Routing Tables Network ID Cost Next Hop Quality of Service Filtering Interface Routed vs Routing Protocols Routed Protocols are protocols that get routed. Web E-mail IPX Routing Protocols define how and what routers share Routing Information Protocol (RIP) Open Shortest Path First (OSP) Cisco Proprietary: IGRP, EIGRP, BRP What do Routers Do? Operational Forward Packets towards destination Access Control (Firewall Functions) Types of Routes Static: non-adaptive, created manually. Distance-Vector RP: Cost calculated for each path Link-State: creates a (flood) map of network Path-Vector Protocol: Good for large inter-domain routing Routing Table