* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Overlay networks
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
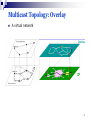
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
UniPro protocol stack wikipedia , lookup
Impact of Topology on Overlay Multicast Suat Mercan Outline Multicast IP Multicast Overlay Multicast Performance Metrics Simulator Topology Generator 2 One to many communication Multiple Unicast Multicast R S R S R R R R 3 Why Multicast Better bandwidth utilization (eliminates traffic redundancy) For the equivalent amount of multicast traffic, the sender needs much less processing power and bandwidth Less host/router processing (reduces server and network load) Multicast packets do not impose as high a rate of bandwidth utilization as unicast packets, so there is a greater possibility that they will arrive almost simultaneously at the receivers 4 IP Multicast Rely on network layer to replicate and deliver data packets to receivers 5 IP Multicast Advantage:efficient data distribution Difficulties: Limited router support Per-group/source state in routers Reliability difficulties Congestion-control difficulties Undefined pricing model Alternative:application layer multicast, to control and maintain an efficient overlay for data transmission 6 Multicast Topology: Overlay A virtual network 7 Multicast Topology: Overlay Flexible Easy to implement Not as efficient as IP Multicast Mesh-based, tree-based 8 Mesh-based multiple paths exist between any sender and receiver pair Quick reconfigurable and robust Excessive message overhead 9 Tree-based Shared Multicast Tree Less control overhead Vulnerable to node failure 10 Overlay techniques 11 Overlay techniques Narada Yoid HostCast Directional Multicast 12 Factors that affect choice of multicast technique Scalability Fault tolerance Performance Quality of service Security 13 Performance Quality of data path Stress Stretch Recovery from failure Control traffic overhead 14 Performance Stress Number of identical packets sent by the protocol over the same link. For IP Multicast there is no redundant packet replication Stretch Resource usage Control Overhead Each member on the overlay exchanges refresh messages with all its peers. 15 Simulation P2P Sim OverSim PlanetSim GPS NS2 16 NS2 Academic project over 10 years old freely distributed, open source Based on C++ and TCL Discrete event simulator NAM, the Network AniMator pre-processing: traffic and topology generators post-processing: simple trace analysis 17 NS2 18 Topology Generation BRITE PLRG INET GT-ITM 19 GT-ITM Georgia Tech Internet Topology Models A collection of routines to generate and analyze graphs using a wide variety of models for internetwork topology Waxman method, Transit-Stub method Included as part of NS-2 20 GT-ITM 21 Our Project Implement ‘Directional Multicast’ in NS-2 Generate different topologies Measure performance metrics under different topologies Analyze how underlying topology affects performance 22 Thank You! 23