* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download IPv6 Security Aspects
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Authentication Protocol wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
SIP extensions for the IP Multimedia Subsystem wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
UniPro protocol stack wikipedia , lookup
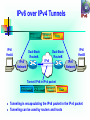
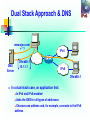
CS 265 – Project IPv6 Security Aspects Surekha Shinde IPv6 Security Aspects Agenda • • • • • • • Introduction to IPv6 IPv4 and IPv6 Comparison Current issues in IPv4 IPv6 solutions for IPv4 issues New issues of new protocol Hacking Tools Conclusion Introduction to IPv6 • Why IPv6 • IPv6 Important features : Wish-list • Faster Packet Processing • Enhanced QOS • Improved Security • Greater protocol Flexibility • Dual-Stack approach The IPv6 Header 40 Octets, 8 fields 0 4 Version 12 Class 16 24 31 Flow Label Payload Length Next Header 128 bit Source Address 128 bit Destination Address Hop Limit The IPv4 Header 20 octets + options : 13 fields, including 3 flag bits 0 4 Ver 8 IHL 16 Service Type Identifier Time to Live 24 Total Length Flags Protocol Fragment Offset Header Checksum 32 bit Source Address 32 bit Destination Address Options and Padding Shaded fields are absent from IPv6 header 31 IPv6 Addressing IPv6 Addressing rules are covered by multiples RFC’s Architecture defined by RFC 2373 Address Types are : Unicast : One to One Anycast : One to Nearest Multicast : One to Many Reserved A single interface may be assigned multiple IPv6 addresses of any type (unicast, anycast, multicast) No Broadcast Address -> IPv6 Use Multicast Notation & Abbreviation Notation 128 Bits = 16 bytes = 32 Hex digits 1111110111101100 FDEC : BA98 1111111111111111 : 7654 : 3210 : ADBF : BBFF : 2922 : FFFF Abbreviation Unabbreviated FDEC : BA98 : 0074 : 3210 : 000F : BBFF : 0000 : FFFF Abbreviated Abbreviated FDEC : BA98 : 74 : 3210 : F : BBFF : 0 : FFFF FDEC : 0 : 0 : 0 : 0 : BBFF : 0 : FFFF More Abbreviated FDEC : 00 : BBFF : 0 : FFFF IPv6 Addressing for IPv4 IPv4-Compatible IPv6 Address format 96 Bits 32 Bits 0 IPv4 Address 192.168.10.10 0:0:0:0:0:0 IPv4 Compatible Address = 0:0:0:0:0:0:192.168.10.10 = ::192.168.10.10 IPv4-Mapped IPv6 Address format 80 Bits 0 0:0:0:0:0:0 16 Bits FFFF 32 Bits IPv4 Address 192.168.10.10 IPv4-Mapped Address = 0:0:0:0:0:FFFF:192.168.10.10 IPv6 over IPv4 Tunnels IPv6 Header IPv6 HostA Transport Header Dual-Stack RouterA Data IPv4 IPv6 Network IPv6 HostB Dual-Stack RouterB IPv6 Network Tunnel: IPv6 in IPv4 packet IPv4 Header IPv6 Header Transport Header Data Tunneling is encapsulating the IPv6 packet in the IPv4 packet Tunneling can be used by routers and hosts Dual Stack Approach & DNS www.sjsu.com =*? 3ffe:b00::1 10.1.1.1 DNS Server IPv4 IPv6 3ffe:b00::1 In a dual stack case, an application that: Is IPv4 and IPv6-enabled Asks the DNS for all types of addresses Chooses one address and, for example, connects to the IPv6 address Security Advantages of IPv6 Over IPv4 IPv4 - NAT breaks end-to-end network security IPv6 - Huge address range – No need of NAT IPv4 – IPSEC is Optional IPv6 - Mandatory in v6 IPv4 - Security extension headers(AH,ESP) – Back ported IPv6 - Built-in Security extension headers IPv4 - External Firewalls introduce performance bottlenecks IPv6 - Confidentiality and data integrity without need for additional firewalls Security Advantages of IPv6 Over IPv4 (2) IPv4 - Security issues related to ICMPV4. IPv6 - ICMPV6 uses IPSEC authentication and encryption. IPv4 - No mechanism for resistance to scanning IPv6 - RTS possible only in IPV6 IPV4 - Doesn’t support Auto configuration IPv6 - Built in Auto configuration support Ignorance of network administrator to IPV6 But, Thanks to the transitional efforts of IETF Important Security fields in IPv6 • IPV4 - Security option field and Optional IPSEC • IPV6 - IPSEC part of protocol suite-mandatory IPSEC provides network-level security • IPSEC uses:AH ( Authentication Header) ESP( Encapsulating Security Payload) Header Authentication Header(AH) • Data integrity • Data authentication • Anti-replay protection Next Header Hdr Ext Len Reserved Security Parameters Index (SPI) Sequence Number Authentication Data Fig.- Authentication Header(AH) Packet Format Authentication Header fields • SPI:-Security parameter index • Sequence number field :- Anti-replay protection • Authentication data :- ICV-authentication and data integrity • HMAC(Hash message authentication code)+MD5 & HMAC+SHA-1 • AH supports several authentication algorithms • Prevents IP spoofing attacks • Prevents DOS attacks Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) • Data confidentiality • Data integrity • Data authentication • Anti-replay protection • Authentication applied only to data being encrypted • Optional services-select at least one ESP Packet Header Format Security Parameters Index (SPI) Sequence Number Payload Padding Padding Length Authentication Data Next Header ESP Packet Header ESP Header Fields: • SPI:-Security parameter index • Sequence number field :- Anti-replay protection • ESP header with confidentiality service – prevents sniffing Ex.TCP dump & Windump • ESP - symmetric key algorithms like DES, 3DES and AES But ?????? Security issues in IPV6: • IPSEC Relies on PKI , Not yet fully Standardized • Scanning possible – If poorly designed • No protection against all denial of service attack (DoS attacks difficult to prevent in most cases) • No many firewalls in market with V6 capable By The Way… IPv6 Hacking Tools •Sniffer/packet capture Analyzer Snort TCP dump Ethereal Windump WinPcap •Scanners IPV6 security scanner Halfscan6 Nmap •DOS Tools 6tunneldos 4to6DDOS Imps6-tools •Packet forgers SendIP Packit Spak6 •Worms Slapper RealSecure & Proventia Tools Conclusion ‘Black Hats’ Vs ‘White Hats’ Time for ignoring IPV6…..PAST Time for understanding,recognizing and deploying it……NOW References • http://www.ipv6.org • http://www.cisco.com/ipv6/ • http://netscreen.com • http://www.sans.org • Computer Networks By Larry Peterson and Bruce Davie Questions ?