* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Routers
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Telephone exchange wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
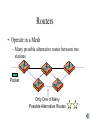
Routers • Operate in a Mesh – Many possible alternative routes between two stations Packet Only One of Many Possible Alternative Routes Routers • Benefits of Alternative Routes – Can route around a router or trunk line failure – Can route around congestion – Can select an optimal route based on cost, latency, security, or other goal • In Contrast – Ethernet deals poorly with failures – ATM can change virtual circuits in case of failure, but this takes time Routing is Complex • For each packet, router must consider all possible alternative routes • As noted earlier, it must do complex calculations on each router forwarding table row • This complexity requires a complex and expensive router for relatively low packet forwarding rates ? Switches Versus Routers • • • • Switches Fast Inexpensive No benefits of alternative routing • • • • Routers Slow Expensive benefits of alternative routing “Switch where you can; route where you must” Early Site Networks • Organization – LANs (subnets) based on hubs – Routers link hubs – Hierarchy of Routers Router Hub The Switching Revolution • Switches Push Routers to the Edge – Switches replace most routers in site networks – Because switches are cheaper than routers External Switch The Switching Revolution • Switches Push Routers to the Edge – Router still needed at the edge of the site network to communicate with outside world because routers handle expensive long-distance links very well External Switch The Switching Revolution • Layer 3 Switches – Traditional switches operate at Layer 2; Switch based on MAC addresses – Layer 3 switches switch based on internet layer IP addresses External Layer 3 Switch The Switching Revolution • Layer 3 Switches – Layer 3 switches are replacing many Layer 2 switches in site networks because of their ability to switch based on IP addresses External Layer 3 Switch The Switching Revolution • Layer 3 Switches versus Routers – Layer 3 switches are much faster than routers – Layer 3 switches cost less than routers External Layer 3 Switch The Switching Revolution • Layer 3 Switches versus Routers – At the internetworking layer, Layer 3 switches normally only support IP and sometimes IPX; Routers route many more internet layer protocols, including those of AppleTalk, SNA, and others – At the data link layer, Layer 3 switches normally support only Ethernet; Rarely ATM The Switching Revolution • Layer 3 Switches versus Routers – Layer 3 switches rarely support Layer 2 WAN protocols – Routers usually are still needed at the edge of the site network, to communicate with external links External Layer 3 Switch The Switching Revolution • Routers – Forward based on IP addresses and other internet layer addresses – Expensive and slow – Handle multiple internet layer protocols – Handle multiple LAN and WAN subnet protocols • Layer 3 Switches – Forward based on IP addresses, sometimes IPX addresses – Inexpensive and Fast – Do not handle multiple internet layer protocols – Do not handle multiple LAN and WAN subnet protocols The Switching Revolution • Layer 4 Switches – Examine port fields in TCP and UDP – These fields describe the application – Therefore, can switch based on application (to give priority by application, etc.) Layer 4 Switch