* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Combining circuit and packet based services in converging networks
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
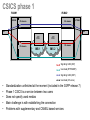
COMBINING CIRCUIT AND PACKET BASED SERVICES IN CONVERGING NETWORKS Sauli Österman [email protected] About •Written at TeliaSonera Finland, in the Mobile System Planning department. •Supervised by Prof. Raimo Kantola •Instructed by M.Sc. Ville Helenius Outline • • • • Background & Objective 3GPP release 6 network IP Multimedia subsystem Circuit Switched IMS Combinational Services • Conferencing service utilising CSICS • Conclusion Background & outline • When using GERAN as access network, the experienced delay is too much for real-time IMS services • Using GERAN as access network is appealing, because of the large coverage area • The problem may be solved with utilising mobile network CS services for real-time media and PS services for other types of media • For this purpose the 3rd Generation Partnership Project has standardised Circuit Switched IMS Combinational Services (CSICS) • The objective is: – To study in which stage the standardization process at the moment – What features are included in the standardised first phase solution – To study how conferecing with this type of service might be implemented • The study was performed as a literature study 3GPP release 6 network GERAN CS domain PSTN/PLMN IP networks UTRAN PS domain IMS • Different domains for CS and PS services • IMS is connected to both PS domain and CS domain IP multimedia subsystem • 3GPP specified access network independent service creation environment • Two main signalling protocols: – SIP for call control – Diameter for database queries • The signalling is always routed trough the controlling nodes, but the user data is routed via shortest path CSICS phase 1 PLMN1 GERAN PLMN2 CS domaín CS domaín UTRAN UE1 UE2 AS PS domaín AS PS domaín IMS 1 IMS 2 Signalling traffic (SIP) User data (RTP/MSRP) Signalling traffic (SS7) User data (CS voice) • • • • • Standardization unfinished at the moment (included in the 3GPP release 7) Phase 1 CSICS is a service between two users Does not specify used medias Main challenge is with establishing the connection Problems with supplementary and CAMEL based services Conferencing service utilising CSICS approach 1 approach 2 Terminal 1 CS domain CS domain Terminal 1 Terminal 2 Terminal 2 IMS IMS Terminal 3 Terminal 3 approach 3 approach 4 CS domain Terminal 1 CS domain Terminal 1 Terminal 2 Terminal 2 IMS Terminal 3 IMS Terminal 3 Conference service • • Recognised 4 approaches with how to implement this type of service These were studied from the connection establishing point of view CS voice call IMS session Conclusion • Service offers support for real-time services, even when GERAN is only available access network • The best approaches for implementing the CSICS conferencing service were concluded to be approaches 3 or 4 • CSICS requires a lot from terminal. The success depends heavily on the amount of the capable terminals • Synchronization of two separate media streams may cause problems to some applications • Subjects fo further study: – Final CSICS phase 1 functionality (when standardization is finished) – CSICS phase 2 (when more information is published) – Other types of services with which the mobile operator may differ from the service providers in the internet